Abstract
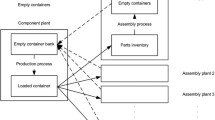
Companies that operate a commodity delivery service, lumber for instance, often own trucks to ship from a warehouse to their customers. One of these companies may consider purchasing new trucks to reduce operation costs, when operating new trucks is cheaper than operating old ones. That is, a company can save on future operational expenditures at the cost of purchasing new trucks. Once new trucks have been bought, the fleet consists of two sub-fleets: the subfleet of new and the subfleet of old trucks. The cheaper operation [currency units/min] of new trucks makes them preferable to old trucks. Thus, old trucks start servicing orders only when all new trucks are busy. For a given time horizon, the optimal cost of the project is a trade-off between the times serviced with old trucks, new trucks, and the cost of the new trucks to be purchased. This article puts forward a method to determine the number of new trucks to purchase that maximizes the expected present value of the project that applies to full payload deliveries. It uses historical information on hour-specific expected intensities of delivery requests and delivery services. Our approach can incorporate restrictions preventing deliveries to specific customers during certain time windows.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barros, O., & Weintraub, A. (1982). Planning for a vertically integrated forest industry. Operations Research, 30(6), 1168–1182.
Buehlmann, U., Espinoza, O., Bumgardner, M., & Smith, B. (2010). Trends in the US hardwood lumber distribution industry: changing products, customers, and services. Forest Products Journal and Index, 60(6), 547.
Carlsson, D., & Rönnqvist, M. (2005). Supply chain management in forestry–case studies at Södra Cell AB. European Journal of Operational Research, 163(3), 589–616.
Childress, S., & Durango-Cohen, P. (2005). On parallel machine replacement problems with general replacement cost functions and stochastic deterioration. Naval Research Logistics, 52(5), 409–419.
Cordeau, J., & Laporte, G. (2003). A tabu search heuristic for the static multi-vehicle dial-a-ride problem. Transportation Research, 37b(6), 579–594.
Epstein, R., Morales, R., Seron, J., & Weintraub, A. (1999). Use of OR systems in the Chilean forest industries. Interfaces, 29(1), 7–29.
Etezadi, T., & Beasley, J. E. (1983). Vehicle fleet composition. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 34(1), 87–91.
Figliozzi, M. A., Boudart, J. A., & Feng, W. (2011). Economic and environmental optimization of vehicle fleets. Transportation research record. Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2252(1), 1–6.
Friday, J. B., Yangida, J. F., Illukpitiya, P., Mamiit, R. J., & Edwards, Q. (2006). Characteristics of Hawai’i’s Retail Forest Industry in 2001.
González, E., Epstein, L. D., & Godoy, V. (2012). Optimal number of bypasses: minimizing cost of calls to wireless phones under Calling Party Pays. Annals of Operations Research, 199(1), 179–191.
Gross, D., & Harris, C. M. (1985). Fundamentals of queueing theory (2nd ed.). New York: Wiley.
Haartveit, E. Y., Kozak, R. A., & Maness, T. C. (2004). Supply chain management mapping for the forest products industry: Three cases from western Canada. Journal of Forest Products Business Research, 1(5), 1.
Hartman, J. C. (2004). Multiple asset replacement analysis under variable utilization and stochastic demand. European Journal of Operational Research, 159(1), 145–165.
Hebuterne, G. (1987). Traffic in switching systems. Noorwood: Artech House.
Ichoua, S., Gendreau, M., & Potrin, J.-Y. (2003). Vehicle dispatching with time-dependent travel times. European Journal of Operational Research, 144(2), 379–396.
Jain, H. C. (1966). An inventory problem applied to a rental situation. Australian Journal of Statistics, 8(3), 154–162.
Koole, G., & Mandelbaum, A. (2002). Queueing models of call centers: an introduction. Annals of Operations Research, 113, 41–59.
List, G. F., Wood, B., Nozick, L. K., Turnquist, M. A., Jones, D. A., Kjeldgaard, E. A., & Lawton, C. R. (2003). Robust optimization for fleet planning under uncertainty. Transportation Research. Part E, Logistics and Transportation Review, 39(3), 209–227.
Masjuán, F. (2007). Análisis de la Eficiencia Energética en el Transporte Interurbano de Carga, SIMA Ingeniería E.I.R.L. www.subtrans.gob.cl/upload/estudios/EEInterurbanoCarga-RE.pdf. Accessed 24 October 2011.
Michelsen, O., Solli, C., & Strømman, A. H. (2008). Environmental impact and added value in forestry operations in Norway. Journal of Industrial Ecology, 12(1), 69–81.
McClurg, T., & Chand, S. (2002). A parallel machine replacement model. Naval Research Logistics, 49(3), 275–287.
Redmer, A., Sadicki, P., & Zak, J. (2000). Multiobjective Optimisation of the Fleet Size in the Road Freight Transportation Company. In Proceedings of Rome Jubilee 2000 Conference: Meeting of the Euro Working Group Transportation—EWGT, Roma, Italy, September 2000.
Rosa-Hatko, G., & Gunn, E. A. (1997). Queues with switchover: A review and critique. Annals of Operations Research, 69, 299–322.
Spinelli, R., Magagnotti, N., & Picchi, G. (2012). A supply chain evaluation of slash bundling under the conditions of mountain forestry. Biomass & Bioenergy, 36, 339–345.
Tainiter, M. (1964). Some stochastic inventory models for rental situations. Management Science, 11(2), 316–326.
Whisler, W. D. (1967). A stochastic inventory model for rented equipment. Management Science, 13(9), 640–647.
Acknowledgements
We thank three reviewers whose comments enriched our discussions. We also thank Prof. Rodrigo Garrido for bringing to our attention reference (Masjuán 2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
González, E., Epstein, L.D. Minimum cost in a mix of new and old reusable items: an application to sizing a fleet of delivery trucks. Ann Oper Res 232, 135–149 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-013-1466-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-013-1466-5