Abstract
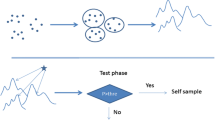
Support vector data description (SVDD) procedure fits a spherically shaped boundary around the normal data by minimizing the volume of the description. However, the SVDD may not find an efficient boundary if the normal data consist of multiple classes. In addition to the multi-class normal data, some anomaly observations can be available. We propose a generalized SVDD procedure which finds multiple spheres around the multi-class data by incorporating the anomaly observations into the training procedure. Thus, descriptions for each class include as many as their corresponding class observations by keeping the other class and anomaly observations as far as possible. Moreover, we introduce a generalized Bayesian framework which utilizes the relationships among the classes by not only considering the prior information from normal classes but also the anomaly class. Experiments with various simulation studies and real-life applications demonstrate that the proposed approach can effectively identify the anomalies in multi-class data.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aleskerov, E., Freisleben, B. & Rao, B. (1997). Cardwatch: A neural network-based database mining system for credit card fraud detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/IAFE 1997 IEEE computational intelligence for financial Engineering (CIFEr (pp. 220–226).
Amer, M., Goldstein, M. & Abdennadher, S., (2013). Enhancing one-class support vector machines for unsupervised anomaly detection. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD workshop on outlier detection and description ACM (pp. 8–15).
Azzalini, A., & Capitanio, A. (1999). Statistical applications of the multivariate skew normal distribution. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Statistical Methodology), 61, 579–602.
Azzalini, A., & Dalla Valle, A. (1996). The multivariate skew-normal distribution. Biometrika, 83, 715–726.
Bovolo, F., Camps-Valls, G., & Bruzzone, L. (2010). A support vector domain method for change detection in multitemporal images. Pattern Recognition Letters, 31, 1148–1154.
Chandola, V., Banerjee, A., & Kumar, V. (2009). Anomaly detection: A survey. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 41, 15.
Demšar, J. (2006). Statistical comparisons of classifiers over multiple data sets. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 7, 1–30.
Duin, R., Juszczak, P., Paclik, P., Pekalska, E., De Ridder, D., Tax, D., & Verzakov, S. (2000). A matlab toolbox for pattern recognition. Prtools Version, 3, 109–111.
Erfani, S. M., Rajasegarar, S., Karunasekera, S., & Leckie, C. (2016). High-dimensional and large-scale anomaly detection using a linear one-class SVM with deep learning. Pattern Recognition, 58, 121–134.
Ghasemi, A., Rabiee, H. R., Manzuri, M. T. & Rohban, M. H. (2016). A bayesian approach to the data description problem. arXiv preprint arXiv:1602.07507
Guo, S. M., Chen, L. C., & Tsai, J. S. H. (2009). A boundary method for outlier detection based on support vector domain description. Pattern Recognition, 42(1), 77–83.
Hodge, V., & Austin, J. (2004). A survey of outlier detection methodologies. Artificial Intelligence Review, 22, 85–126.
Huang, G., Chen, H., Zhou, Z., Yin, F., & Guo, K. (2011). Two-class support vector data description. Pattern Recognition, 44, 320–329.
Kang, J. H., & Kim, S. B. (2013). A clustering algorithm-based control chart for inhomogeneously distributed TFT-LCD processes. International Journal of Production Research, 51(18), 5644–5657.
Kang, P., & Cho, S. (2012). Support vector class description (SVCD): Classification in kernel space. Intelligent Data Analysis, 16, 351–364.
Kumar, V. (2005). Parallel and distributed computing for cybersecurity. IEEE Distributed System Online, 6, 10.
Lee, K., Kim, D.-W., Lee, D., & Lee, K. H. (2005). Improving support vector data description using local density degree. Pattern Recognition, 38, 1768–1771.
Lee, K., Kim, D.-W., Lee, K. H., & Lee, D. (2007). Density-induced support vector data description. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 18, 284–289.
Lee, S.-W., Park, J., & Lee, S.-W. (2006). Low resolution face recognition based on support vector data description. Pattern Recognition, 39, 1809–1812.
Li, K.-L., Huang, H.-K., Tian, S.-F. & Xu, W. (2003). Improving one-class SVM for anomaly detection. In 2003 International conference on machine learning and cybernetics. IEEE (pp. 3077–3081).
Moya. M., Koch M. & Hostetler L. (1993). One-class classifier networks for target recognition applications. In Proceedings of the world congresson neural networks, Portland (pp. 797–801).
Mu, T., & Nandi, A. K. (2009). Multiclass classification based on extended support vector data description. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics), 39, 1206–1216.
Ning, X., & Tsung, F. (2013). Improved design of kernel distance-based charts using support vector methods. IIE Transactions, 45, 464–476.
Phaladiganon, P., Kim, S. B., & Chen, V. C. (2014). A density-focused support vector data description method. Quality and Reliability Engineering International, 30(6), 879–890.
Schölkopf, B., Platt, J. C., Shawe-Taylor, J., Smola, A. J., & Williamson, R. C. (2001). Estimating the support of a high-dimensional distribution. Neural Computation, 13, 1443–1471.
Sotiris, V. A., Peter, W. T., & Pecht, M. G. (2010). Anomaly detection through a bayesian support vector machine. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 59, 277–286.
Spence, C., Parra, L., & Sajda, P. (2001). Detection, synthesis and compression in mammographic image analysis with a hierarchical image probability model. In Proceedings of the IEEE workshop on mathematical methods in biomedical image analysis. IEEE Computer Society, 3.
Tax, D. M., & Duin, R. P. (1999). Support vector domain description. Pattern Recognition Letters, 20, 1191–1199.
Tax, D. M., & Duin, R. P. (2004). Support vector data description. Machine Learning, 54, 45–66.
Thornhill, N. F., Patwardhan, S. C., & Shah, S. L. (2008). A continuous stirred tank heater simulation model with applications. Journal of Process Control, 18, 347–360.
Turkoz, M., Kim, S., Son, Y., Jeong, M. K. & Elsayed, E. A. (2020). Generalized support vector data description for anomaly detection. Pattern Recognition, 100, 107119.
Turkoz, M., Kim, S., Jeong, Y. S., Al-Khalifa, K. N., & Hamouda, A. M. (2016). Distribution-free adaptive step-down procedure for fault identification. Quality and Reliability Engineering International, 32(8), 2701–2716.
Turkoz, M., Kim, S., Jeong, Y. S., Jeong, M. K., Elsayed, A. E., Al-Khalifa, K. N., & Hamouda, A. M. (2019). Bayesian framework for fault variable identification. Journal of Quality Technology, 51(4), 375–391.
Vapnik, V. (1995). The nature of statistical learning theory. Springer.
Zhang, Y., Lu, H., Zhang, L., & Ruan, X. (2016). Combining motion and appearance cues for anomaly detection. Pattern Recognition, 51, 443–452.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Turkoz, M., Kim, S. Multi-class Bayesian support vector data description with anomalies. Ann Oper Res 317, 287–312 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-021-04364-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-021-04364-x