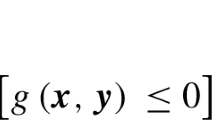Abstract
The CoMirror algorithm, by Beck et al. (Oper Res Lett 38(6):493–498, 2010), is designed to solve convex optimization problems with one functional constraint. At each iteration, it performs a mirror-descent update using either the subgradient of the objective function or the subgradient of the constraint function, depending on whether or not the constraint violation is below some tolerance. In this paper, we combine the CoMirror algorithm with inexact cut generation to create the SIP-CoM algorithm for solving semi-infinite programming (SIP) problems. First, we provide general error bounds for SIP-CoM. Then, we propose two specific random constraint sampling schemes to approximately solve the cut generation problem for generic SIP. When the objective and constraint functions are generally convex, randomized SIP-CoM achieves an \({\mathcal {O}}(1/\sqrt{N})\) convergence rate in expectation (in terms of the optimality gap and SIP constraint violation). When the objective and constraint functions are all strongly convex, this rate can be improved to \({\mathcal {O}}(1/N)\).



Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
24 September 2020
This erratum is published as due to some technical error author names appeared reversed in the final publication.
References
Aliprantis, C. D., & Border, K. C. (2005). Infinite dimensional analysis. A hitchhiker’s guide (3rd ed.). Berlin: Springer.
Anderson, E. J., & Nash, P. (1987). Linear programming in infinite-dimensional spaces: Theory and applications. Chichester: Wiley.
Aragón, F. J., Goberna, M. A., López, M. A., & Rodríguez, M. M. (2019). Nonlinear optimization. New York: Springer.
Auslender, A., Ferrer, A., Goberna, M. A., & López, M. A. (2015). Comparative study of RPSALG algorithm for convex semi-infinite programming. Computational Optimization and Applications, 60, 59–87.
Auslender, A., Goberna, M. A., & López, M. A. (2009). Penalty and smoothing methods for convex semi-infinite programming. Mathematics of Operations Research, 34, 303–319.
Beck, A., Ben-Tal, A., Guttmann-Beck, N., & Tetruashvili, L. (2010). The comirror algorithm for solving nonsmooth constrained convex problems. Operations Research Letters, 38, 493–498.
Betrò, B. (2004). An accelerated central cutting plane algorithm for linear semi-infinite programming. Mathematical Programming, 101A, 479–495.
Bhat, N., Farias, V., & Moallemi, C. C. (2012). Non-parametric approximate dynamic programming via the kernel method. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (pp. 386–394).
Calafiore, G., & Campi, M. (2005). Uncertain convex programs: Randomized solutions and confidence levels. Mathematical Programming, 102A, 25–46.
Campi, M. C., & Garatti, S. (2008). The exact feasibility of randomized solutions of uncertain convex programs. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 19, 1211–1230.
Dentcheva, D., & Ruszczynski, A. (2003). Optimization with stochastic dominance constraints. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 14, 548–566.
Dentcheva, D., & Ruszczyński, A. (2004). Optimality and duality theory for stochastic optimization problems with nonlinear dominance constraints. Mathematical Programming, 99A, 329–350.
Dentcheva, D., & Ruszczyński, A. (2009). Optimization with multivariate stochastic dominance constraints. Mathematical Programming, 117A, 111–127.
Dentcheva, D., & Wolfhagen, E. (2015). Optimization with multivariate stochastic dominance constraints. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 25, 564–588.
Farias, D Pd, & Roy, B. V. (2004). On constraint sampling in the linear programming approach to approximate dynamic programming. Mathematics of Operations Research, 29, 462–478.
Fonseca, I., & Leoni, G. (2007). Modern methods in the calculus of variations:\(L ^{\wedge } p\)spaces. New York: Springer.
Goberna, M. A., & López, M. A. (2014). Post-optimal analysis in linear semi-infinite optimization. New York: Springer.
Goberna, M. A., & López, M. A. (2017). Recent contributions to linear semi-infinite optimization. 4OR, 15, 221–264.
Goberna, M. A., & López, M. A. (2018). Recent contributions to linear semi-infinite optimization: An update. Annals of Operations Research, 271, 237–278.
Gribik, P. (1979). A central-cutting-plane algorithm for semi-infinite programming problems. In Semi-infinite programming (pp. 66–82). Berlin: Springer.
Haskell, W. B., Shanthikumar, J. G., & Shen, Z. M. (2013). Optimization with a class of multivariate integral stochastic order constraints. Annals of Operations Research, 206, 147–162.
Haskell, W. B., Shanthikumar, J. G., & Shen, Z. M. (2017). Primal-dual algorithms for optimization with stochastic dominance. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 27, 34–66.
Homem-de Mello, T., & Mehrotra, S. (2009). A cutting-surface method for uncertain linear programs with polyhedral stochastic dominance constraints. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 20, 1250–1273.
Hu, J., Homem-de Mello, T., & Mehrotra, S. (2012). Sample average approximation of stochastic dominance constrained programs. Mathematical Programming, 133A, 171–201.
Ito, S., Liu, Y., & Teo, K. L. (2000). A dual parametrization method for convex semi-infinite programming. Annals of Operations Research, 98, 189–213.
Jin, P., Ling, C., & Shen, H. (2015). A smoothing Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm for semi-infinite programming. Computational Optimization and Applications, 60, 675–695.
Kanamori, T., & Takeda, A. (2012). Worst-case violation of sampled convex programs for optimization with uncertainty. Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications, 152, 171–197.
Kortanek, K. O., & No, H. (1993). A central cutting plane algorithm for convex semi-infinite programming problems. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 3, 901–918.
Küçükyavuz, S., & Noyan, N. (2016). Cut generation for optimization problems with multivariate risk constraints. Mathematical Programming, 159A, 165–199.
Lan, G., Nemirovski, A., & Shapiro, A. (2012). Validation analysis of mirror descent stochastic approximation method. Mathematical Programming, 134A, 425–458.
Lan, G., & Zhou, Z. (2020). Algorithms for stochastic optimization with function or expectation constraints. Computational Optimization and Applications, 76(2), 461–498.
Li, D.-H., Qi, L., Tam, J., & Wu, S.-Y. (2004). A smoothing newton method for semi-infinite programming. Journal of Global Optimization, 30, 169–194.
Lin, Q., Nadarajah, S., & Soheili, N. (2020). Revisiting approximate linear programming: Constraint-violation learning with applications to inventory control and energy storage. Management Science, 66, 1544–1562.
Ling, C., Ni, Q., Qi, L., & Wu, S.-Y. (2010). A new smoothing newton-type algorithm for semi-infinite programming. Journal of Global Optimization, 47, 133–159.
Liu, Y., & Teo, K. L. (2002). An adaptive dual parametrization algorithm for quadratic semi-infinite programming problems. Journal of Global Optimization, 24, 205–217.
Liu, Y., Teo, K. L., & Wu, S.-Y. (2004). A new quadratic semi-infinite programming algorithm based on dual parametrization. Journal of Global Optimization, 29, 401–413.
López, M., & Still, G. (2007). Semi-infinite programming. European Journal of Operational Research, 180, 491–518.
Luenberger, D. G. (1968). Optimization by vector space methods. New York: Wiley.
Mehrotra, S., & Papp, D. (2014). A cutting surface algorithm for semi-infinite convex programming with an application to moment robust optimization. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 24, 1670–1697.
Mohajerin Esfahani, P., & Kuhn, D. (2018). Data-driven distributionally robust optimization using the wasserstein metric: Performance guarantees and tractable reformulations. Mathematical Programming, 171A, 115–166.
Mohajerin Esfahani, P., Sutter, T., Kuhn, D., & Lygeros, J. (2018). From infinite to finite programs: Explicit error bounds with applications to approximate dynamic programming. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 28, 1968–1998.
Mohajerin Esfahani, P., Sutter, T., & Lygeros, J. (2015). Performance bounds for the scenario approach and an extension to a class of non-convex programs. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 60, 46–58.
Nemirovski, A., Juditsky, A., Lan, G., & Shapiro, A. (2009). Robust stochastic approximation approach to stochastic programming. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 19, 1574–1609.
Ni, Q., Ling, C., Qi, L., & Teo, K. L. (2006). A truncated projected newton-type algorithm for large-scale semi-infinite programming. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 16, 1137–1154.
Noyan, N., & Rudolf, G. (2013). Optimization with multivariate conditional value-at-risk constraints. Operations Research, 61, 990–1013.
Noyan, N., & Rudolf, G. (2018). Optimization with stochastic preferences based on a general class of scalarization functions. Operations Research, 66, 463–486.
Okuno, T., Hayashi, S., Yamashita, N., & Gomoto, K. (2016). An exchange method with refined subproblems for convex semi-infinite programming problems. Optimization Methods and Software, 31, 1305–1324.
Pang, L.-P., Lv, J., & Wang, J.-H. (2016). Constrained incremental bundle method with partial inexact oracle for nonsmooth convex semi-infinite programming problems. Computational Optimization and Applications, 64, 433–465.
Qi, L., Ling, C., Tong, X., & Zhou, G. (2009). A smoothing projected newton-type algorithm for semi-infinite programming. Computational Optimization and Applications, 42, 1–30.
Qi, L., Wu, S.-Y., & Zhou, G. (2003). Semismooth newton methods for solving semi-infinite programming problems. Journal of Global Optimization, 27, 215–232.
Robert, C., & Casella, G. (2004). Monte Carlo statistical methods. New York: Springer.
Stein, O. (2012). How to solve a semi-infinite optimization problem. European Journal of Operational Research, 223, 312–320.
Still, G. (2001). Discretization in semi-infinite programming: The rate of convergence. Mathematical Programming, 91A, 53–69.
Teo, K. L., Yang, X., & Jennings, L. S. (2000). Computational discretization algorithms for functional inequality constrained optimization. Annals of Operations Research, 98, 215–234.
Wei, B., Haskell, W. B., & Zhao, S. (2020). An inexact primal-dual algorithm for semi-infinite programming. Mathematical Methods of Operations Research, 91(3), 501–544.
Xu, Q.-J., & Jian, J.-B. (2013). A nonlinear norm-relaxed method for finely discretized semi-infinite optimization problems. Nonlinear Dynamics, 73, 85–92.
Zhang, L., Wu, S.-Y., & López, M. A. (2010). A new exchange method for convex semi-infinite programming. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 20, 2959–2977.
Funding
Funding was provided by Singapore A*STAR (Grant No. 1421200078)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, B., Haskell, W.B. & Zhao, S. The CoMirror algorithm with random constraint sampling for convex semi-infinite programming. Ann Oper Res 295, 809–841 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-020-03766-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-020-03766-7