Abstract
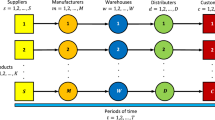
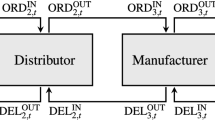
This paper presents an integrated approach for short-term supply chain management (SCM) at a fast moving consumer goods production plant. The problem is to determine the production quantities, to provide a detailed production schedule, to trigger the relevant express deliveries of raw material, and to manage the distribution. We propose a linear integer model, which integrates all of these decisions within scheduling. To find high quality solutions in a reasonable amount of time, various solution methods are proposed, such as a greedy constructive heuristic, two tabu search metaheuristics, a basic variable neighborhood search and an enhanced one, which uses a variable shaking operator. Experiments on realistic instances show that the latter method is efficient and robust. This paper is a contribution to the SCM literature (indeed, only few references address the integration of short term decisions) and to the general metaheuristics field (as the variable neighborhood search paradigm is extended).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allahverdi, A., Gupta, J. N., & Aldowaisan, T. (1999). A review of scheduling research involving setup considerations. Omega, 27(2), 219–239.
Amrani, H., Martel, A., Zufferey, N., & Makeeva, P. (2011). A variable neighborhood search heuristic for the design of multicommodity production–distribution networks with alternative facility configurations. OR Spectrum, 33(4), 989–1007.
Azoury, K. S., & Miyaoka, J. (2013). Managing production and distribution for supply chains in the processed food industry. Production and Operations Management, 22(5), 1250–1268.
Bard, J. F., & Nananukul, N. (2009). The integrated production–inventory–distribution–routing problem. Journal of Scheduling, 12(3), 257–280.
Bartal, Y., Leonardi, S., Marchetti-Spaccamela, A., Sgall, J., Stougie, L. (1996). Multiprocessor scheduling with rejection. In: Proceedings of the seventh annual ACM-SIAM symposium on discrete algorithms (SODA’ 96). Philadelphia, USA.
Bierlaire, M., Thémans, M., & Zufferey, N. (2010). A heuristic for nonlinear global optimization. INFORMS Journal on Computing, 22(1), 59–70.
Bilgen, B., & Günther, H. O. (2010). Integrated production and distribution planning in the fast moving consumer goods industry: A block planning application. OR Spectrum, 32(4), 927–955.
Cao, Z., & Yang, X. (2009). A PTAS for parallel batch scheduling with rejection and dynamic job arrivals. Theoretical Computer Science, 410(27–29), 2732–2745.
Chen, Z. L. (2010). Integrated production and outbound distribution scheduling: Review and extensions. Operations Research, 58(1), 130–148.
Clark, A. R., & Clark, S. J. (2000). Rolling-horizon lot-sizing when set-up times are sequence-dependent. International Journal of Production Research, 38(10), 2287–2307.
Dastidar, S. G., & Nagi, R. (2005). Scheduling injection molding operations with multiple resource constraints and sequence dependent setup times and costs. Computers & Operations Research, 32(11), 2987–3005.
Dolgui, A., Eremeev, A. V., Kovalyov, M. Y., & Kuznetsov, P. M. (2010). Multi-product lot sizing and scheduling on unrelated parallel machines. IIE Transactions, 42(7), 514–524.
Dósa, G., & He, Y. (2006). Preemptive and non-preemptive on-line algorithms for scheduling with rejection on two uniform machines. Computing, 76, 149–164.
Ebben, M., Hans, E., & Olde Weghuis, F. (2005). Workload based order acceptance in job shop environments. OR Spectrum, 27, 107–122.
Gendreau, M., & Potvin, J.-Y. (Eds.). (2010). Handbook of Metaheuristics (2nd ed.). Berlin: Springer.
Gerstl, E., & Mosheiov, G. (2012). Scheduling on parallel identical machines with job-rejection and position-dependent processing times. Information Processing Letters, 112(19), 743–747.
Hoogeveen, H., Skutella, M., & Woeginger, G. J. (2000). Preemptive scheduling with rejection. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 1879, 268–277.
Jans, R., & Degraeve, Z. (2007). Meta-heuristics for dynamic lot sizing: A review and comparison of solution approaches. European Journal of Operational Research, 177(3), 1855–1875.
Józefowska, J., & Zimniak, A. (2008). Optimization tool for short-term production planning and scheduling. International Journal of Production Economics, 112(1), 109–120.
Kreipl, S., & Pinedo, M. (2004). Planning and scheduling in supply chains: An overview of issues in practice. Production and Operations Management, 13(1), 77–92.
Lee, B. K., Kang, K. H., & Lee, Y. H. (2008). Decomposition heuristic to minimize total cost in a multi-level supply chain network. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 54(4), 945–959.
Li, C. L., & Ou, J. (2005). Machine scheduling with pickup and delivery. Naval Research Logistics, 52(7), 617–630.
Li, S., & Yuan, J. (2010). Parallel-machine scheduling with deteriorating jobs and rejection. Theoretical Computer Science, 411(40–42), 3642–3650.
Lu, L., Zhang, L., & Yuan, J. (2008). The unbounded parallel batch machine scheduling with release dates and rejection to minimize makespan. Theoretical Computer Science, 396, 283–289.
Lu, L., Cheng, T., Yuan, J., & Zhang, L. (2009). Bounded single-machine parallel-batch scheduling with release dates and rejection. Computers and Operations Research, 36, 2748–2751.
Melo, R. A., & Wolsey, L. A. (2010). Optimizing production and transportation in a commit-to-delivery business mode. European Journal of Operational Research, 203(3), 614–618.
Meyr, H. (2002). Simultaneous lotsizing and scheduling on parallel machines. European Journal of Operational Research, 139(2), 277–292.
Mladenovic, N., & Hansen, P. (1997). Variable neighborhood search. Computers & Operations Research, 24, 1097–1100.
Oğuz, C., Salman, S. F., & Yalçın, B. Z. (2010). Order acceptance and scheduling decisions in make-to-order systems. International Journal of Production Economics, 125(1), 200–211.
Seiden, S. S. (2001). Preemptive multiprocessor scheduling with rejection. Theoretical Computer Science, 262, 437–458.
Shirvani, N., & Shadrokh, S. (2013). Coordination of a cyclic three-stage supply chain for fast moving consumer goods. Iranian Journal of Operations Research, 4(2), 175–190.
Slotnick, S. A. (2011). Order acceptance and scheduling: A taxonomy and review. European Journal of Operational Research, 212(1), 1–11.
Stadtler, H. (2005). Supply chain management and advanced planning—basics, overview and challenges. European Journal of Operational Research, 163(3), 575–588.
Stecke, K. E., & Zhao, X. (2007). Production and transportation integration for a make-to-order manufacturing company with a commit-to-delivery business mode. Manufacturing & Service Operations Management, 9(2), 206–224.
Thevenin, S., Zufferey, N. (2014). Variable neighborhood search for a scheduling problem with time window penalties. In: Proceedings of the 14th international workshop on project management and scheduling (PMS), Munchen, Germany.
ten Kate, H. A. (1994). Towards a better understanding of order acceptance. International Journal of Production Economics, 37(1), 139–152.
Wang, H., & Lee, C. Y. (2005). Production and transport logistics scheduling with two transport mode choices. Naval Research Logistics, 52(8), 796–809.
Wang, X., & Cheng, T. (2009). Production scheduling with supply and delivery considerations to minimize the makespan. European Journal of Operational Research, 194(3), 743–752.
Zhong, W., Chen, Z. L., & Chen, M. (2010). Integrated production and distribution scheduling with committed delivery dates. Operations Research Letters, 38(2), 133–138.
Zhu, X., & Wilhelm, W. E. (2006). Scheduling and lot sizing with sequence-dependent setup: A literature review. IIE transactions, 38(11), 987–1007.
Zufferey, N. (2012). Metaheuristics: Some principles for an efficient design. Computer Technology and Applications, 3, 446–462.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thevenin, S., Zufferey, N. & Glardon, R. Model and metaheuristics for a scheduling problem integrating procurement, sale and distribution decisions. Ann Oper Res 259, 437–460 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-017-2498-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-017-2498-z