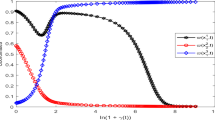
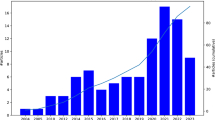
Abstract
We propose a model for interaction between a user-set (market) and a service-provider (firm) when the offered demand is sensitive to the offered Quality of Service which in turn depends on the offered demand. We show that, under fairly mild conditions, an equilibrium point or an equilibrium set exists either when the service-provider bases its operational decisions as per a revenue optimal policy of an average reward Markov decision model or when it uses a discounted reward Markov decision model. We also consider the cases when the firm has to meet functional constraints on consumption of resources for its operations. If an equilibrium set exists, then the interaction can suitably be interpreted as one explanation of the business cycles phenomena. We illustrate these and related issues via a model for vehicle relocation system which may be of independent interest.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman, E. (1999). Constrained Markov decision processes. London: Chapman & Hall/CRC.
Bertsekas, D. P. (2012). Dynamic programming and optimal control. Belmont: Athena Scientific.
Dantzig, G. B., Folkman, J., & Shapiro, N. (1967). On the continuity of the minimal set of a continuous function. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 17, 519–548.
Feinberg, E., & Shwartz, A. (2001). Handbook of Markov decision processes. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic.
Feinberg, E. A., & Shwartz, A. (1996). Constrained discounted dynamic programming. Mathematics of Operations Research, 21(4), 922–945.
Hemachandra, N., & Gupta, M. (2015). Nash equilibrium in pricing surplus server capacity model and equilibrium sets in some related models. Communicated.
Hemachandra, N., Tripathi, S., & Patil, K. (2015). Equilibrium sets of some \(GI/M/1\) queues. Working paper.
Iyer, K., & Hemachandra, N. (2010). Sensitivity analysis and optimal ultimately stationary deterministic policies in some constrained discounted cost models. Mathematical Methods of Operations Research, 71(3), 401–425.
Kallenberg, L. (2013). Derman’s book as inspiration: Some results on LP for MDPs. Annals of Operations Research, 208(1), 63–94.
Kallenberg, L.C. (2010). Markov decision processes. Lecture notes. http://www.math.leidenuniv.nl/~kallenberg/Lecture-notes-MDP.pdf
Kim, W. S. (2007). Price-based quality-of-service control framework for two-class network services. Journal of Communications and Networks, 9(3), 319–329.
Martin, E., Shaheen, S., & Lidicker, J. (2010). Impact of carsharing on household vehicle holdings: Results from North American shared-use vehicle survey. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2143, 150–158.
Puterman, M. L. (2005). Markov decision processes: Discrete stochastic dynamic programming. Hoboken: Wiley.
Qavi, M.A. (2013). Firm user-set interactions—modeling and analysis of carsharing and queue admission control systems. Master’s thesis, IIT Bombay.
Rajesh, K.S.N. (2012). Firm-market interactions, parameterized MDPs and some models for carsharing systems. Master’s thesis, IIT Bombay.
Satish, T.K. (2015). Firm market equilibrium in network systems with two interacting parameters. Master’s thesis, IIT Bombay.
Shaheen, S., Sperling, D., & Wagner, C. (1998). Carsharing in Europe and North America: Past, present, and future. Transportation Quarterly, 52(3), 35–52.
Sinha, S. K., Rangaraj, N., & Hemachandra, N. (2010). Pricing surplus server capacity for mean waiting time sensitive customers. European Journal of Operational Research, 205, 159–171.
Wets, R. J. B. (1985). On the continuity of the value of a linear program and of related polyhedral-valued multifunctions. Mathematical Programming Study, 24, 14–29.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank the Reviewers for their comments and suggestions that helped us improve the presentation of this paper. We also thank the Guest Editors of this Special Issue for their encouragement. Both Rajesh and Abdul were partially supported by a Teaching Assistantship offered by Govt. of India during their MTech program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hemachandra, N., Rajesh, K.S.N. & Qavi, M.A. A model for equilibrium in some service-provider user-set interactions. Ann Oper Res 243, 95–115 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-015-2037-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-015-2037-8