Abstract
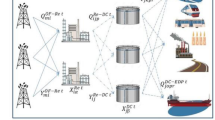
Optimization of oil-imports portfolio has attracted considerable attention from corporate operators as well as government and its strategic planners. This paper proposes a methodology of oil-importing portfolio optimization based on the fundamental process of intelligent knowledge management (IKM). Centering on the maritime system, optimal solutions are derived for different risk scenarios. Specifically, three main steps are involved: formulating a multi-objective programming (MOP) model, integrating the composite risk exposure with domain knowledge, as well as knowledge acquisition on risk scenarios and influence of transportation risk. For illustration, optimization of the maritime structure of China’s oil imports is performed to verify the practicability of the novel methodology. Experimental results suggest that the risk-adjusted factors’ augmentation can spread the risk wider and eventually enhance risk optimization capability in the MOP model. With a given risk-adjusted factor, the influence of transportation risk on an optimal plan is simulated and analyzed. The paper uses the fundamental IKM process for transforming the data (rough knowledge) into intelligent knowledge (transformation from T1 to T2) in the empirical study on risk integration and optimization of oil-importing maritime system. It is helpful to explore hidden patterns. What’s more, results suggest that it is necessary to highlight the influence of transportation risk in order to support decision makers from different domains to obtain more reasonable optimal solutions.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, J. M., Rudiger, F., & Paul, E. (2005). Quantitative risk management: Concept, techniques, and tools. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Al-Othman, W. B. E., Lababidi, H. M. S., Alatiqi, I. M., & Al-Shayji, K. (2008). Supply chain optimization of petroleum organization under uncertainty in market demands and prices. European Journal of Operational Research, 189(3), 822–840.
Arin, K., Ciferri, D., & Spagnolo, N. (2008). The price of terror: The effects of terrorism on stock market returns and volatility. Economics Letters, 101, 164–167.
Bae, Y. M., & Lee, Y. H. (2012). Integrated framework of risk evaluation and risk allocation with bounded data. Expert Systems with Applications, 39(9), 7853–7859.
Benítez, P. C., McCallum, I., Obersteiner, M., & Yamagata, Y. (2007). Global potential for carbon sequestration: Geographical distribution, country risk and policy implications. Ecological Economics, 60, 572–583.
Blyth, W., & Lefevre, N. (2004). Energy security and climate change: an assessment framework. Paris: OECD/International Energy Agency Information Paper.
Bouchet, E. C., Groslambert, B., & Groslambert, B. (2003). Country risk assessment: A guide to global investment strategy. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Chen, C. L., & Lee, W. C. (2004). Multi-objective optimization of multi-echelon supply chain networks with uncertain product demands and prices. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 28(6), 1131–1144.
Cheng, L. F., & Duran, M. A. (2004). Logistics for worldwide crude oil transportation using discrete event simulation and optimal control. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 28(6–7), 897–911.
Chuang, M. C., & Ma, H. W. (2013). Energy security and improvements in the function of diversity indices—Taiwan energy supply structure case study. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 24(C), 9–20.
Coello, C.A., & Lechuga, M.S. (2002). MOPSO: a proposal for multiple objective particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC 2002) (pp. 1051–1056). Piscataway: IEEE Service Center.
Cohen, G., Joutz, F., & Loungani, P. (2011). Measuring energy security: Trends in the diversification of oil and natural gas supplies. Energy Policy, 39(9), 4860–4869.
Gupta, E. (2008). Oil vulnerability index of oil-importing countries. Energy Policy, 36(3), 1195–1211.
Hammer, P. L., Kogan, A., & Lejeune, M. A. (2006). Modeling country risk ratings using partial orders. European Journal of Operational Research, 175, 836–859.
He, W., Sun, X., Tang, L., & Li, J. (2009). Modeling on oil-importing risk under risk correlation. In Proceedings of 2009 International Joint Conference on Computational Sciences and Optimization, IEEE Computer Society CPS, part 2, (pp 434–438).
Hogarth, R. M., & Kunreuther, H. (1995). Decision making under ignorance: Arguing with yourself. Journal of Risk and Uncertainty, 10(1), 15–36.
Hoti, S. (2005). Modelling country spillover effects in country risk ratings. Emerging Markets Review, 6(4), 324–354.
Iakovou, E. T. (2001). An interactive multi-objective model for the strategic maritime transportation of petroleum products: risk analysis and routing. Safety Science, 39, 19–29.
Iakovou, E., Douligeris, C., Ip, C., Li, H., & Yudhbir, L. (1999). A maritime global route planning model for hazardous materials transportation. Transportation Science, 33(1), 34–48.
IEA. (2001). World Energy Outlook. Paris: OECD.
Julka, N., Karimi, I., & Srinivasan, R. (2002). Agent-based supply chain management-2: A refinery application. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 26(12), 1771–1781.
Koo, L. Y., Adhitya, A., Srinivasan, R., & Karimi, I. A. (2008). Decision support for integrated refinery supply chains: Part 2. Design and operation. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 32(11), 2787–2800.
Le Coq, C., & Paltseva, E. (2009). Measuring the security of external energy supply in the European Union. Energy Policy, 37(11), 4474–4481.
Lesbirel, S. H. (2004). Diversification and energy security risks: The Japanese case. Japanese Journal of Political Science, 5(1), 1–22.
Li, H., Iakovou, E., & Douligeris, C. (1996). A strategic planning model for marine oil transportation in the Gulf of Mexico. Transportation Research Record, 1522, 108–115.
Li, J., Sun, X., He, W., Tang, L., & Xu, W. (2009). Modeling dynamic correlations and spillover effects of country risk: Evidence from Russia and Kazakhstan. International Journal of Information Technology & Decision Making, 8(4), 803–818.
Li, J., Tang, L., Sun, X., & Wu, D. (2014). Oil-importing Optimal Decision Considering Country Risk with Extreme Events: A Multi-Objective Programming Approach. Computers & Operations Research, 42, 108–115.
Li, J., Tang, L., Sun, X., Yu, L., He, W., & Yang, Y. (2012). Country risk forecasting for major oil exporting countries: a decomposition hybrid approach. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 63, 641–651.
Marler, R. T., & Arora, J. S. (2004). Survey of multi-objective optimization methods for engineering. Structural and multidisciplinary optimization, 26(6), 369–395.
MirHassani, S. A. (2008). An operational planning model for petroleum products logistics under uncertainty. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 196(2), 744–751.
Neiro, S. M. S., & Pinto, J. M. (2004). A general modeling framework for the operational planning of petroleum supply chain. Computer & Chemical Engineering, 28(6–7), 65–69.
Nie, G., Zhang, L., Zhang, Y., Deng, W., & Shi, Y. (2010). Find Intelligent Knowledge by Second-Order Mining: Three Cases from China. In IEEE International Conference on Data Mining—ICDM, (pp. 1189–1195).
Oshiro, N., & Saruwatari, Y. (2008). Quantification of sovereign risk: Using the information in equity market prices. Emerging Markets Review, 6, 346–362.
Raquel, C. R., & Naval, P. C. (2005). An effective use of crowding distance in multi-objective particle swarm optimization. ACM, 257–264.
Rios-Morales, R., Gamberger, D., Smuc, T., & Azuaje, F. (2009). Innovative methods in assessing political risk for business internationalization. Research in International Business and Finance, 23, 144–156.
Rodrigue, J. P., Comtois, C., & Slack, B. (2006). The Geography of Transport Systems. New York: Routledge.
Rottenstreich, Y., & Kivetz, R. (2006). On decision making without likelihood judgment. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 101(1), 74–88.
Shi, Y. (2001). Multiple Criteria Multiple Constraint-level (MC2) Linear Programming: Concepts. Techniques and Applications: World Scientific Publishing.
Shi, Y. (2010). Multiple Criteria Optimization based Data Mining Methods and Applications: A Systematic Survey. Knowledge and Information Systems, 24(3), 369–391.
Shi, Y., & Li, X. (2007). Knowledge management platforms and intelligent knowledge data mining. In Y. Shi & Y. Shi (Eds.), Advances in multiple criteria decision making and human systems management: Knowledge and wisdom (pp. 272–281). Amsterdam: IOS Press.
Shi, Y., Tian, Y. J., Kou, G., Peng, Y., & Li, J. P. (2011). Optimization based data mining: Theory and applications. New York: Springer.
Stern, J. P. (2006). The new security environment for European gas: worsening geopolitics and increasing global competition for LNG. Oxford: Oxford Institute for energy Studies NG 15.
Sun, X. L., Li, J. P., Wu, D. S., & Yi, S. L. (2012). Energy Geopolitics and Chinese Strategic Decision of the Energy Supply Security: A Multiple-Attribute Analysis. Journal of Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis, 18(1–2), 151–160.
Van Gestel, T., Baesens, B., Van Dijcke, P., Garcia, J., Suykens, J. A. K., & Vanthienen, J. (2006). A process model to develop an internal rating system: sovereign credit ratings. Decision Support Systems, 42(2), 1131–1151.
Vivoda, V. (2009). Diversification of oil import sources and energy security: A key strategy or an elusive objective? Energy Policy, 37(11), 4615–4623.
Wabiri, N., & Amusa, H. (2010). Quantifying South Africa’s crude oil import risk: a multi-criteria portfolio model. Economic Modellig, 27, 445–453.
Yim, J., & Mitchell, H. (2005). Comparison of country risk models: hybrid neural networks, logit models, discriminant analysis and cluster techniques. Expert Systems with Applications, 28, 137–148.
Yudhbir, L. (1999). A maritime risk and transportation model for the transport of crude oil and petroleum products. Coral Gables: University of Miami Coral Gables.
Zhang, H., Ji, Q., & Fan, Y. (2013). An evaluation framework for oil import security based on the supply chain with a case study focused on China. Energy Economics, 38(7), 87–95.
Zhang, L., Li, J., Shi, Y., & Liu, X. (2009). Foundations of intelligent knowledge management. Human Systems Management, 28, 145–161.
Zhang, Y., Zhang, Li., Liu, Y., & Shi, Y. (2010). Mining intelligent knowledge from a two-phase association rules mining. Int. J. Data Mining, Modelling and Management, 2(4), 403–419.
Acknowledgments
First of all, the authors extend sincere gratitude to Dr. Lingling Zhang for her instructive advice and useful suggestions. Also, we gratefully acknowledge the financial support from National Science Foundation of China (No. 71003091, 71133005, 71071148, and 71373009), Youth Innovation Promotion Association of the Chinese Academy of Sciences., Key Research Program of Institute of Policy and Management, Chinese Academy of Sciences. We wish to express our sincere gratitude to the anonymous referees for their constructive comments on and review of the earlier draft of our paper according to which we have improved the content.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Sun, X., Wang, F. et al. Risk integration and optimization of oil-importing maritime system: a multi-objective programming approach. Ann Oper Res 234, 57–76 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-014-1550-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-014-1550-5