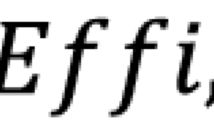Abstract
Islamic banking is among rapidly-growing components in the world's financial system. Within its institutions, continuous criteria of efficiency facilitate the evaluation of the impact of the reforms and policies on the banks' performance. In this paper, we employ the Multivariate Adaptive Regression Splines (MARS) method for estimating the efficiency of Islamic banks in developed and developing countries. MARS is a well-known efficient method for the flexible modelling of high-dimensional data. Unlike previous work, using a nonparametric technique of such a robustness instead of parametric approaches contributes to the improvement of the various estimates, which provides investors with accurate and timely information they can immediately react upon for a better decision-making in turbulent times. On the one hand, the results of the experiments show that, in the emerging region, there is evidence of a strong linkage between Islamic banking efficiency and gross domestic product. On the other hand, in the developed region, the efficiency is rather based upon Sharia Supervisory Board and board committees. These outcomes confirm previous works showing that governance-related variables have a significant positive effect on Islamic banking efficiency. Furthermore, the overall MARS-based predictions reveal that Islamic banks operating in developed countries are relatively more efficient than their counterparts in emerging countries.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
References
Abduh, M., Hasan, S., & Pananjung, A. (2013). Efficiency and performance of Islamic Banks in Bangladesh. Journal of Islamic Banking and Finance, 30(2), 94–106.
Abdul-Majid, M., Saal, D. S., & Battisti, G. (2010). Efficiency in Islamic and conventional banking: An international comparison. Journal of Productivity Analysis, 34(1), 25–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11123-009-0165-3
Aburrous, M., Hossain, M. A., Dahal, K., & Thabtah, F. (2010). Intelligent phishing detection system for e-banking using fuzzy data mining. Expert Systems with Applications, 37(12), 7913–7921.
Adnan, M. A., Htay, S. N. N., Rashid, H. M. A., & Meera, A. K. M. (2011). A panel data analysis on the relationship between corporate governance and bank efficiency. Journal of Accounting, Finance and Economics, 1(1), 1–16.
Affes, Z., & Hentati-Kaffel, R. (2019). Forecast bankruptcy using a blend of clustering and MARS model: Case of US banks. Annals of Operations Research, 281, 27–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-018-2845-8
Alqahtani, F., Mayes, D. G., & Brown, K. (2017). Islamic bank efficiency compared to conventional banks during the global crisis in the GCC region. Journal of International Financial Markets, Institutions and Money, 51, 58–74.
Al-Suhaibani, M., & Naifar, N. (2014). Islamic corporate governance: Risk-sharing and Islamic preferred shares. Journal of Business Ethics, 124(4), 623–632.
Anouze, A. L., & Bou-Hamad, I. (2021). Inefficiency source tracking: Evidence from data envelopment analysis and random forests. Annals of Operations Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-020-03883-3
Anwar, S. M., Junaidi, J., Salju, S., Wicaksono, R., & Mispiyanti, M. (2020). Islamic bank contribution to Indonesian economic growth. International Journal of Islamic and Middle Eastern Finance and Management, 13(3), 519–532. https://doi.org/10.1108/IMEFM-02-2018-0071
Bakin, S., Hegland, M., & Osborne, M. R. (2000). Parallel MARS algorithm based on B-splines. Computational Statistics, 15, 463–484. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00022715
Belanès, A., Ftiti, Z., & Regaïeg, R. (2015). What can we learn about Islamic banks efficiency under the subprime crisis? Evidence from GCC Region. Pacific-Basin Finance Journal, 33, 81–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pacfin.2015.02.012
Bhambri, V. (2011). Application of data mining in banking sector. International Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 2(2), 199–202.
Bhasin, M. L. (2006). Data mining: A competitive tool in the banking and retail industries. The Chartered Accountant, 55(4), 588–594.
Bitar, M., Hassan, M. K., & Walker, T. (2017). Political systems and the financial soundness of Islamic banks. Journal of Financial Stability, 31, 18–44.
Bosman, N., & Frecher, F. (1992). Une étude comparative de l’efficacité technique du secteur de la santé au sein des pays de l’O.C.D.E, Working Paper, 92/08, CIRIEC, Université de Liège.
Boukhatem, J., & Moussa, F. B. (2018). The effect of Islamic banks on GDP growth: Some evidence from selected MENA countries. Borsa Istanbul Review, 18(3), 231–247.
Bourakba, C. (2014). The Impact of corporate governance in the financial performance of Islamic banks: Evidence from the GCC region. Journal of US-China Public Administration, 11(8), 633–641.
Cai, S., & Zhang, J. (2020). Exploration of credit risk of P2P platform based on data mining technology. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 372, 112–718.
Chen, Y. J., Lin, J. A., Chen, Y. M., & Wu, J. H. (2019). Financial forecasting with multivariate adaptive regression splines and queen genetic algorithm-support vector regression. IEEE Access, 7, 112931–112938.
Choong, Y. V., Thim, C. K., & Kyzy, B. T. (2012). Performance of Islamic commercial banks in Malaysia: An empirical study. Journal of Islamic Economics Banking and Finance, 8(2), 67–79.
Choudhury, M. A., & Alam, M. N. (2013). Corporate governance in Islamic perspective. International Journal of Islamic and Middle Eastern Finance and Management, 6(3), 180–199.
Chowdhury, N. T., & Abduh, M. (2012). Does Islamic banking matter for economic growth in Bangladesh? Journal of Islamic Economics, Banking and Finance, 113(467), 1–10.
Denison, D. G. T., Mallick, B. K., & Smith, A. F. M. (1998). Bayesian MARS. Statistics and Computing, 8(4), 337–346.
Eber, N. (2000). Efficience du système bancaire, structure du marché de crédit et activité économique. Revue Economique, 51(6), 1333–1353.
Farag, H., Mallin, C., & Ow-Yong, K. (2018). Corporate governance in Islamic banks: New insights for dual board structure and agency relationships. Journal of International Financial Markets, Institutions and Money, 54, 59–77.
Farrell, M. J. (1957). The measurement of productive efficiency. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series A, 120(3), 253–290.
Friedman, J. H. (1991). Multivariate adaptive regression splines. The Annals of Statistics, 19(1), 1–67.
Ghaffar, A. (2014). Corporate governance and profitability of Islamic banks pperating in Pakistan. Interdisciplinary Journal of Contemporary Research in Business, 6(2), 320–336.
Hamza, H. (2013). Sharia governance in Islamic banks: Effectiveness and supervision model. International Journal of Islamic and Middle Eastern Finance and Management, 6(3), 226–237.
Hassan Al-Tamimi, H. A. (2010). Factors influencing performance of UAE Islamic and conventional banks. Global Journal of Business Research, 4(2), 1–9.
Hassan, V., Bala, S., & Vignesen, P. (2005). Corporate Governance: An Islamic Paradigm. Universiti Putra Malaysia Press.
Hopt, K. J. (2021). Corporate governance of banks and financial institutions: Economic theory, supervisory practice, evidence and policy. European Business Organization Law Review, 22, 13–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40804-020-00201-z
Huynh, T. L. D., Nasir, M. A., Nguyen, S. P., & Duong, D. (2020). An assessment of contagion risks in the banking system using non-parametric and copula approaches. Economic Analysis and Policy, 65, 105–116.
Ihsan, I., & Kabir, H. M. (2002). Technical, scale and allocative efficiencies of Turkish banking industry. Journal of Banking and Finance, 26(4), 719–766.
Iqbal, M., & Molyneux, P. (2005). Thirty years of Islamic banking: History, performance and prospects. London, UK: Palgrave Macmillan.
Jekabsons, G. (2011). ARESLab: Adaptive regression splines toolbox for matlab/Octave, http://www.cs.rtu.lv/jekabsons/
Kalaycı, B., Özmen, A., & Weber, G.-W. (2020). Mutual relevance of investor sentiment and finance by modeling coupled stochastic systems with MARS. Annals of Operations Research, 295, 183–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-020-03757-8
Kao, L. J., Chiu, C. C., Lu, C. J., & Chang, C. H. (2013). A hybrid approach by integrating wavelet-based feature extraction with MARS and SVR for stock index forecasting. Decision Support Systems, 54(3), 1228–1244.
Kassim, S. (2016). Islamic finance and economic growth: The Malaysian experience. Global Finance Journal, 30, 66–76.
Kusuma, H., & Ayumardani, A. (2016). The corporate governance efficiency and Islamic bank performance: An Indonesian evidence. Polish Journal of Management Studies, 13(1), 111–120.
Liébana-Cabanillas, F., Nogueras, R., Herrera, L. J., & Guillén, A. (2013). Analysing user trust in electronic banking using data mining methods. Expert Systems with Applications, 40(14), 5439–5447.
Manickavasagam, J., Visalakshmi, S., & Apergis, N. (2020). A novel hybrid approach to forecast crude oil futures using intraday data. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 158, 120–126.
Mensi, W., Hammoudeh, S., Al-Jarrah, I. M. W., Al-Yahyaee, K. H., & Kang, S. H. (2019). Risk spillovers and hedging effectiveness between major commodities, and Islamic and conventional GCC banks. Journal of International Financial Markets, Institutions and Money, 60, 68–88.
Milborrow, S. (2019). Notes on the earth package, http://www.milbo.org/doc/earth-notes.pdf
Mirakhor, A. (2008). Lesson of the recent crisis for Islamic finance. IIUM Journal of Economics and Management, 16(2), 132–138.
Miyan, M. (2017). Applications of data mining in banking sector. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science, 8(1), 108–114.
Mollah, S., & Zaman, M. (2015). Shari’ah supervision, corporate governance and performance: Conventional vs. Islamic banks. Journal of Banking and Finance, 58, 418–435.
Naushad, M., & Malik, S. A. (2015). Corporate governance and bank performance: A study of selected banks in GCC region. Asian Social Science, 11(9), 226–234.
Nawaz, T. (2019). Exploring the nexus between human capital, corporate governance and performance: Evidence from Islamic Banks. Journal of Business Ethics, 157(2), 567–587.
Ngo, T. T., Le, M. Q., & Ngo, T. P. (2019). Incorporating risk into technical efficiency for Vietnam’s and ASEAN banks. Journal of Asian Business and Economic Studies, 26(1), 2–16. https://doi.org/10.1108/JABES-10-2018-0083
Nkuutu, G., Ntayi, J. M., Nkote, I. N., Munene, J., & Kaberuka, W. (2020). Board governance quality and risk disclosure compliance among financial institutions in Uganda. Journal of Asian Business and Economic Studies, 28(1), 64–81. https://doi.org/10.1108/JABES-04-2020-0036
Olson, D., & Zoubi, T. (2017). Convergence in bank performance for commercial and Islamic banks during and after the Global Financial Crisis. The Quarterly Review of Economics and Finance, 65, 71–87.
Ongore, V. O., & Kusa, G. B. (2013). Determinants of financial performance of commercial banks in Kenya. International Journal of Economics and Financial Issues, 3(1), 237–252.
Özmen, A. (2021). Sparse regression modeling for short- and long-term natural gas demand prediction. Annals of Operations Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-021-04089-x
Peral, J., Maté, A., & Marco, M. (2017). Application of data mining techniques to identify relevant key performance indicators. Computer Standards and Interfaces, 50, 55–64.
Platonova, E., Asutay, M., Dixon, R., & Mohammad, S. (2018). The impact of corporate social responsibility disclosure on financial performance: evidence from the GCC Islamic banking sector. Journal of Business Ethics, 151, 451–471.
Quttainah, M. A., Song, L., & Wu, Q. (2013). Do Islamic banks employ less earnings management? Journal of International Financial Management and Accounting, 24(3), 203–233.
Rabbouch, H., Saâdaoui, F., & Mraihi, R. (2018). A vision-based statistical methodology for automatically modeling continuous urban traffic flows. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 38, 392–403.
Riaz, S., & Mehar, A. (2013). The impact of bank specific and macroeconomic indicators on the profitability of commercial banks. Romanian Economic Journal, 16(47), 91–110.
Richardson, S., Wang, S., & Jennings, L. S. (2008). A multivariate adaptive regression B-spline algorithm (BMARS) for solving a class of nonlinear optimal feedback control problems. Automatica, 44(4), 1149–1155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.automatica.2007.09.001
Roghanian, P., Rasli, A., & Gheysar, H. (2012). Productivity through effectiveness and efficiency in the banking industry. Procedia—Social and Behavioral Sciences, 40, 550–556.
Rosman, R., Wahab, N. A., & Zainol, Z. (2014). Efficiency of Islamic banks during the financial crisis: An analysis of Middle Eastern and Asian countries. Pacific-Basin Finance Journal, 28, 76–90.
Saâdaoui, F. (2012). A probabilistic clustering method for US interest rate analysis. Quantitative Finance, 12(1), 135–148. https://doi.org/10.1080/14697681003591712
Saâdaoui, F. (2018). Testing for multiufractality of Islamic stock Markets. Physica a: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 496, 263–273.
Saâdaoui, F., & Ben Messaoud, O. (2020). Multiscaled neural autoregressive distributed lag: A new empirical mode decomposition model for nonlinear time series forecasting. International Journal of Neural Systems, 30(8), 2050039. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0129065720500392
Saâdaoui, F., Bertrand, P. R., Boudet, G., Rouffiac, K., Dutheil, F., & Chamoux, A. (2015). A dimensionally reduced clustering methodology for heterogeneous occupational medicine data mining. IEEE Transactions on NanoBioscience, 14(7), 707–715. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNB.2015.2477407
Saâdaoui, F., Naifar, N., & Aldohaiman, M. S. (2017). Predictability and co-movement relationships between conventional and Islamic stock market indexes: A multiscale exploration using wavelets. Physica a: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 482, 552–568.
Safiullah, M., & Shamsuddin, A. (2019). Risk-adjusted efficiency and corporate governance: Evidence from Islamic and conventional banks. Journal of Corporate Finance, 55, 105–140.
Samad, A. (1999). Comparative efficiency of the Islamic bank vis-à-vis conventional banks in Malaysia. IIUM Journal of Economics and Management, 7(1), 1–27.
Shahid, M. N., Abbas, A., Latif, K., Attique, A., & Khalid, S. (2020). The mediating role of board size, philanthropy and working capital management between basic corporate governance factors and firm’s performance. Journal of Asian Business and Economic Studies, 27(2), 135–151. https://doi.org/10.1108/JABES-07-2018-0050
Shibani, O., & De Fuentes, C. (2016). The differences and the similarities between corporate. Economics, 34(8), 506–524.
Soumya, S. B., & Deepika, N. (2016). Data mining with predictive analytics for financial applications. International Journal of Scientific Engineering and Applied Science, 2(1), 310–317.
Taffé, P. (1998). Frontière d’efficacité et évaluation de la performance énergétique des bâtiments. Doctoral Thesis in Economics, University of Geneva.
Tsumoto, S., & Hirano, S. (2016). Multidimensional temporal mining in hospital information system. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Studies, 5(3/4), 317–337.
Ur Rehman, R., & Mangla, I. U. (2010). Corporate governance and performance of financial institutions in Pakistan: A comparison between conventional and Islamic banks in Pakistan. The Pakistan Development Review, 49(4), 461–475.
Yucel, M., Aslan, Z., and Burunkaya, M., (2020). Classification of the temperature-dependent gain of an erbium-doped fiber amplifier by using data mining methods, Optik, vol. 208, Article Number: 164515.
Zeitun, R. (2012). Determinants of Islamic and conventional banks performance in GCC countries using panel data analysis. Global Economy and Finance Journal, 5(1), 53–72.
Zhu, Y., Zhou, L., Xie, C., Wang, G. J., & Nguyen, T. V. (2019). Forecasting SMEs’ credit risk in supply chain finance with an enhanced hybrid ensemble machine learning approach. International Journal of Production Economics, 211, 22–33.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their insightful and constructive comments that greatly contributed to improving the paper. Our many thanks go also to the editorial staff for their generous support and assistance during the review process. Monjia Khalfi would like to extend her thanks to Professor Ali Benhissi and acknowledges his lab’s financial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saâdaoui, F., Khalfi, M. Revisiting Islamic banking efficiency using multivariate adaptive regression splines. Ann Oper Res 334, 287–315 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-022-04545-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-022-04545-2