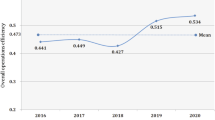
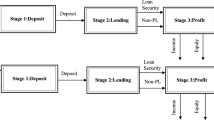
Abstract
This study explored how dramatic changes in ownership structure and operational technologies have influenced Chinese bank efficiency over the past decade. The study included an empirical analysis using 5 years (2011–2015) of operational data for 71 Chinese commercial banks. Two two-stage meta-frontier data envelopment analysis network models and multiple regression models were used to estimate and analyze impacts of variations in bank ownership structure. The main empirical results show that irrespective of deposits or loans efficiency, State-owned Banks (SOBs) have the highest technology and management levels. In contrast, City Commercial Banks should improve both technology and management levels, narrowing the gap with SOBs and Joint-stock Banks. The deposit efficiency of a bank was found to be mainly influenced by the nature of ownership (national shareholding ratio and the shareholding ratio of the domestic legal entities) and ownership concentration. The loan efficiency of a bank was mainly affected by the nature of ownership (the shareholding ratio of the foreign legal entities) and ownership liquidity.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggelopoulos, E., & Georgopoulos, A. (2017). Bank branch efficiency under environmental change: A bootstrap DEA on monthly profit and loss accounting statements of Greek retail branches. European Journal of Operational Research,261(3), 1170–1188.
Alirezaee, M. R., & Afsharian, M. (2007a). A complete ranking of DMUs using restrictions in DEA models. Applied Mathematics and Computation,189, 1550–1559.
Alirezaee, M. R., & Afsharian, M. (2007b). Model improvement for computational difficulties of DEA technique in the presence of special DMUs. Applied Mathematics and Computation,186, 1600–1611.
An, Q., Chen, H., Wu, J., et al. (2015). Measuring slacks-based efficiency for commercial banks in China by using a two-stage DEA model with undesirable output. Annals of Operations Research,235(1), 13–35.
Ariff, M., & Can, L. (2008). Cost and profit efficiency of Chinese banks: A non-parametric analysis. China Economic Review,19, 260–273.
Athanassopoulos, A. D. (1998). Nonparametric frontier models for assessing the market and cost efficiency of large-scale bank branch networks. Journal of Money, Credit, and Banking,30, 172–192.
Aysan, A. F., Karakaya, M. M., & Uyanik, M. (2011). Panel stochastic frontier analysis of profitability and efficiency of Turkish banking sector in the post crisis era. Journal of Business Economics and Management,12(4), 629–654.
Azizi, H., & Ajirlu, S. F. (2010). Measurement of overall performances of decision-making units using ideal and anti-ideal decision-making units. Computers & Industrial Engineering,59, 411–418.
Battese, G. E., Rao, D. S. P., & O’Donnell, C. J. (2004). A meta frontier production function for estimation of technical efficiencies and technology gaps for firms operating under different technologies. Journal of Productivity Analysis,21(1), 91–103.
Berger, A. N., & Humphrey, D. B. (1997). Efficiency of financial institutions: International survey and directions for future research. European Journal of Operational Research,98(2), 175–212.
Bonin, J. P., Hasan, I., & Wachtel, P. (2005). Bank performance, efficiency and ownership in transition countries. Journal of Banking & Finance,29(1), 31–53.
Camanho, A. S., & Dyson, R. G. (2005). Cost efficiency measurement with price uncertainty: A DEA application to bank branch assessments. European Journal of Operational Research,161, 432–446.
Camanho, A. S., & Dyson, R. G. (2008). A generalization of the Farrell cost efficiency measure applicable to non-fully competitive settings. Omega,36, 147–162.
Chambers, R. G., Chung, Y., & Färe, R. (1996). Benefit and distance functions. Journal of Economic Theory,70(2), 407–419.
Chambers, R. G., Chung, Y., & Färe, R. (1998). Profit, directional distance functions, and Nerlovian efficiency. Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications,98(2), 351–364.
Chang, T. P., Hu, J. L., Chou, R. Y., & Sun, L. (2012). The sources of bank productivity growth in China during 2002–2009: A disaggregation view. Journal of Banking & Finance,36, 1997–2006.
Charnes, A., Cooper, W. W., & Rhodes, E. (1978). Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. European Journal of Operational Research,2(6), 429–444.
Cheng, M., Zhao, H., & Zhang, J. (2014). What precludes the development of noninterest activities in Chinese commercial banks from the perspective of the price of interest activities? Applied Economics,46(21), 2453–2461.
Chiu, C. R., Liou, J. L., Wu, P. I., et al. (2012). Decomposition of the environmental inefficiency of the meta-frontier with undesirable output. Energy Economics,34(5), 1392–1399.
Chung, Y. H., Färe, R., & Grosskopf, S. (1997). Productivity and undesirable outputs: A directional distance function approach. Journal of Environmental Management,51(3), 229–240.
De, Y. R., & Hasan, I. (1998). The performance of de novo commercial banks: A profit efficiency approach. Journal of Banking & Finance,22(5), 565–587.
Dekker, D., & Post, T. (2001). A quasi-concave DEA model with an application for bank branch performance evaluation. European Journal of Operational Research,132, 296–311.
Färe, R., & Grosskopf, S. (2010). Directional distance functions and slacks-based measures of efficiency. European Journal of Operational Research,200(1), 320–322.
Färe, R., Grosskopf, S., Noh, D. W., & Weber, W. L. (2005). Characteristics of a polluting technology: Theory and practice. Journal of Econometrics,126(2), 469–492.
Färe, R., Grosskopf, S., & Pasurka, C. A. (2007). Environmental production functions and environmental directional distance functions. Energy,32(7), 1055–1066.
Färe, R., Grosskopf, S., & Weber, W. L. (2004). The effect of risk-based capital requirements on profit efficiency in banking. Applied Economics,36(15), 1731–1743.
Fethi, M. D., & Pasiouras, F. (2010). Assessing bank efficiency and performance with operational research and artificial intelligence techniques: A survey. European Journal of Operational Research,204, 189–198.
Fukuyama, H., & Matousek, R. (2017). Modelling bank performance: A network DEA approach. European Journal of Operational Research,259(2), 721–732.
Fukuyama, H., & Weber, W. L. (2008). Japanese banking inefficiency and shadow pricing. Mathematical and Computer Modelling,48(11–12), 1854–1867.
Kao, C. (2017). Efficiency measurement and frontier projection identification for general two-stage systems in data envelopment analysis. European Journal of Operational Research,261(2), 679–689.
Kwon, H. B., & Lee, J. (2015). Two-stage production modeling of large US banks: A DEA-neural network approach. Expert Systems with Applications,42(19), 6758–6766.
Lensink, R., & Meesters, A. (2014). Institutions and bank performance: A stochastic frontier analysis. Oxford Bulletin of Economics and Statistics,76(1), 67–92.
Lewis, H. F., & Sexton, T. R. (2004). Network DEA: efficiency analysis of organizations with complex internal structure. Computers & Operations Research,31(9), 1365–1410.
Lin, B., & Du, K. (2013). Technology gap and China’s regional energy efficiency: A parametric metafrontier approach. Energy Economics,40, 529–536.
Löthgren, M., & Tambour, M. (1999). Productivity and customer satisfaction in Swedish pharmacies: A DEA network model. European Journal of Operational Research,115(3), 449–458.
Matthews, K. (2013). Risk management and managerial efficiency in Chinese banks: A network DEA framework. Omega,41(2), 207–215.
Noulas, A. G., Glaveli, N., & Kiriakopoulos, I. (2008). Investigating cost efficiency in the branch network of a Greek bank: An empirical study. Managerial Finance,34, 160–171.
O’Donnell, C. J., Rao, D. S. P., & Battese, G. E. (2008). Metafrontier frameworks for the study of firm-level efficiencies and technology ratios. Empirical Economics,34(2), 231–255.
Oh, D. (2010). A metafrontier approach for measuring an environmentally sensitive productivity growth index. Energy Economics,32(1), 146–157.
Palme, U., & Tillman, A. M. (2008). Sustainable development indicators: How are they used in Swedish water utilities? Journal of Cleaner Production,16(13), 1346–1357.
Paradi, J. C., & Zhu, H. (2013). A survey on bank branch efficiency and performance research with data envelopment analysis. Omega,41(1), 61–79.
Park, K. H., & Weber, W. L. (2006). A note on efficiency and productivity growth in the Korean banking industry, 1992–2002. Journal of Banking & Finance,30(8), 2371–2386.
Prieto, A. M., & Zofío, J. L. (2007). Network DEA efficiency in input–output models: With an application to OECD countries. European Journal of Operational Research,178(1), 292–304.
Ray, S. C. (1991). Resource-use efficiency in public schools: A study of connecticut data. Management Science,37(12), 1620–1628.
Ruggiero, J. (1996). On the measurement of technical efficiency in the public sector. European Journal of Operational Research,90(3), 553–565.
Seiford, L. M., & Zhu, J. (1999). Profitability and marketability of the top 55 US commercial banks. Management Science,45(9), 1270–1288.
Sherman, H. D., & Gold, F. (1985). Bank branch operating efficiency: Evaluation with data envelopment analysis. Journal of Banking & Finance,9(2), 297–315.
Sun, J., Wang, C., Ji, X., & Wu, J. (2017). Performance evaluation of heterogeneous bank supply chain systems from the perspective of measurement and decomposition. Computers & Industrial Engineering,113, 891–903.
Wang, C. H., Gopal, R. D., & Zionts, S. (1997). Use of data envelopment analysis in assessing information technology impact on firm performance. Annals of Operations Research,73, 191–213.
Wang, K., Huang, W., Wu, J., et al. (2014). Efficiency measures of the Chinese commercial banking system using an additive two-stage DEA. Omega,44, 5–20.
Wanke, P., Barros, C. P., & Emrouznejad, A. (2016). Assessing productive efficiency of banks using integrated Fuzzy-DEA and bootstrapping: A case of Mozambican banks. European Journal of Operational Research,249(1), 378–389.
Wu, D., Yang, Z., & Liang, L. (2006). Efficiency analysis of cross-region bank branches using fuzzy data envelopment analysis. Applied Mathematics and Computation,181, 271–281.
Xu, L., & Lin, C. T. (2007). Can Chinese banks compete after accession to WTO? Journal of Asian Economics,18(6), 883–903.
Yang, C. C. (2012). Service, investment, and risk management performance in commercial banks. The Service Industries Journal,32(12), 2005–2025.
Yang, C., & Liu, H. M. (2012). Managerial efficiency in Taiwan bank branches: A network DEA. Economic Modelling,29(2), 450–461.
Yavas, B. F., & Fisher, D. M. (2005). Performance evaluation of commercial bank branches using data envelopment analysis. Journal of Business and Management,11, 89–102.
Zha, Y., Liang, N. N., Wu, M. G., & Bian, Y. W. (2016). Efficiency evaluation of banks in China: A dynamic two-stage slacks-based measure approach. Omega,60, 85–97.
Acknowledgements
This research is partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 71501139, 71871153, 71571173, 71631006), Natural Science Funds of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20150307), and Research Project of Philosophy and Social Sciences in Universities of Jiangsu (2018SJA1299).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Sun, J., Yang, F. et al. How ownership structure affects bank deposits and loan efficiencies: an empirical analysis of Chinese commercial banks. Ann Oper Res 290, 983–1008 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-018-3106-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-018-3106-6