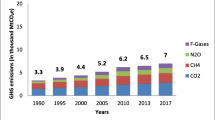
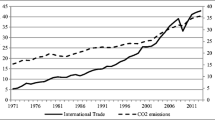
Abstract
We explore the moderating role of trade openness (TO) by gauging its main and interaction effects on the economic growth and environmental quality nexus. In this direction, we implement a novel approach by using three different measures of pollution emissions (CO2–CH4–PM2.5) in the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis and applying a structural equation modelling methodology to 115 countries, grouped into low-, middle- and high-income countries, spanning the period 1992–2018. The evidence suggests that energy consumption has a positive impact on CO2 emissions for all income panels whilst the moderating effect of TO appears to be a key degrading factor of environmental quality in low- and middle-income countries. In addition, TO’s interaction with GDP growth is found to negatively affect environmental quality across all income groups. Given that global economies are on the verge of returning to pre-pandemic levels of industrial operations along with emissions in the wake of the failure of COP26 and that COVID-19 has reminded the world the urgency of developing sustainable approaches in fostering ‘green economic growth’ models; a host of policy measures are proposed in support of this whilst their likely implications are discussed with reference to different income level countries.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi, F., & Riaz, K. (2016). CO2 emissions and financial development in an emerging economy: An augmented VAR approach. Energy Policy, 90, 102–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2015.12.017
Abdouli, M., & Hammami, S. (2016). Investigating the causality links between environmental quality, foreign direct investment and economic growth in MENA countries. International Business Review, 26(2), 264–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibusrev.2016.07.004
Abid, M. (2017). Does economic, financial and institutional developments matter for environmental quality? A comparative analysis of EU and MEA countries. Journal of Environmental Management, 188, 183–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.12.007
Adedoyin, F., Ozturk, I., Abubakar, I., Kumeka, T., Folarin, O., & Bekun, F. V. (2020). Structural breaks in CO2 emissions: Are they caused by climate change protests or other factors? Journal of Environmental Management, 266, 110628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110628
Al-Mulali, U., Solarin, S. A., Sheau-Ting, L., & Ozturk, I. (2016). Does moving towards renewable energy cause water and land inefficiency? An empirical investigation. Energy Policy, 93, 303–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2016.03.023
Amar, A. B. (2021). Economic growth and environment in the United Kingdom: Robust evidence using more than 250 years data. Environmental Economics and Policy Studies, 23, 667–681. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10018-020-00300-8
Arvanitis, S., & Ley, M. (2013). Factors determining the adoption of energy-saving technologies in Swiss firms: An analysis based on micro data. Environmental and Resource Economics, 54(3), 389–417.
Aslanidis, N., & Xepapadeas, A. (2006). Smooth transition pollution-income paths. Ecological Economics, 57(2), 182–189.
Balezentis, T., Liobikien, G., Streimikiene, D., & Sun, K. (2020). The impact of income inequality on consumption-based greenhouse gas emissions at the global level: A partially linear approach. Journal of Environmental Management, 267, 1–13.
Belloumi, M., & Alshehry, A.(2020). The Impact of International Trade on Sustainable Development in Saudi Arabia. Sustainability, 12, 1-17. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12135421
Bergasse, E., Paczynski, W., Dabrowski, M., & Wulf, L. (2013). The relationship between energy and socio-economic development in the Southern and Eastern Mediterranean. Working Paper. CASE Network Reports, Center for Social and Economic Research (CASE).
Bernard, J., & Mandal, S. K. (2016). The impact of trade openness on environmental quality: An empirical analysis of emerging and developing economies. WIT Transactions on Ecology and the Environment. https://doi.org/10.2495/EID160181
Bollen, K. A., & Noble, M. D. (2011). Structural equation models and the quantification of behavior. PNAS, 108(3), 15639–15646. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1010661108
Bollen, K. A., & Pearl, J. (2013). Eight myths about causality and structural equation models. In S. L. Morgan (Ed.), Handbook of causal analysis for social research (pp. 301–328). Springer.
Brenton, P., & Chemutai, V. (2021). The trade and climate change nexus: the urgency and opportunities for developing countries. World Bank Publication. [Online] https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/36294.
Brommer, J. E., Karell, P., Ahola, K., & Karstinen, T. (2014). Residual correlations, and not individual properties, determine a nest defense boldness syndrome. Behavioral Ecology, 25(4), 802–812. https://doi.org/10.1093/beheco/aru057
Browne, M. W., & Cudeck, R. (1993). Alternative ways of assessing model fit. Sage Focus Editions, 154, 136–136.
Busa, J. H. M. (2013). Dynamite in the EKC tunnel? Inconsistencies in resource stock analysis under the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis. Ecological Economics, 94, 116–126.
Caviglia-Harris, J. L., Chambers, D., & Kahn, J. R. (2009). Taking the “U” out of Kuznets: A comprehensive analysis of the EKC and environmental degradation. Ecological Economics, 68(4), 1149–1159.
Chen, C. F., & Myagmarsuren, O. (2013). Exploring the moderating effects of value offerings between market orientation and performance in tourism industry. International Journal of Tourism Research, 15(6), 595–610.
Chen, J., Xian, Q., Zhou, J., & Li, D. (2020). Impact of income inequality on CO2 emissions in G20 countries. Journal of Environmental Management, 271, 110987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110987
Chen, Q., Loschel, A., Pei, J., Peters, G., Xue, J., & Zhao, Z. (2019). Processing trade, foreign outsourcing and carbon emissions in China. Structural Change and Economic Dynamics, 49, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strueco.2019.03.004
Chen, Y., & Fang, Z. (2018). Industrial electricity consumption, human capital investment and economic growth in Chinese cities. Economic Modelling, 69, 205–219.
Cohen, J., Cohen, P., West, S., & Aiken, L. (2003). Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences, 3rd edn. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Datta, A., Das, S., Manjunath, K. R., & Adhya, T. K. (2012). Comparison of two methods for the estimation of greenhouse gas flux from rice ecosystems in India. Greenhouse Gas Measurement and Management, 2(1), 43–49.
Demirel, P., & Kesidou, E. (2011). Stimulating different types of eco-innovation in the UK: Government policies and firm motivations. Ecological Economics, 70(8), 1546–1557.
Dubey, R., Gunasekaran, A., Childe, S. J., Luo, Z., Wamba, S. F., Roubaud, D., & Foropon, C. (2018). Examining the role of big data and predictive analytics on collaborative performance in context to sustainable consumption and production behaviour. Journal of Cleaner Production, 196, 1508–1521.
EEA. (2020). Train or plane? Transport and environment report 2020. European Environment Agency (EEA). EEA Report No. 19/2020.
Emerson, J. W., Esty, D. C., Srebotnjak, T., & Connett, D. (2015). Exploring trade & the environment an empirical examination of trade openness and national environmental performance. Yale Center for Environmental Law & Policy, US: Yale.
EPA. (2017). Sources of greenhouse gas emission. Overview of greenhouse gases. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
EPA. (2021). Inventory of US greenhouse gas emissions and sinks, 1990–2019. Sources of greenhouse gas emission. Overview of greenhouse gases. Report published on April 14, 2021. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
Ergun, S. J., & Rivas, M. F. (2020). Testing the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in Uruguay using ecological footprint as a measure of environmental degradation. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy, 10(4), 473–485.
Espoir, D. K., & Sunge, R. (2021). Co2 emissions and economic development in Africa: Evidence from a dynamic spatial panel model. ZBW—Leibniz Information Centre for Economics, Kiel, Hamburg.
Fang, Z., Huang, B., & Yang, Z. (2018). How does trade openness affect the environmental Kuznets curve?. Economics, Environment, Industry And Trade. Retrieved on July 13, 2020 from https://www.asiapathways-adbi.org/2018/10/how-does-trade-openness-affect-the-environmental-kuznets-curve/
Farhadi, M. (2015). Transport infrastructure and long-run economic growth in OECD countries. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 74(C), 73–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tra.2015.02.006
Farhani, S., Shahbaz, M., & Arouri, M. E. H. (2013). Panel analysis of CO2 emissions, GDP, energy consumption, trade openness and urbanization for MENA countries. MPRA Paper. Retrieved on July 12, 2019 from https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/49258/1/MPRA_paper_49258.pdf
Forabosco, F., Chitchyan, Z., & Mantovani, R. (2017). Methane, nitrous oxide emissions and mitigation strategies for livestock in developing countries: A review. South African Journal of Animal Science, 47(3), 268–280.
Frondel, M., Ritter, N., Schmidt, C. M., & Vance, C. (2010). Economic impacts from the promotion of renewable energy technologies: The German experience. Energy Policy, 38, 4048–4056.
Gamso, J. (2018). Is China worsening the developing world’s environmental crisis?. The Conversation, United Kingdom, August 22. Retrieved on July 19, 2020 from https://theconversation.com/is-china-worsening-the-developing-worlds-environmental-crisis-100284
Grossman, G. M., & Krueger, A. B. (1995). Economic growth and the environment. Quarterly Journal of Economics, 110, 353–377.
Hakimi, A., & Hamdi, H. (2016). Trade liberalisation, FDI inflows, environmental quality and economic growth: A comparative analysis between Tunisia and Morocco. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 58, 1–13.
Halkos, G. E., & Polemis, M. L. (2018a). The impact of economic growth on environmental efficiency of the electricity sector: A hybrid window DEA methodology for the USA. Journal of Environmental Management, 211, 334–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.01.067
Hasan, S. F., Lings, I., Neale, L., & Mortimer, G. (2014). The role of customer gratitude in making relationship marketing investments successful. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 21(5), 788–796.
He, Z., Xu, S., Shen, W., Long, R., & Chen, H. (2017). Impact of urbanization on energy related CO2 emission at different development levels: Regional difference in China based on panel estimation. Journal of Cleaner Production, 140, 1719–1730.
Hu, L.-T., & Bentler, P. M. (1998). Fit indices in covariance structure modeling: Sensitivity to underparameterized model misspecification. Psychological Methods, 3(4), 424.
Inglesi-Lotz, R., & Bohlmann, J. (2014). Environmental Kuznets curve in South Africa: To confirm or not to confirm?. Prepared for EcoMod. Bali, Indonesia.
Jalil, A., & Feridun, M. (2011). The impact of growth, energy and financial development on the environment in China: A cointegration analysis. Energy Economics, 33(2), 284–291.
Jalil, A., & Mahmud, S. F. (2009). Environment Kuznets curve for CO2 emissions: A cointegration analysis for China. Energy Policy, 37(12), 5167–5172.
Jaunky, V. C. (2011). The CO2 emissions-income nexus: Evidence from rich countries. Energy Policy, 39(3), 1228–1240.
Jayanthakumaran, K., Verma, R., & Liu, Y. (2012). CO2 emissions, energy consumption, trade and income: A comparative analysis of China and India. Energy Policy, 42, 450–460.
Jobert, T., Karanfil, F., & Tykhonenko, A. (2016). Trade and environment: Further empirical evidence from heterogeneous panels using aggregate data. Working Papers-01295613, HAL.
Jun, W., Mahmood, H., & Zakaria, M. (2020). Impact of trade openness on environment in China. Journal of Business Economics and Management, 21(4), 1185–1202.
Kanjilal, K., & Ghosh, S. (2013). Environmental Kuznet’s curve for India: Evidence from tests for cointegration with unknown structuralbreaks. Energy Policy, 56, 509–515.
Kasman, A., & Duman, Y. S. (2015). CO2 emissions, economic growth, energy consumption, trade and urbanization in new EU member and candidate countries: A panel data analysis. Economic Modelling, 44, 97–103.
Kassouri, Y., & Altintas, H. (2020). Human well-being versus ecological footprint in MENA countries: A trade-off. Journal of Environmental Management, 263, 1–16.
Katircioğlu, S. T., & Taşpinar, N. (2017). Testing the moderating role of financial development in an environmental Kuznets curve: Empirical evidence from Turkey. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 68, 572–586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.09.127
Kijima, M., Nishide, K., & Ohyama, A. (2010). Economic models for the environmental Kuznets curve: A survey. Journal of Economic Dynamics & Control, 34, 1187–1201.
Kim, D., Suen, Y., & Lin, S. (2019). Carbon dioxide emissions and trade: Evidence from disaggregate trade data. Energy Economics, 78, 13–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2018.08.019
Le, T.-H., Chang, Y., & Park, D. (2016). Trade openness and environmental quality: International evidence. Energy Policy, 92, 45–55.
Lean, H. H., Huang, W., & Hong, J. (2014). Logistics and economic development: Experience from China. Transport Policy, 32, 96–104.
Li, G., Fang, C., Wang, S., & Sun, S. (2016a). The effect of economic growth, urbanization, and industrialization on fine particulate matter (PM2.5) concentrations in China. Environmental Science & Technology, 50(21), 11452–11459.
Li, T., Wang, Y., & Zhao, D. (2016b). Environmental Kuznets curve in China: New evidence from dynamic panel analysis. Energy Policy, 91, 138–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2016.01.002
Liddle, B., & Lung, S. (2013). The long-run causal relationship between transport energy consumption and GDP: Evidence from heterogeneous panel methods robust to cross-sectional dependence. Economics Letters, 121(3), 524–527.
Lin, J., Shen, Y., Li, X., & Hasnaoui, A. (2021). BRICS carbon neutrality target: Measuring the impact of electricity production from renewable energy sources and globalization. Journal of Environmental Management, 298, 113460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113460
MacCallum, R. C., & Austin, J. T. (2000). Applications of structural equation modeling in psychological research. Annual Review of Psychology, 51, 201–226.
Mahadevan, R., & Sun, Y. (2020). Effects of foreign direct investment on carbon emissions: Evidence from China and its Belt and Road countries. Journal of Environmental Management, 276, 1–9.
Masi, D., Kumar, V., Garza-Reyes, J. A., & Godsell, J. (2018). Towards a more circular economy: Exploring the awareness, practices, and barriers from a focal firm perspective. Production Planning & Control, 29(6), 539–550.
Mishra, M. K. (2020). The Kuznets curve for the sustainable environment and economic growth. EconStor Preprints 216734, ZBW—Leibniz Information Centre for Economics.
Nasir, M. A., Canh, N. P., & Le, T. N. L. (2021). Environmental degradation & role of financialisation, economic development, industrialisation and trade liberalisation. Journal of Environmental Management, 277, 111471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111471
Nasr, A. B., Gupta, R., & Sato, J. R. (2015). Is there an environmental Kuznets curve for South Africa? A Co-summability approach using a century of data. Energy Economics, 52, 136–141.
NOAA (2021). Despite pandemic shutdowns, carbon dioxide and methane surged in 2020. Research News of the United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
Onafowora, O. A., & Owoye, O. (2014). Bounds testing approach to analysis of the environment Kuznets curve hypothesis. Energy Economics, 44, 47–62.
Panayotou, T. (1993). Empirical tests and policy analysis of environmental degradation at different stages of economic development. Working Paper WP238, Technology and Employment Programme, ILO, Geneva.
Pothen, F., & Welsch, H. (2019). Economic development and material use. Evidence from international panel data. World Development, 115, 107–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2018.06.008
PWC. (2018). Fourth industrial revolution for the earth: Harnessing artificial intelligence for the earth. Pricewatercoopers publication. January 2018 edition.
Rafindadi, A. A., & Usman, O. (2019). Globalization, energy use, and environmental degradation in South Africa: Startling empirical evidence from the Maki-cointegration test. Journal of Environmental Management, 244, 265–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.05.048
Rahman, M. M. (2020). Environmental degradation: The role of electricity consumption, economic growth and globalisation. Journal of Environmental Management, 253, 109742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109742
Ren, J., Hu, J., & Chen, X. (2020). The effect of production- versus consumption-based emission tax under demand uncertainty. International Journal of Production Economics, 219(1), 82–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2019.05.009
Richter, N. F., Sinkovics, R. R., Ringle, C. M., & Schlägel, C. (2016). A critical look at the use of SEM in international business research. International Marketing Review, 33(3), 376–404. https://doi.org/10.1108/IMR-04-2014-0148
Sam, A. G., & Zhang, X. (2020). Value relevance of the new environmental enforcement regime in China. Journal of Corporate Finance, 62, 101573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcorpfin.2020.101573
Sarkodie, S. A., & Strezov, V. (2018). Empirical study of the environmental Kuznets curve and environmental sustainability curve hypothesis for Australia, China, Ghana and USA. Journal Cleaner Production, 201, 98–110.
Selden, T. M., & Song, D. (1995). Neoclassical growth, the J curve for abatement and the inverted U curve for pollution. Journal of Environmental Economics and Management, 29(2), 162–168.
Shafik, N. (1994). Economic development and environmental quality: An econometric analysis. Oxford Economic Papers, 46, 757–773.
Shafik, N., & Bandyopadhyay, S. (1992). Economic growth and environmental quality: Time series and cross-country evidence. Background Paper for World Development Report 1992. World Bank, Washington, DC.
Shah, R., & Goldstein, S. M. (2006). Use of structural equation modeling in operations management research: Looking back and forward. Journal of Operations Management, 24(2), 148–169.
Shahbaz, M. (2019). Globalization-emissions nexus: Testing the EKC hypothesis in Next-11 countries. Global Business Review. https://doi.org/10.1177/0972150919858490
Shahbaz, M., Nasreen, S., Ahmed, K., & Hammoudeh, S. (2017). Trade openness—carbon emissions nexus: The importance of turning points of trade openness for country panels. Energy Economics, 61, 221–232.
Shahbaz, M., Tiwari, A. K., & Nasir, M. (2013). The effects of financial development, economic growth, coal consumption and trade openness on CO2 emissions in South Africa. Energy Policy, 61, 1452–1459.
Sin-Yu, H., & Njindan, I. B. (2019). Trade openness and carbon emissions: Evidence from central and eastern European countries. Review of Economics, 70(1), 41–67.
Song, M., Zhu, S., Wang, J., & Zhao, J. (2019). Share green growth: Regional evaluation of green output performance in China. International Journal of Production Economics, 219, 152–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2019.05.012
Stein, C. M., Morris, N. J., & Nocl, N. L. (2017). Structural equation modelling. In Robert C. Elston et al. (Ed.), Statistical human genetics: Methods and protocols, methods in molecular biology, vol. 850, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-555-8_27
Umar, M., Ji, X., Kirikkaleli, D., & Xu, Q. (2020). COP21 Roadmap: Do innovation, financial development, and transportation infrastructure matter for environmental sustainability in China? Journal of Environmental Management, 271, 111026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111026
UN (United Nations). (2019). UN launches drive to highlight environmental cost of staying fashionable. UN News. Retrieved on March 25, 2019 from https://news.un.org/en/story/2019/03/1035161.
UNEP. (2021). Global methane assessment: Benefits and costs of mitigating methane emissions. Joint Report of the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and Climate and Clean Air Coalition. Nairobi: United Nations Environment Programme.
Vehmas, J., Luukkanen, J., & Kaivo-oja, J. (2007). Linking analyses and environmental Kuznets curves for aggregated material flows in the EU. Journal of Cleaner Production, 15(17), 1662–1673.
Wang, S., & Ge, M. (2019). Everything you need to know about the fastest-growing source of global emissions: Transport. World Resources Institute, USA, October 16.
Wang, L., Chang, H.-L., Rizvi, S. K. A., & Sari, A. (2020a). Are eco-innovation and export diversification mutually exclusive to control. Journal of Environmental Management, 270, 1–8.
Wang, L., Vo, X. V., Shahbaz, M., & Ak, A. (2020b). Globalization and carbon emissions: Is there any role of agriculture value-added, financial development, and natural resource rent in the aftermath of COP21? Journal of Environmental Management, 268, 1–8.
Wang, R., Mirza, N., Vasbieva, D. G., Abbas, Q., & Xiong, D. (2020c). The nexus of carbon emissions, financial development, renewable energy consumption, and technological innovation: What should be the priorities in light of COP 21 Agreements? Journal of Environmental Management, 271, 1–7.
World Development Indicators (WDI). (2018). World Bank: Washington, DC, USA. Retrieved on July 15, 2020 from https://databank.worldbank.org/source/worlddevelopment-indicators.
World Bank. (2007). International trade and climate change: Economic, legal, and institutional perspectives. World Bank. https://doi.org/10.1596/978-0-8213-7225-8
World Bank. (2020). Transport: The essential connector. World Bank Report. February, 2020. https://thedocs.worldbank.org/en/doc/157201585683713721-0190022020/original/WBTransportNarrative.pdf
WTO (World Trade Organization) (2017). WTO’s Trade facilitation agreement enters into force. Retrieved on July 19, 2020 from www.wto.org/english/news_e/news17_e/fac_31jan17_e.htm.
WTO (World Trade Organization). (2021a). Chair summary following COVID-19 and vaccine equity: What can the WTO contribute. Speech by D. G. Okonjo. WTO, Geneva. Retrieved on August 12, 2021 from https://www.wto.org/english/news_e/spno_e/spno5_e.htm.
WTO (World Trade Organization). (2021b). Global trade rebound beats expectations but marked by regional divergences. WTO Press Release No. 889. Retrieved on October 12, 2021 from https://www.wto.org/english/news_e/pres21_e/pr889_e.pdf
Wu, W., Zhang, M., & Ding, Y. (2020). Exploring the effect of economic and environment factors on PM2.5 concentration: A case study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Journal of Environmental Management, 268, 1–9.
Xu, F., Huang, Q., Yue, H., He, C., Wang, C., & Zhang, H. (2020). Reexamining the relationship between urbanization and pollutant emissions in China based on the STIRPAT model. Journal of Environmental Management, 273, 111134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111134
Yu, W., Chavez, R., & Feng, M. (2017). Green supply management and performance: A resource-based view. Production Planning & Control, 28(6–8), 659–670.
Yunfeng, Y., & Laike, Y. (2010). China’s foreign trade and climate change: A case study of CO2 emissions. Energy Policy, 38(1), 350–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2009.09.025
Zafar, M. W., Qin, Q., Malik, M. N., & Zaidi, S. A. H. (2020). Foreign direct investment and education as determinants of environmental quality: The importance of post Paris Agreement (COP21). Journal of Environmental Management, 270, 110827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110827
Zhang, K., Shao, S., & Fan, S. (2020). Market integration and environmental quality: Evidence from the Yangtze river delta region of China. Journal of Environmental Management, 261, 110208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110208
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
See Tables
5,
6,
7 and
8.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharif, T., Uddin, M.M.M. & Alexiou, C. Testing the moderating role of trade openness on the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: a novel approach. Ann Oper Res 345, 597–635 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-021-04501-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-021-04501-6