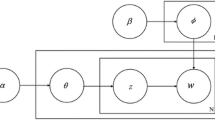
Abstract
The Bass diffusion model has been successfully applied in product sales forecasting, and it performs particularly well in consumer durables sales forecasting. However, the traditional Bass model only uses historical sales data and cannot contain important market information concerning products. How to improve the Bass model through user-generated Internet information and macroeconomic data to achieve more accurate predictions is addressed in this paper. First, a sentiment analysis is adopted to convert online reviews concerning various attributes of a product into sentiment scores, and then, the product word-of-mouth index (WoM index), which is integrated into the imitation coefficient of the Bass model, is calculated by the entropy weight method. Subsequently, the Baidu product index is calculated through the Baidu search traffic of product-related words and is integrated into the innovation coefficient of the Bass model. Finally, macroeconomic data are collected to estimate the total number of potential adopters, which relaxes the assumption that the market potential in the Bass model remains unchanged over time. We conduct comparison experiments of forecasting automobile product sales, and the results are as follows. (1) The improved Bass model can significantly improve the forecast accuracy, and its average forecast accuracy (0.9983) is approximately 2.15% higher than the traditional Bass model (0.9773). The RMSE (0.3124) and WAPE (0.0017) are 90.98% and 92.38% lower compared with the traditional Bass model, respectively. (2) as for the calculation of WoM index, it is better to divide a whole review into separate reviews concerning each attribute. (3) Macroeconomic data play the biggest role in improving the prediction power of the Bass model, followed by online review data and search traffic data.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aras, S., Kocakoç, İ. D., & Polat, C. (2017). Comparative study on retail sales forecasting between single and combination methods. Journal of Business Economics & Management, 18(5), 2017.
Archak, N., Ghose, A., & Ipeirotis, P. G. (2011). Deriving the pricing power of product features by mining consumer reviews. Management Science, 57(8), 1485–1509. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.1110.1370.
Bangwayo-Skeete, P. F., & Skeete, R. W. (2015). Can Google data improve the forecasting performance of tourist arrivals? Mixed-data sampling approach. Tourism Management, 46, 454–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2014.07.014.
Bass, F. M. (1969). A new product growth for model consumer durables. Management Science, 15(5), 215–227. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.15.5.215.
Bass, F. M. (2004). Comments on “A new product growth for model consumer durables the bass model”. Management Science, 50(12_supplement), 1833–1840. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.1040.0300.
Bayus, B. L. (1993). High-definition television: assessing demand forecasts for a next generation consumer durable. Management Science, 39(11), 1319–1333. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.39.11.1319.
Boone, T., Ganeshan, R., Hicks, R. L., & Sanders, N. R. (2018). Can Google trends improve your sales forecast? Production and Operations Management, 27(10), 1770–1774. https://doi.org/10.1111/poms.12839.
Chen, H. L. (2010). Using financial and macroeconomic indicators to forecast sales of large development and construction firms. The Journal of Real Estate Finance and Economics, 40(3), 310–331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11146-008-9158-7.
Chen, Y., & Xie, J. (2008). Online consumer review: Word-of-mouth as a new element of marketing communication mix. Management Science, 54(3), 477–491. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.1070.0810.
Chern, C.-C., Wei, C.-P., Shen, F.-Y., & Fan, Y.-N. (2015). A sales forecasting model for consumer products based on the influence of online word-of-mouth. Information Systems and e-Business Management, 13(3), 445–473. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10257-014-0265-0.
Chevalier, J. A., & Mayzlin, D. (2006). The effect of word of mouth on sales: Online book reviews. Journal of Marketing Research, 43(3), 345–354. https://doi.org/10.1509/jmkr.43.3.345.
Cui, R., Gallino, S., Moreno, A., & Zhang, D. J. (2018). The operational value of social media information. Production and Operations Management, 27(10), 1749–1769. https://doi.org/10.1111/poms.12707.
Fan, Z.-P., Che, Y.-J., & Chen, Z.-Y. (2017). Product sales forecasting using online reviews and historical sales data: A method combining the Bass model and sentiment analysis. Journal of Business Research, 74, 90–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2017.01.010.
Fang, J., Wu, W., Lu, Z., & Cho, E. (2019). Using baidu index to nowcast mobile phone sales in China. The Singapore Economic Review, 64(01), 83–96. https://doi.org/10.1142/S021759081743007X.
Fantazzini, D., & Toktamysova, Z. (2015). Forecasting German car sales using Google data and multivariate models. International Journal of Production Economics, 170, 97–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2015.09.010.
Fernández-Durán, J. J. (2014). Modeling seasonal effects in the Bass forecasting diffusion model. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 88, 251–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2014.07.004.
Gao, J., Xie, Y., Cui, X., Yu, H., & Gu, F. (2018). Chinese automobile sales forecasting using economic indicators and typical domestic brand automobile sales data: A method based on econometric model. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 10(2), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1177/1687814017749325.
Ginsberg, J., Mohebbi, M. H., Patel, R. S., Brammer, L., Smolinski, M. S., & Brilliant, L. (2009). Detecting influenza epidemics using search engine query data. Nature, 457(7232), 1012. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07634.
Huang, X., Zhang, L., & Ding, Y. (2017). The Baidu index: Uses in predicting tourism flows: A case study of the Forbidden City. Tourism Management, 58, 301–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TOURMAN.2016.03.015.
Kahneman, D., & Tversky, A. (1979). Prospect theory: An analysis of decision under risk. Econometrica, 47(2), 263. https://doi.org/10.2307/1914185.
Ku, L.-W., & Chen, H.-H. (2007). Mining opinions from the Web: Beyond relevance retrieval. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 58(12), 1838–1850.
Ku, L. W., & Chen, H. H. (2010). Mining opinions from the Web: Beyond relevance retrieval. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 58(12), 1838–1850.
Kuhn, M., & Johnson, K. (2013). Applied predictive modeling. New York: Springer.
Lau, R. Y. K., Zhang, W., & Xu, W. (2018). Parallel aspect-oriented sentiment analysis for sales forecasting with big data. Production and Operations Management, 45(8), 130–148. https://doi.org/10.1111/poms.12737.
Lee, C., Xun, X., & Chia-Chun, L. (2019). Using online user-generated reviews to predict offline box-office sales and online DVD Store sales in the O2O Era. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-18762019000100106.
Lee, H., Kim, S. G., Park, H., & Kang, P. (2014). Pre-launch new product demand forecasting using the Bass model: A statistical and machine learning-based approach. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 86, 49–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2013.08.020.
Lee, N.-U., Shim, J.-S., Ju, Y.-W., & Park, S.-C. (2018a). Design and implementation of the SARIMA–SVM time series analysis algorithm for the improvement of atmospheric environment forecast accuracy. Soft Computing, 22(13), 4275–4281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-017-2825-y.
Lee, S., Cho, C., Hong, E., & Yoon, B. (2016). Forecasting mobile broadband traffic: Application of scenario analysis and Delphi method. Expert Systems with Applications, 44, 126–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2015.09.030.
Lee, W. S., Choi, H. S., & Sohn, S. Y. (2018b). Forecasting new product diffusion using both patent citation and web search traffic. PLoS ONE, 13(4), e0194723. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0194723.
Li, S., Tao, C., Lin, W., & Ming, C. (2018). Effective tourist volume forecasting supported by PCA and improved BPNN using Baidu index. Tourism Management, 68, 116–126.
Li, X., Pan, B., Law, R., & Huang, X. (2017). Forecasting tourism demand with composite search index. Tourism Management, 59, 57–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2016.07.005.
Liang, X., Xie, L., & Yan, H. (2015). Self-restraining bass models. Journal of Forecasting, 34(6), 472–477. https://doi.org/10.1002/for.2346.
Marshall, P., Dockendorff, M., & Ibáñez, S. (2013). A forecasting system for movie attendance. Journal of Business Research, 66(10), 1800–1806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2013.01.013.
Mentzer, J. T., & Moon, M. A. (2005). Sales forecasting management: A demand management approach. Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications, Inc. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781452204444.
Norton, J. A., & Bass, F. M. (1987). A diffusion theory model of adoption and substitution for successive generations of high-technology products. Management Science, 33(9), 1069–1086. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.33.9.1069.
Sagaert, Y. R., Aghezzaf, E.-H., Kourentzes, N., & Desmet, B. (2018). Tactical sales forecasting using a very large set of macroeconomic indicators. European Journal of Operational Research, 264(2), 558–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2017.06.054.
Satoh, D. (2000). A discrete bass model and its parameter estimation. Journal of the Operations Research Society of Japan, 44(1), 1–18.
Schaer, O., Kourentzes, N., & Fildes, R. (2019). Demand forecasting with user-generated online information. International Journal of Forecasting, 35(1), 197–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijforecast.2018.03.005.
Schmidt, U., Starmer, C., & Sugden, R. (2008). Third-generation prospect theory. Journal of Risk and Uncertainty, 36(3), 203–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11166-008-9040-2.
See-To, E. W. K., & Ngai, E. W. T. (2018). Customer reviews for demand distribution and sales nowcasting: A big data approach. Annals of Operations Research, 270(1–2), 415–431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-016-2296-z.
Shemshadi, A., Shirazi, H., Toreihi, M., & Tarokh, M. J. (2011). A fuzzy VIKOR method for supplier selection based on entropy measure for objective weighting. Expert Systems with Applications, 38(10), 12160–12167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2011.03.027.
Shi, X., Li, F., & Bigdeli, A. Z. (2016). An examination of NPD models in the context of business models. Journal of Business Research, 69(7), 2541–2550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2015.10.087.
Song, Y., Lee, S., Zo, H., & Lee, H. (2015). A hybrid Bass–Markov model for the diffusion of a dual-type device-based telecommunication service: The case of WiBro service in Korea. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 79, 85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2014.10.020.
Speece, M. W., & Maclachlan, D. L. (1995). Application of a multi-generation diffusion model to milk container technology. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 49(3), 281–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-1625(95)00006-V.
Vana, P. M., & Lambrecht, A. M. (2018). Online reviews: Star ratings, position effects and purchase likelihood. Social Science Electronic Publishing, 10(3), 14–23.
Varian, H. R., & Choi, H. (2012). Predicting the present with Google trends. Economic Record, 88(s1), 2–9.
Wang, T. C., & Lee, H. Da. (2009). Developing a fuzzy TOPSIS approach based on subjective weights and objective weights. Expert Systems with Applications, 36, 8980–8985. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2008.11.035.
Xu, Q., & Liu, Z. (2014). Sales forecast of dual-channel supply chain based on improved bass and SVM model. Applied Mathematics & Information Sciences;, 8(2), 891–900. https://doi.org/10.12785/amis/080252.
Yang, X., Pan, B., Evans, J. A., & Lv, B. (2015). Forecasting Chinese tourist volume with search engine data. Tourism Management, 46, 386–397.
Yu, L., Zhao, Y., Tang, L., & Yang, Z. (2019). Online big data-driven oil consumption forecasting with Google trends. International Journal of Forecasting, 61(2), 183–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijforecast.2017.11.005.
Yu, X., Liu, Y., Huang, X., & An, A. (2012). Mining online reviews for predicting sales performance: A case study in the movie domain. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 24(4), 720–734. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2010.269.
Zhang, C., Tian, Y.-X., Fan, Z.-P., Liu, Y., & Fan, L.-W. (2019). Product sales forecasting using macroeconomic indicators and online reviews: A method combining prospect theory and sentiment analysis. Soft Computing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-018-03742-1.
Zhang, D., Xiao, M., Yang, X., & He, Y. (2015). The analysis of manufacturing PMI potential trends of the US, EU, Japan and China. Procedia Computer Science, 55, 43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PROCS.2015.07.006.
Zhang, L., Luo, J., & Yang, S. (2009). Forecasting box office revenue of movies with BP neural network. Expert Systems with Applications, 36(3), 6580–6587. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ESWA.2008.07.064.
Zhou, S., Mao, M., & Jianhui, S. U. (2011). Prediction of wind power based on principal component analysis and artificial neural network. Power System Technology, 35(9), 128–132.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Social Science Fund of China (19BGL229).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
1.1 Appendix 1: The sales volume data of Volkswagen Lavida
See Table 14.
1.2 Appendix 2: The WoM index of Volkswagen Lavida at each period
See Table 15.
1.3 Appendix 3: Keyword Thesaurus of Baidu Search concerning Volkswagen Lavida
See Table 16.
1.4 Appendix 4: Result of BPI calculated by Baidu Search data at each period
See Table 17.
1.5 Appendix 5: Names of the collected macroeconomic indicators
See Table 18.
1.6 Appendix 6: Result of PMI calculated by macroeconomic indicator data at each period
See Table 19.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Tian, YX. & Fan, LW. Improving the Bass model’s predictive power through online reviews, search traffic and macroeconomic data. Ann Oper Res 295, 881–922 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-020-03716-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-020-03716-3