Abstract
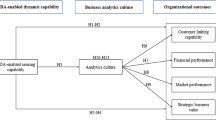
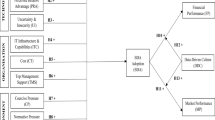
In the present digital environment, a data-driven organizational culture has become a vital emerging driver of organizational growth. This data-driven culture has assumed an advanced shape due to adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) integrated business analytics tools in the organization. Data-driven culture in the organization could considerably impact product innovation strategy as well as organizational process alteration. In this context, the aim of this study is to investigate how an organization’s data-driven culture impacts process performance and product innovation that led to enhanced organizational overall performance and higher business value. Methodologically, supported by relevant extant literature and inputs from the resource-based view and dynamic capability theories (organizational context), a conceptual model and a set of hypotheses are initially developed. These are subsequently statistically validated through a survey involving 513 usable responses from employees of different organizations using business analytics tools embedded with AI capability. The findings demonstrate that an organizational data-driven culture has considerable moderating impact on product innovation and process improvement, which ultimately enhance business value through improved organizational overall performance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi, A., Sarker, S., & Chiang, R. (2016). Big data research in information systems: Toward an inclusive research agenda. Journal of the Association for Information Systems, 17(2), 1–32.
Akter, S., & Wamba, S. F. (2016). Big data analytics in E-commerce: A systematic review and agenda for future research. Electronic Markets, 26, 173–194.
Akter, S., Bandara, R., Hani, U., Fosso Wamba, S., Foropon, C., & Papadopoulos, T. (2019a). Analytics-based decision-making for service systems: A qualitative study and agenda for future research. International Journal of Information Management, 48, 85–95.
Akter, S., D’Ambra, J., & Ray, P. (2011). Trustworthiness in mHealth information services: An assessment of a hierarchical model with mediating and moderating effects using partial least squares (PLS). Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 62(1), 100–116.
Akter, S., Fosso Wamba, S., & Dewan, S. (2017). Why PLS-SEM is suitable for complex modelling? An empirical illustration in big data analytics quality. Production Planning & Control, 28(11/12), 1011–1021.
Akter, S., McCarthy, G., Sajib, S., Michael, K., Dwivedi, Y. K., D’Ambra, J., & Shen, K. N. (2021). Algorithmic bias in data-driven innovation in the age of AI. International. Journal of Information Management. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2021.102387
Akter, S., Michael, K., Uddin, M. R., McCarthy, G., & Rahman, M. (2020). Transforming business using digital innovations: The application of AI, blockchain, cloud and data analytics. Annals of Operations Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-020-03620-w
Akter, S., Wamba, S. F., & D’Ambra, J. (2019b). Enabling a transformative service system by modeling quality dynamics. International Journal of Production Economics, 207, 210–226.
Apostolopoulos, N., & Liargovas, P. (2016). Regional parameters and solar energy enterprises: Purposive sampling and group AHP approach. International Journal of Energy Sector Management, 10(1), 19–37.
Appelbaum, D., Kogan, A., Vasarhelyi, M., & Yan, Z. (2017). Impact of business analytics and enterprise systems on managerial accounting. International Journal of Accounting Information Systems, 25, 29–44.
Armstrong, J. S., & Overton, T. S. (1977). Estimating nonresponse bias in mail surveys. Journal of Marketing Research, 14(3), 396–402.
Augusto, M., & Coelho, F. (2009). Market orientation and new-to-the-world products: Exploring the moderating effects of innovativeness, competitive strength, and environmental forces. Industrial Marketing Management, 38(1), 94–108.
Bacon, L. D. (1999). Using LISREL and PLS to Measure Customer Satisfaction, Sawtooth Software Conference Proceedings, La Jolla, California, Feb 2–5, 305–306.
Barney, J. (1991). Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. Journal of Management, 17, 99–120.
Barney, J. B. (1986). Organizational culture: Can it be a source of sustained competitive advantage? Academy of Management Review, 11(3), 656–665.
Bayrak, T. (2015). A review of business analytics: A business enabler or another passing fad. Procedia – Social and Behavioral Sciences, 195, 230–239.
Bichler, M., Heinzl, A., & Van der Aalst, W. M. P. (2017). Business analytics and data science: Once again? Business & Information Systems Engineering, 59(2), 77–79.
Bozic, K., & Dimovski, V. (2019). Business intelligence and analytics for value creation: The role of absorptive capacity. International Journal of Information Management, 46, 93–103.
Chae, B., Yang, C., Olson, D., & Sheu, C. (2014). The impact of advanced analytics and data accuracy on operational performance: A contingent resource-based theory (RBT) perspective. Decision Support Systems, 59(1), 119–126.
Chatterjee, S., & Kar, A. K. (2018). Effects of successful adoption of information technology enabled services in proposed smart cities of India: From user experience perspective. Journal of Science and Technology Policy Management., 9(2), 189–209.
Chatterjee, S. (2020). AI strategy of India: Policy framework, adoption challenges and actions for government. People, Process and Policy. https://doi.org/10.1108/TG-05-2019-0031
Chatterjee, S., Chaudhuri, R., Vrontis, D., Thrassou, A., Ghosh, S., & Chaudhuri, S. (2020). Social customer relationship management factors and business benefits. International Journal of Organizational Analysis, in Press. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOA-11-2019-1933
Chen, D. Q., Preston, D. S., & Swink, M. (2015). How the use of big data analytics affects value creation in supply chain management. Journal of Management Information Systems, 32(4), 4–39.
Chidlow, A., Ghauri, P., Yeniyurt, S., & Cavusgil, S. T. (2015). Establishing rigor in mail survey procedures in international business research. Journal of World Business, 50(1), 26–36.
Chin, W. W. (2010). How to write up and report PLS analyses. In V. E. Vinzi, W. W. Chin, J. Henseler, & H. Wang (Eds.), Handbook of Partial Least Squares (pp. 655–690). Springer.
Christofi, M., Pereira, V., Vrontis, D., Tarba, S., & Thrassou, A. (2021). Agility and flexibility in international business research: A comprehensive review and future research directions. Journal of World Business, 56(3), 101194.
Christofi, M., Vrontis, D., Thrassou, A., & Shams, R. M. S. (2019). Triggering technological innovation through cross-border mergers and acquisitions: A micro-foundational perspective. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 146, 148–166.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 2nd. Hillsdale, NJ, Erlbaum. USA.
Cohen, W. M., & Levinthal, D. A. (1990). Absorptive capacity: A new perspective on learning and innovation. Administrative Science Quarterly, 15(1), 128–152.
Cosic, R., Shanks, G., & Maynard, S. (2015). A business analytics capability framework. Australasian Journal of Information Systems, 19, 5–19.
Dahlander, L., & Gann, D. M. (2010). How open is innovation? Research Policy, 39(6), 699–709.
Davenport, T. H., Harris, J. G., De Long, D. W., & Jacobson, A. L. (2001). Data to knowledge to results: Building an analytic capability. California Management Review, 43(2), 117–138.
de Camargo, F. P., Roman Pais Seles, B. M., Chiappetta Jabbour, C. J., Barberio Mariano, E., & de Sousa Jabbour, A. B. L. (2018). Management theory and big data literature: From a review to a research agenda. International Journal of Information Management, 43, 112–129.
Delen, D., & Demirkan, H. (2013). Data, information and analytics as services. Decision Support Systems, 55(1), 359–363.
Delen, D., & Zolbanin, H. M. (2018). The analytics paradigm in business research. Journal of Business Research, 90, 186–195.
Droge, C., Calantone, R., & Harmancioglu, N. (2008). New product success: Is it really controllable by managers in highly turbulent environments? Journal of Product Innovation Management, 25(3), 272–286.
Duan, Y., Cao, G., & Edwards, J. S. (2018). Understanding the impact of business analytics on innovation. European Journal of Operational Research, in Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2018.06.021
Duan, Y., Edwards, J. S., & Dwivedi, Y. (2019). Artificial intelligence for decision making in the era of Big Data – Evolution, challenges and research agenda. International Journal of Information Management, 48, 63–71.
Dubey, R., Gunasekaran, A., Childe, S. J., Blome, C., & Papadopoulos, T. (2019). Big data and predictive analytics and manufacturing performance: Integrating institutional theory, resource-based view and big data culture. British Journal of Management, 30, 341–361.
Dutta, D., & Bose, I. (2015). Managing a big data project: The case of Ramco Cements Limited. International Journal of Production Economics, 165(3), 293–306.
Fitzgerald, B., & O’Kane, T. (1999). A longitudinal study of software process improvement. IEEE Software, 16(3), 37–45.
Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research, 18(1), 39–50.
Garg, S. (2019). Research methodology in HR initiatives in building inclusive and accessible workplaces. Emerald Publishing Limited.
Geisser, S. (1975). The predictive sample reuse method with applications. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 70(350), 320–328.
Gnizy, I. (2019). Big data and its strategic path to value in international firms. International Marketing Review, 36(3), 318–341.
Gunasekaran, A., Papadopoulos, T., Dubey, R., Wamba, S. F., Childe, S. J., Hazen, B., & Akter, S. (2017). Big data and predictive analytics for supply chain and organizational performance. Journal of Business Research, 70, 308–317.
Hair, J. F., Jr., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C., & Sarstedt, M. (2016). A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). Sage Publications.
Hair, J. F., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2011). PLS-SEM: Indeed a silver bullet. Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice, 19(2), 139–151.
Hair, J. F., Ringle, C. M., Gudergan, S. P., Fischer, A., Nitzl, C., & Menictas, C. (2018). Partial least squares structural equation modeling-based discrete choice modeling: An illustration in modeling retailer choice. Business Research, 12, 115–142.
Hair, J. F., Risher, J. J., Sarstedt, M., & Ringle, C. M. (2019). When to use and how to report the results of PLS-SEM. European Business Review, 31(1), 2–24.
Hair, J. F., Sarstedt, M., Ringle, C. M., & Mena, J. A. (2012). An assessment of the use of partial least squares structural equation modeling in marketing research. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 40(3), 414–433.
Hambrick, D. C. (1982). Environmental scanning and organizational strategy. Strategic Management Journal, 3(2), 159–174.
Harman, H.H. (1976). Modern Factor Analysis, 3rd ed. revised, University of Chicago Press. Chicago, IL.
Harzing, A. W., Brown, M., Köster, K., & Zhao, S. (2012). Response style differences in cross-national research: Dispositional and situational determinants. Management International Review, 52(3), 341–363.
Helfat, C. E., & Peteraf, M. A. (2009). Understanding dynamic capabilities: Progress along a developmental path. Strategic Organization, 7, 91–102.
Henseler, J., Ringle, C. M., & Sinkovics, R. R. (2009). The use of partial least squares path modeling in international marketing. Advances in International Marketing, 20(1), 277–319.
Henseler, J., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2014). A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science., 43(1), 115–135.
Higgins, J. M., & McAllaster, C. (2002). Want Innovation? Then use cultural artifacts that support It. Organizational Dynamics, 31(1), 74–84.
Hindle, G. A., & Vidgen, R. (2017). Developing a business analytics methodology: A case study in the foodbank sector. European Journal of Operational Research, 268(3), 836–851.
Holsapple, C., Lee-Post, A., & Pakath, R. (2014). A unified foundation for business analytics. Decision Support Systems, 64, 130–141.
Hong, J., Song, T. H., & Yoo, S. (2013). Paths to success: How do market orientation and entrepreneurship orientation produce new product success? Journal of Product Innovation Management, 30(1), 44–55.
Hossain, T. M. T., Akter, S., Kattiyapornpong, U., & Dwivedi, Y. (2020). Reconceptualizing integration quality dynamics for omnichannel marketing. Industrial Marketing Management, 87(5), 225–241.
Hu, L., & Bentler, P. M. (1998). Fit indices in covariance structure modeling: Sensitivity to under parameterized model misspecification. Psychological Methods, 3(4), 424–453.
Keller, R. T., & Holland, W. E. (1975). Boundary-spanning roles in a research and development organization: An empirical investigation. Academy of Management Journal, 18(2), 388–393.
Kiron, D., & Shockley, R. (2011). Creating business value with analytics. MIT Sloan Management Review, 53(1), 57–63.
Kiron, D., Ferguson, R. B., & Prentice, P. K. (2013). From value to vision: Reimagining the possible with data analytics. MIT Sloan Management Review, 54(3), 1–19.
Kiron, D., Prentice, P. K., & Ferguson, R. B. (2012). Innovating with analytics. MIT Sloan Management Review, 54(1), 47–52.
Klatt, T., Schlaefke, M., & Moeller, K. (2011). Integrating business analytics into strategic planning for better performance. Journal of Business Strategy, 32(6), 30–39.
Larson, D., & Chang, V. (2016). A review and future direction of agile, business intelligence, analytics and data science. International Journal of Information Management, 36(5), 700–710.
Lau, R. Y., Liao, S. S., Wong, K. F., & Chiu, D. K. (2012). Web 2.0 environmental scanning and adaptive decision support for business mergers and acquisitions. MIS Quarterly, 36(4), 1239–1268.
Li, Y., Thomas, M. A., & Osei-Bryson, K.-M. (2016). A snail shell process model for knowledge discovery via data analytics. Decision Support Systems, 91, 1–12.
Lindell, M. K., & Whitney, D. J. (2001). Accounting for common method variance in cross-sectional research designs. Journal of Applied Psychology, 86(1), 114–121.
Loukis, E., Janssen, M., & Mintchevc, I. (2019). Determinants of software-as-a-service benefits and impact on firm performance. Decision Support System, 117, 38–47.
Maier, J. L., Rainer, R. K., Jr., & Snyder, C. A. (1997). Environmental scanning for information technology: An empirical investigation. Journal of Management Information Systems, 14(2), 177–200.
Manyika, J., Chui, M., Brown, B., Bughin, J., Dobbs, R., Roxburgh, C., & Byers, A. H. (2011). Big data: The next frontier for innovation, competition and productivity. McKinsey Global Institute.
Miller, D., & Friesen, P. H. (1982). Innovation in conservative and entrepreneurial firms: Two models of strategic momentum. Strategic Management Journal, 3(1), 1–25.
Nam, D., Lee, J., & Lee, H. (2019a). Business analytics adoption process: An innovation diffusion perspective. International Journal of Information Management, 49, 411–423.
Nam, D., Lee, J., & Lee, H. (2019b). Business analytics use in CRM: A nomological net from IT competence to CRM performance. International Journal of Information Management, 45, 233–245.
Nitzl, C., Roldan, J. L., & Cepeda, G. (2016). Mediation analysis in partial least squares path modeling: Helping researchers discuss more sophisticated models. Industrial Management and Data Systems, 116(9), 1849–1864.
Pare, G., Guillemette, M. G., & Raymond, L. (2019). IT centrality IT management model, and contribution of the IT function to organizational performance: A study in Canadian hospitals. Information & Management, 57(3), 103198.
Peppard, J., & Ward, J. (2016). The strategic management of information systems: Building a digital strategy. John Wiley & Sons.
Podsakoff, P. M., McKenzie, S. B., Lee, J. Y., & Podsakoff, N. P. (2003). Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. Journal of Applied Psychology, 88(5), 879–903.
Porter, C. E., & Donthu, N. (2006). Using the technology acceptance model to explain how attitudes determine internet usage: The role of perceived access barriers and demographics. Journal of Business Research, 59(9), 999–1007.
Rana, N. P., Chatterjee, S., Dwivedi, Y. K., & Akter, S. (2021). Understanding dark side of artificial intelligence (AI) integrated business analytics: Assessing firm’s operational inefficiency and competitiveness. European Journal of Information Systems. https://doi.org/10.1080/0960085X.2021.1955628
Ranyard, J. C., Fildes, R. A., & Hu, T.-I. (2015). Reassessing the scope of OR practice: The influences of problem structuring methods and the analytics movement. European Journal of Operational Research, 245(1), 1–13.
Reinartz, W. J., Haenlein, M., & Henseler, J. (2009). An empirical comparison of the efficacy of covariance-based and variance-based SEM”. International Journal of Market Research, 26(4), 332–344.
Richter, N. F., Sinkovics, R., Ringle, C. M., & Schlägel, C. (2016). A critical look at the use of SEM in international business research. International Marketing Review, 33(3), 376–404.
Ritala, P., & Hurmelinna-Laukkanen, P. (2013). Incremental and radical innovation in coopetition—The role of absorptive capacity and appropriability. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 30(1), 154–169.
Rodrigues, J., Ruivo, P., & Oliveira, T. (2014). Software as a service value and firm performance – A literature review synthesis in small and medium enterprises. Procedia Technology, 16, 206–211.
Rodrigues, J., Ruivo, P., & Oliveira, T. (2020). Information & Management. In Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2020.103289
Santoro, G., Thrassou, A., Bresciani, S., & Giudice, M. D. (2021). Do knowledge management and dynamic capabilities affect ambidextrous entrepreneurial intensity and firm’s performance? IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management., 68(2), 378–386.
Shanks, G., & Bekmamedova, N. (2012). Integrating Business Analytics Systems with the Enterprise Environment: An Evolutionary Process Perspective. In Proceedings of DSS2012 – 16th IFIP WG8.3 International Conference on Decision Support Systems, Anávissos, Greece, June 28–30.
Sharda, R., Delen, D., & Turban, E. (2016). Business intelligence, analytics, and data science: A managerial perspective (4th ed.). Pearson-Prentice Hall.
Sharma, R., Mithas, S., & Kankanhalli, A. (2014). Transforming decision-making processes: A research agenda for understanding the impact of business analytics on organizations. European Journal of Information Systems, 23(4), 433–441.
Stock, R. M., & Zacharias, N. A. (2013). Two sides of the same coin: How do different dimensions of product program innovativeness affect customer loyalty? Journal of Product Innovation Management, 30(3), 516–532.
Stone, M. (1974). Cross validatory choice and assessment of statistical predictions. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 36(2), 111–147.
Stubbs, E. (2014). Big Data, Big Innovation: Enabling competitive differentiation through business analytics. John Wiley & Sons.
Sultana, S., Akter, S., Kyriazis, E., & Wamba, S. F. (2021). Architecting and developing big data-driven innovation (DDI) in the digital economy. Journal of Global Information Management, 29(3), 165–187.
Sun, Z., Strang, K., & Firmin, S. (2017). Business analytics-based enterprise information systems. The Journal of Computer Information Systems, 57(2), 169–178.
Tan, F. T. C., Guo, Z., Cahalane, M., & Cheng, D. (2016). Developing business analytic capabilities for combating e-commerce identity fraud: A study of Trustev’s digital verification solution. Information and Management, 53(7), 878–891.
Teece, D. J. (2012). Dynamic capabilities: Routines versus entrepreneurial action. Journal of Management Studies, 49(8), 1395–1401.
Thayer, L. O. (1968). Communication and communication systems in organization, management, and interpersonal relations: Homewood. Irwin.
Thrassou, A., Vrontis, D., & Bresciani, S. (2018). The agile innovation pendulum: A strategic marketing multicultural model for family businesses. International Studies of Management and Organization, 48(1), 105–120.
Troilo, M., Bouchet, A., Urban, T. L., & Sutton, W. A. (2016). Perception, reality, and the adoption of business analytics: Evidence from North American professional sport organizations. Omega, 59, 72–83.
Tushman, M. L. (1977). Special boundary roles in the innovation process. Administrative Science Quarterly, 22(4), 587–605.
Upadhyay, P., & Kumar, A. (2020). The intermediating role of organizational culture and internal analytical knowledge between the capability of big data analytics and a firm’s performance. International Journal of Information Management, 52, 102100.
Vidgen, R., Shaw, S., & Grant, D. B. (2017). Management challenges in creating value from business analytics. European Journal of Operational Research, 261(2), 626–639.
Voorhees, C. M., Brady, M. K., Calantone, R., & Ramirez, E. (2016). Discriminant validity testing in marketing: An analysis, causes for concern, and proposed remedies. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 44, 119–134.
Vrontis, D., & Christofi, M. (2019). R&D internationalization and innovation: A systematic review, integrative framework and future research direction. Journal of Business Research, in Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.03.031
Wamba, S. F., Gunasekaran, A., Akter, S., Ren, S. J., Dubey, R., & Childe, S. J. (2016). Big data analytics and firm performance: Effects of dynamic capabilities. Journal of Business Research., 70, 356–365.
Wamba, S. F., Gunasekaran, A., Akter, S., Ren, S. J. F., Dubey, R., & Childe, S. J. (2017). Big data analytics and firm performance: Effects of dynamic capabilities. Journal of Business Research, 70, 356–365.
Wang, Y., Kung, L., & Byrd, T. A. (2018). Big data analytics: Understanding its capabilities and potential benefits for healthcare organizations. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 126, 3–13.
Watson, H. J. (2014). Tutorial: Big data analytics: Concepts, technologies, and applications. Communications of the Association for Information Systems, 34(1), 1247–1268.
Wedel, M., & Kannan, P. (2016). Marketing analytics for data-rich environments. Journal of Marketing, 80(6), 97–122.
Winter, S. G. (2003). Understanding dynamic capabilities. Strategic Management Journal, 24(10), 991–995.
Zahra, S. A., & George, G. (2002). Absorptive capacity: A review, reconceptualization, and extension. Academy of Management Review, 27(2), 185–203.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaudhuri, R., Chatterjee, S., Vrontis, D. et al. Adoption of robust business analytics for product innovation and organizational performance: the mediating role of organizational data-driven culture. Ann Oper Res 339, 1757–1791 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-021-04407-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-021-04407-3