Abstract
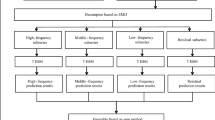
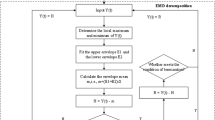
We propose a novel mode-characteristic-based decomposition ensemble model for nuclear energy consumption forecasting. Our method is based on the principles of “data-characteristic-based modeling” and “decomposition and ensemble”. The model improves on existing decomposition ensemble learning techniques (with “decomposition and ensemble”) by using “data-characteristic-based modeling” to forecast the decomposed modes. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition is first used to decompose the original nuclear energy consumption data into a series of comparatively simple modes, reducing the complexity of the data. Then, the extracted modes are thoroughly analyzed to capture hidden data characteristics. These characteristics are used to determine appropriate forecasting models for each mode. Final forecasts are obtained by combining these predicted components using an effective ensemble tool, such as least squares support vector regression. For illustration and verification purposes, we have implemented the proposed model to forecast nuclear energy consumption in China. Our numerical results demonstrate that the novel method significantly outperforms all considered benchmarks. This indicates that it is a very promising tool for forecasting complex and irregular data such as nuclear energy consumption.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Khader, M. M. (2009). Recent advances in nuclear power: A review. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 51(2), 225–235.
Beck, R., & Solow, J. L. (1994). Forecasting nuclear power supply with Bayesian autoregression. Energy Economics, 16(3), 185–192.
Besmann, T. M. (2010). Projections of US GHG reductions from nuclear power new capacity based on historic levels of investment. Energy Policy, 38(5), 2431–2437.
Box, G. E. P., & Jenkins, G. M. (1976). Time series analysis: Forecasting and control (2nd ed.). San Francisco: Holden Day.
Brockwell, P. J., & Davis, R. A. (1987). Time series: Theory and methods. New York: Springer.
Chang, C. C. (2010). A multivariate causality test of carbon dioxide emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in China. Applied Energy, 87(11), 3533–3537.
Choi, T. M., Yu, Y., & Au, K. F. (2011). A hybrid SARIMA wavelet transform method for sales forecasting. Decision Support Systems, 51(1), 130–140.
Comsan, M. N. H. (2010). Nuclear electricity for sustainable development: Egypt a case study. Energy Conversion and Management, 51(9), 1813–1817.
Dickey, D. A., & Fuller, W. A. (1979). Distribution of estimators for autoregressive time series with a unit root. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 74, 427–431.
Dickey, D. A., & Fuller, W. A. (1981). Likelihood ratio statistics for autoregressive time series with a unitroot. Econometrica, 49, 1057–1072.
Diebold, F. X., & Mariano, R. S. (1995). Comparing predictive accuracy. Journal of Business and Economic Statistic, 13(3), 253–263.
Edelman, D. (2007). Adapting support vector machine methods for horserace odds prediction. Annals of Operations Research, 151(1), 325–336.
Eynard, J., Grieu, S., & Polit, M. (2011). Wavelet-based multi-resolution analysis and artificial neural networks for forecasting temperature and thermal power consumption. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 24(3), 501–516.
Fang, Y., Park, J. I., Jeong, Y. S., Jeong, M. K., Baek, S. H., & Cho, H. W. (2011). Enhanced predictions of wood properties using hybrid models of PCR and PLS with high-dimensional NIR spectral data. Annals of Operations Research, 190(1), 3–15.
Ghorashi, A. H. (2007). Prospects of nuclear power plants for sustainable energy development in Islamic Republic of Iran. Energy Policy, 35(3), 1643–1647.
Glover, F., Klingman, D., & Phillips, N. V. (1989). A network-related nuclear power plant model with an intelligent branch-and-bound solution approach. Annals of Operations Research, 21(1), 317–331.
Grassberger, P., & Procaccia, I. (1983). Measuring the strangeness of strange attractors. Physica D, 9, 189–208.
Hochbaum, D. S., & Fishbain, B. (2011). Nuclear threat detection with mobile distributed sensor networks. Annals of Operations Research, 187(1), 45–63.
Hornik, K., Stinchocombe, M., & White, H. (1989). Multilayer feedforward networks are universal ap-proximators. Neural Networks, 2(5), 359–366.
Huang, N. E., Shen, Z., & Long, S. R. (1998). The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and nonstationary time series analysis. Proceedings of the Royal Society A, 454, 903–995.
Jammazi, R., & Aloui, C. (2012). Crude oil price forecasting: Experimental evidence from wavelet decomposition and neural network modeling. Energy Economics, 34(3), 828–841.
Janjarasjitt, S., Scher, M. S., & Loparo, K. A. (2008). Nonlinear dynamical analysis of the neonatal EEG time series: The relationship between sleep state and complexity. Clinical Neurophysiology, 119, 1812–1823.
Jewell, J. (2011). Ready for nuclear energy: An assessment of capacities and motivations for launching new national nuclear power programs. Energy Policy, 39(3), 1041–1055.
Jiao, T. S., Peng, J. M., & Terlaky, T. (2009). A confidence voting process for ranking problems based on support vector machines. Annals of Operations Research, 166(1), 23–38.
Kennel, M. B., Brown, R., & Abarbanel, H. D. I. (1992). Determining embedding dimension for phase-space reconstruction using a geometrical construction. Physical Review, 45(6), 3403–3411.
Kusiak, A., & Wei, X.P. (2011). Prediction of methane production in wastewater treatment facility: A data-mining approach. Annals of Operations Research. doi:10.1007/s10479-011-1037-6.
Li, J. P., Tang, L., Yu, L. A., He, W., Yang, Y. Y., & Sun, X. L. (2012). Country risk forecasting for major oil-exporting countries: A decomposition hybrid approach. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 63(3), 641–651.
Nelson, C. R., & Plosser, C. I. (1982). Trends and random walks in macroeconomics time series: Some evidence and implications. Journal of Monetary Economics, 10, 139–162.
Osowski, S., & Garanty, K. (2007). Forecasting of the daily meteorological pollution using wavelets and support vector machine. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 20(6), 745–755.
Packard, N. H., Crutchfield, J. P., Farmer, J. D., & Shaw, R. S. (1980). Geometry from a time series. Physical Review Letters, 45(3), 712–716.
Partal, T., & Kişi, O. (2007). Wavelet and neuro-fuzzy conjunction model for precipitation forecasting. Journal of Hydrology, 342(15), 199–212.
Sun, X. L., Li, J. P., Wu, D. S., & Yi, S. L. (2011). Energy geopolitics and Chinese strategic decision of the energy supply security: A multiple-attribute analysis. Journal of Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis, 18, 151–160.
Suykens, J. A. K., & Vandewalle, J. (1999). Least squares support vector machine classifiers. Neural Processing Letters, 9(3), 293–300.
Tang, L., Yu, L. A., Liu, F. T., & Xu, W. X. (2013). An integrated data characteristic testing scheme for complex time series data exploration. International Journal of Information Technology and Decision Making, 12(3), 491–521.
Tang, L., Yu, L. A., Wang, S., Li, J. P., & Wang, S. Y. (2012). A novel hybrid ensemble learning paradigm for nuclear energy consumption forecasting. Applied Energy, 93, 432–443.
Tuyttens, D., Pirlot, M., Teghem, J., Trauwaertand, E., & Lidgeois, B. (1994). Homogeneous grouping of nuclear fuel cans through simulated annealing and tabu search. Annals of Operations Research, 50, 575–607.
Vapnik, V. (1995). The nature of statistical learning theory. New York: Springer.
Wang, S., Yu, L. A., Tang, L., & Wang, S. Y. (2011). A novel seasonal decomposition based least squares support vector regression ensemble learning approach for hydropower consumption forecasting in China. Energy, 36(11), 6542–6554.
Wang, S. Y., Yu, L., & Lai, K. K. (2005). Crude oil price forecasting with TEI@I methodology. Journal of Systems Sciences and Complexity, 18(2), 145–166.
White, H. (1990). Connectionist nonparametric regression: Multilayer feedforward networks can learn arbitrary mappings. Neural Networks, 3, 535–549.
Wu, Z., & Huang, N. E. (2004). Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method. Centre for Ocean-Land-Atmosphere Studies, Technical Report No. 193. 51.
Yan, Q., Wang, A. J., Wang, G. S., Yu, W. J., & Chen, Q. S. (2011). Nuclear power development in China and uranium demand forecast: Based on analysis of global current situation. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 53(6), 742–747.
Yu, L. A. (2012). An evolutionary programming based asymmetric weighted least squares support vector machine ensemble learning methodology for software repository mining. Information Sciences, 191, 31–46.
Yu, L. A., & Yao, X. (2013). A total least squares proximal support vector classifier for credit risk evaluation. Soft Computing, 17(4), 643–650.
Yu, L. A., Wang, S. Y., & Lai, K. K. (2008). Forecasting crude oil price with an EMD-based neural network ensemble learning paradigm. Energy Economics, 30(5), 2623–2635.
Zhang, X., Lai, K. K., & Wang, S. Y. (2008). A new approach for crude oil price analysis based on empirical mode decomposition. Energy Economics, 30(3), 905–918.
Zhou, Y. (2010). Why is China going nuclear? Energy Policy, 38(7), 3755–3762.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by grants from the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (NSFC No. 71025005), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC No. 71301006, 71201054 and 91224001), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities in BUCT (Project No. ZY1320 and ZZ1315).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, L., Wang, S., He, K. et al. A novel mode-characteristic-based decomposition ensemble model for nuclear energy consumption forecasting. Ann Oper Res 234, 111–132 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-014-1595-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-014-1595-5