Abstract
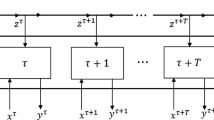
One method for evaluating cost-efficiency of commercial firms is data envelopment analysis. In the real world, data have a time dependency that also affects the cost-efficiency calculation. This article introduces a new model for measuring cost-efficiency under inter-temporal dependency in an assessment window. In the proposed approach, there is a reserve capital for the assessment window that is considered as the input of this period, and at any time of the window, a certain amount of capital is used. For practical application, the proposed model is applied to a real dataset of branches of an Iranian commercial bank to evaluate cost-efficiency under inter-temporal dependency.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akther, S., Fukuyama, H., & Weber, W. L. (2013). Estimating two-stage network slacks-based inefficiency: An application to bangladesh banking. Omega, 41(1), 88–96.
Aparicio, J., Borras, F., Pastor, J. T., & Vidal, F. (2015). Measuring and decomposing firms revenue and cost efficiency: The Russell measures revisited. International Journal of Production Economics, 165, 19–28.
Ashrafi, A., & Mansouri Kaleibar, M. (2017). Cost, revenue and profit efficiency models in generalized fuzzy data envelopment analysis. Fuzzy Information and Engineering, 9(2), 237–246.
Avkiran, N. K. (2015). An illustration of dynamic network dea in commercial banking including robustness tests. Omega, 55, 141–150.
Banker, R. D., Charnes, A., & Cooper, W. W. (1984). Some models for estimating technical and scale inefficiencies in data envelopment analysis. Management Science, 30(9), 1078–1092.
Berger, A.N., & Humphrey, D.B. (1992). Measurement and efficiency issues in commercial banking. In Output measurement in the service sectors (pp. 245–300) University of Chicago Press.
Charnes, A., Cooper, W. W., & Rhodes, E. (1978). Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. European Journal of Operational Research, 2(6), 429–444.
Emrouznejad, A., & Thanassoulis, E. (2005). A mathematical model for dynamic efficiency using data envelopment analysis. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 160, 363–378.
Fare, R., & Grosskopf, S. (1996). Intertemporal production frontiers: With dynamic DEA. Amsterdam: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Fare, R., Grosskopf, S., & Lovell, C. (1985). The measurement of efficiency of production. Amsterdam: Kluwer Academic Publisher.
Farrell, M. J. (1957). The measurement of productive efficiency. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series A (General), 120(3), 253–290.
Ferrier, G. D., & Lovell, C. A. K. (1990). Measuring cost efficiency in banking: Econometric and linear programming evidence. Journal of Econometrics, 46, 229–245.
Fukuyama, H., & Matousek, R. (2017). Modelling bank performance: A network dea approach. European Journal of Operational Research, 259(2), 721–732.
Fukuyama, H., & Weber, W. L. (2010). A slacks-based inefficiency measure for a two-stage system with bad outputs. Omega, 38(5), 398–409.
Ghobadi, S., Jahanshahloo, G., Lotfi, F. H., & Rostamy-Malkhalifeh, M. (2018). Efficiency measure under inter-temporal dependence. International Journal of Information Technology and Decision Making, 17(02), 657–675.
Holod, D., & Lewis, H. F. (2011). Resolving the deposit dilemma: A new dea bank efficiency model. Journal of Banking and Finance, 35(11), 2801–2810.
Jahanshahloo, G. R., & Soleimani-damaneh, M. (2006). On the pareto (dynamically) efficient paths. International Journal of Computer Mathematics, 63, 629–633.
Jahanshahloo, G. R., Soleimani-damaneh, M., & Ghobadi, S. (2015). Inverse dea under inter-temporal dependence using multiple-objective programming. European Journal of Operational Research, 240, 447–456.
Kourtzidis, S. A., Matousek, R., & Tzeremes, N. G. (2019). Productivity growth in network models: An application to banking during the financial crisis. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 70(1), 111–124.
Kuosmanen, T., & Post, T. (2001). Measuring economic efficiency with incomplete price information: With an application to european commercial banks. European Journal of Operational Research, 134(1), 43–58.
Lozano, S. (2016). Slacks-based inefficiency approach for general networks with bad outputs: An application to the banking sector. Omega, 60, 73–84.
Mahmoudabadi, M. Z., & Emrouznejad, A. (2019). Comprehensive performance evaluation of banking branches: A three-stage slacks-based measure (SBM) data envelopment analysis. International Review of Economics and Finance, 64, 359–376.
Mostafaee, A., & Saljooghi, F. (2010). Cost efficiency measures in data envelopment analysis with data uncertainty. European Journal of Operational Research, 202(2), 595–603.
Mozaffari, M., Kamyab, P., Jablonsky, J., & Gerami, J. (2014). Cost and revenue efficiency in DEA-R models. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 78, 188–194.
Mukherjee, A., Nath, P., & Pal, M. (2003). Resource, service quality and performance triad: A framework for measuring efficiency of banking services. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 54(7), 723–735.
Nemoto, J., & Goto, M. (1999). Dynamic data envelopment analysis: Modeling intertemporal behavior of a firm in the presence of productive inefficiencies. Economics Letters, 64(1), 51–56.
Nemoto, J., & Goto, M. (2003). Measurement of dynamic efficiency in production: An application of data envelopment analysis to japanese electric utilities. Journal of Productivity Analysis, 19(2–3), 191–210.
Puig-Junoy, J. (2000). Partitioning input cost efficiency into its allocative and technical components: An empirical dea application to hospitals. Socio-Economic Planning Sciences, 34, 199–218.
Ray, S. C., & Kim, H. J. (1995). Cost efficiency in the US steel industry: A nonparametric analysis using data envelopment analysis. European Journal of Operational Research, 80, 654–671.
Sahoo, B. K., Mehdiloozad, M., & Tone, K. (2014). Cost, revenue and profit efficiency measurement in DEA: A directional distance function approach. European Journal of Operational Research, 237(3), 921–931.
Sengupta, J. (1996). Dynamics of data envelopment analysis: Theory of systems efficiency. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 47(11), 1421.
Soleimani-damaneh, M. (2013). Another approach for estimating RTS in dynamic DEA. Journal of Productivity Analysis, 39(1), 75–81.
Soleimani-Damaneh, M. (2013). An enumerative algorithm for solving nonconvex dynamic DEA models. Optimization Letters, 7(1), 101–115.
Sueyoshi, T., & Sekitani, K. (2005). Returns to scale in dynamic DEA. European Journal of Operational Research, 161(2), 536–544.
Toloo, M. (2016). A cost efficiency approach for strategic vendor selection problem under certain input prices assumption. Measurement, 85, 175–183.
Tone, K. (2002). A strange case of the cost and allocative efficiencies in DEA. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 53(11), 1225–1231.
Tone, K., & Tsutsui, M. (2010). Dynamic DEA: A slacks-based measure approach. Omega, 38(3–4), 145–156.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soleimani-Chamkhorami, K., Ghobadi, S. Cost-efficiency under inter-temporal dependence. Ann Oper Res 302, 289–312 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-021-03989-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-021-03989-2