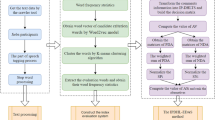
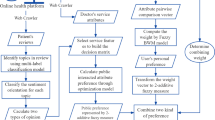
Abstract
Currently, patients tend to browse online reviews before choosing a satisfactory doctor. To better help patients make such choices, a doctor recommendation model under a probabilistic linguistic environment with an unbalanced semantic distribution is developed. First, a probabilistic linguistic term set (PLTS) is utilized to represent online evaluation information on doctors via natural language processing tools due to its advantage in modeling uncertainty in the online linguistic context. Then, to depict the different impacts of positive and negative evaluations in the context of doctor recommendations, the unbalanced semantic functions of a PLTS are proposed. Moreover, a comprehensive weight-determining method that combines the term frequency-inverse document frequency algorithm and the Word2Vec algorithm is developed considering the interrelationship among different criteria on patients’ decisions. An extended technique for order performance by similarity to the ideal solution method based on PLTS is proposed. Finally, the proposed method is verified in a case study on haodf.com. The findings show that it is vital to consider patients’ different risk preferences when building an online doctor recommendation model.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alharbi, S., & Naderpour, M. (2016). E-commerce development risk evaluation using MCDM techniques. Lecture Notes in Business Information Processing, 250, 88–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-32877-5_7
Al-Smadi, M., Al-Ayyoub, M., Jararweh, Y., & Qawasmeh, O. (2019). Enhancing aspect-based sentiment analysis of Arabic Hotels’ reviews using morphological, syntactic and semantic features. Information Processing and Management, 56(2), 308–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2018.01.006
Ana, R. M., Jose, R. S., & Cesar, A. A. (2018). Understanding #WorldEnvironmentDay user opinions in Twitter: A topic-based sentiment analysis approach. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15, 2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15112537
Bai, C., Zhang, R., Qian, L., & Wu, Y. (2017). Comparisons of probabilistic linguistic term sets for multi-criteria decision making. Knowledge-Based Systems, 119, 284–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2016.12.020
Boo, S., & Busser, J. A. (2018). Meeting planners’ online reviews of destination hotels: A twofold content analysis approach. Tourism Management, 66, 287–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2017.11.014
Chen, X., Lin, J., Li, X., & Ma, Z. (2020). A novel framework for selecting sustainable healthcare waste treatment technologies under Z- number environment. Journal of the Operational Research Society. https://doi.org/10.1080/01605682.2020.1759382
De Clercq, D., Wen, Z., & Song, Q. (2019). Innovation hotspots in food waste treatment, biogas, and anaerobic digestion technology: A natural language processing approach. Science of the Total Environment, 673, 402–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.051
De Pelsmacker, P., van Tilburg, S., & Holthof, C. (2018). Digital marketing strategies, online reviews and hotel performance. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 72, 47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2018.01.003
Deng, X., & Huangfu, F. (2019). Collaborative variational deep learning for healthcare recommendation. IEEE Access, 7, 55679–55688. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2913468
Gou, X., & Xu, Z. (2016). Novel basic operational laws for linguistic terms, hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets and probabilistic linguistic term sets. Information Science, 372, 407–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2016.08.034
Hadi-Vencheh, A., & Mirjaberi, M. (2014). Fuzzy inferior ratio method for multiple attribute decision making problems. Information Science, 277, 263–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2014.02.019
Hao, H. (2015). The development of online doctor reviews in China: An analysis of the largest online doctor review website in China. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 17(6), e134. https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.4365
Hao, H., Zhang, K., Wang, W., & Gao, G. (2017). A tale of two countries: International comparison of online doctor reviews between China and the United States. International Journal of Medical Informatics, 99, 37–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2016.12.007
Hoens, T. R., Blanton, M., Steele, A., & Chawla, N. V. (2013). Reliable medical recommendation systems with patient privacy. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 4(4), 67. https://doi.org/10.1145/2508037.2508048
Huang, J., Liu, H., Duan, C., & Song, M. (2019). An improved reliability model for FMEA using probabilistic linguistic term sets and TODIM method. Annals of Operations Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-019-03447-0
Hu, J., Pan, L., & Chen, X. (2017). An interval neutrosophic projection-based VIKOR method for selecting doctors. Cognitive Computation, 9(6), 801–816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-017-9499-8
Hu, J., Zhang, X., Yang, Y., Liu, Y., & Chen, X. (2020). New doctors ranking system based on VIKOR method. International Transactions in Operational Research, 27(2), 1236–1261. https://doi.org/10.1111/itor.12569
Ji, P., Zhang, H., & Wang, J. (2019). A fuzzy decision support model with sentiment analysis for items comparison in e-Commerce: The case study of http://PConline.com. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 49(10), 1993–2004
Kadry, B., Chu, L., Kadry, B., Gammas, D., & MacArio, A. (2011). Analysis of 4999 online physician ratings indicates that most patients give physicians a favorable rating. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 13(4), e95. https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.1960
Kalagara, S., Eltorai, A. E. M., DePasse, J. M., & Daniels, A. H. (2019). Predictive factors of positive online patient ratings of spine surgeons. Spine Journal, 19(1), 182–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2018.07.024
Khatua, A., Khatua, A., & Cambria, E. (2019). A tale of two epidemics: Contextual Word2Vec for classifying twitter streams during outbreaks. Information Processing and Management, 56(1), 247–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2018.10.010
Kim, D., Seo, D., Cho, S., & Kang, P. (2019). Multi-co-training for document classification using various document representations: TF–IDF, LDA, and Doc2Vec. Information Sciences, 477, 15–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2018.10.006
Krishankumar, R., Ravichandran, K., Ahmed, M., Kar, S., & Tyagi, S. (2019). Probabilistic linguistic preference relation-based decision framework for multi-attribute group decision making. Symmetry. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11010002
Li, J., Liu, M., Li, X., Liu, X., & Liu, J. (2018). Developing embedded taxonomy and mining patients’ interests from web-based physician reviews: Mixed-methods approach. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 20(8), e254. https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.8868
Li, X., & Chen, X. (2018a). D-intuitionistic hesitant fuzzy sets and their application in multiple attribute decision making. Cognitive Computation, 10(3), 496–505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-018-9544-2
Li, X., & Chen, X. (2018b). Value determination method based on multiple reference points under a trapezoidal intuitionistic fuzzy environment. Applied Soft Computing Journal, 63, 39–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.11.003
Li, Y., Zhang, Y., & Xu, Z. (2020). A decision-making model under probabilistic linguistic circumstances with unknown criteria weights for online customer reviews. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 22(3), 777–789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-020-00812-1
Liao, H., Jiang, L., Xu, Z., Xu, J., & Herrera, F. (2017). A linear programming method for multiple criteria decision making with probabilistic linguistic information. Information Science, 415, 341–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2017.06.035
Liao, H., Jiang, L., Lev, B., & Fujita, H. (2019). Novel operations of PLTSs based on the disparity degrees of linguistic terms and their use in designing the probabilistic linguistic ELECTRE III method. Applied Soft Computing Journal, 80, 450–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.04.018
Liao, H., Mi, X., & Xu, Z. (2020). A survey of decision-making methods with probabilistic linguistic information: Bibliometrics, preliminaries, methodologies, applications and future directions. Fuzzy Optimization and Decision Making, 19, 81–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10700-019-09309-5
Liao, H., & Wu, X. (2020). DNMA: A double normalization-based multiple aggregation method for multi-expert multi-criteria decision making. Omega. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2019.04.001
Liu, R., Mou, X., & Liu, H. (2020). Occupational health and safety risk assessment based on combination weighting and uncertain linguistic information: Method development and application to a construction project. IISE Transactions on Occupational Ergonomics & Human Factors, 8(4), 175–186. https://doi.org/10.1080/24725838.2021.1875519
Liu, N., Finkelstein, S. R., Kruk, M. E., & Rosenthal, D. (2018). When waiting to see a doctor is less irritating: Understanding patient preferences and choice behavior in appointment scheduling. Management Science, 64(5), 1975–1996. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.2016.2704
Liu, P., & Li, Y. (2019). Multi-attribute decision making method based on generalized maclaurin symmetric mean aggregation operators for probabilistic linguistic information. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 131, 282–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2019.04.004
Liu, P., & Teng, F. (2019). Probabilistic linguistic TODIM method for selecting products through online product reviews. Information Sciences, 485, 441–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.02.022
Liu, R., Liu, Z., Liu, H., & Shi, H. (2021a). An improved alternative queuing method for occupational health and safety risk assessment and its application to construction excavation. Automation in Construction, 126, 103672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2021a.103672
Liu, H., Chen, X., You, J., & Li, Z. (2021b). A new integrated approach for risk evaluation and classification with dynamic expert weights. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 70(1), 163–174. https://doi.org/10.1109/TR.2020.2973403
Luo, G., Thomas, S. B., & Tang, C. (2012). Automatic home medical product recommendation. Journal of Medical Systems, 36(2), 383–398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-010-9483-2
Meng, Q., & Xiong, H. (2021). A doctor recommendation based on graph computing and LDA topic model. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems, 14(1), 808–817. https://doi.org/10.2991/ijcis.210205.002
Mikolov, T., Sutskever, I., Chen, K., Corrado, G., & Dean, J. (2013). Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 26, 3111–3119.
Nawangsari, R. P., Kusumaningrum, R., & Wibowo, A. (2019). Word2vec for Indonesian sentiment analysis towards hotel reviews: An evaluation study. Procedia Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2019.08.178
Nie, R., Tian, Z., Wang, J., & Chin, K. (2020). Hotel selection driven by online textual reviews: Applying a semantic partitioned sentiment dictionary and evidence theory. International Journal of Hospitality Management. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2020.102495
Pan, L., Ren, P. J., & Xu, Z. S. (2018). Therapeutic schedule evaluation for Brain-Metastasized non-small cell lung cancer with a probabilistic linguistic ELECTRE II Method. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(9), 1799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15091799
Pan, X., Song, J., & Zhang, F. (2019). Dynamic recommendation of physician assortment with patient preference learning. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 16(1), 115–126. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASE.2018.2839651
Pang, Q., Wang, H., & Xu, Z. (2016). Probabilistic linguistic term sets in multi-attribute group decision making. Information Sciences, 369, 128–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2016.06.021
Peng, H., Zhang, H., & Wang, J. (2018). Cloud decision support model for selecting hotels on TripAdvisor.com with probabilistic linguistic information. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 68, 124–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2017.10.001
Simon, H. A. (1947). Effects of increased productivity upon the ratio of urban to rural population. Econometrica, 15, 31–42. https://doi.org/10.2307/1905813
Wang, L., Wang, X. kang, Peng, J. juan, & Wang, J. Qiang. (2020). The differences in hotel selection among various types of travellers: A comparative analysis with a useful bounded rationality behavioural decision support model. Tourism Management. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2019.103961
Wang, X., Wang, S., Zhang, H., Wang, J., & Li, L. (2021). The recommendation method for hotel selection under traveller preference characteristics: A cloud-based multi-criteria group decision support model. Group Decision and Negotiation, 30(6), 1433–1469. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10726-021-09735-0
Waqar, M., Majeed, N., Dawood, H., Daud, A., & Aljohani, N. R. (2019). An adaptive doctor-recommender system. Behaviour and Information Technology, 38(9), 959–973. https://doi.org/10.1080/0144929X.2019.1625441
Wen, H., Song, J., & Pan, X. (2020). Physician Recommendation on Healthcare Appointment Platforms Considering Patient Choice. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 17(2), 886–899. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASE.2019.2950724
Wojtczak, A., Armstrong, E. G., Bandaranayake, R. C., Oriol i Bosch, A., Cravioto, A., Dohner, C., Dunn, M. R., Gonnella, J. S., Hamilton, J. D., Harden, R. M., Hawkins, D., Patiño, J. F., Schwarz, M. R., Stern, D. T., Tuchinda, P., van Nickerk, J. P., & Tongfu, Z. (2002). Global minimum essential requirements in medical education. Medical Teacher, 24(2), 130–135. https://doi.org/10.1080/01421590220120731
Wu, H., Luk, R. W. P., Wong, K., & Kwok, K. L. (2008). Interpreting TF-IDF term weights as making relevance decisions. ACM Transactions on Information Systems, 26(3), 55–59. https://doi.org/10.1145/1361684.1361686
Wu, X., & Liao, H. (2019). A consensus-based probabilistic linguistic gained and lost dominance score method. European Journal of Operational Research, 272(3), 1017–1027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2018.07.044
Wu, X., & Liao, H. (2021a). Modeling personalized cognition of customers in online shopping. Omega-International Journal of Management Science, 104, 102471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2021.102471
Wu, X., & Liao, H. (2021b). Learning judgment benchmarks of customers from online reviews. Or Spectrum, 43(4), 1125–1157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00291-021-00639-8
Wu, X., Liao, H., Xu, Z., Arian, H., & Francisco, H. (2018). Probabilistic linguistic multimoora: A multicriteria decision making method based on the probabilistic linguistic expectation function and the improved borda rule. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 26, 3688–3702. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2018.2843330
Wu, X., Zhang, C., Jiang, L., & Liao, H. (2019). An improved PROMETHEE method integrating conflict analysis with cognitive complex linguistic information: Case study of site selection for wind power plants. Cognitive Computation. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-019-09675-7
Yang, Y., & Guo, Z. (2021). Research on the evaluation of public emergency management intelligence capability in probabilistic language environment. Annals of Operations Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-021-04342-3
Yang, Y., Hu, J., Liu, Y., & Chen, X. (2020). Doctor recommendation based on an intuitionistic normal cloud model considering patient preferences. Cognitive Computation, 12(2), 460–478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-018-9616-3
Yang, Z., Gao, Y., & Fu, X. (2021). A decision-making algorithm combining the aspect-based sentiment analysis and intuitionistic fuzzy-VIKOR for online hotel reservation. Annals of Operations Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-021-04339-y
Yao, Y., Li, X., Liu, X., Liu, P., Liang, Z., Zhang, J., & Mai, K. (2017). Sensing spatial distribution of urban land use by integrating points-of-interest and Google Word2Vec model. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 31(4), 825–848. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658816.2016.1244608
Ye, Y., Zhao, Y., Shang, J., & Zhang, L. (2019). A hybrid IT framework for identifying high-quality physicians using big data analytics. International Journal of Information Management, 47, 65–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2019.01.005
Yu, S., Wang, J., & Wang, J. (2017). An interval type-2 fuzzy likelihood-based MABAC approach and its application in selecting hotels on a tourism website. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 19, 47–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-016-0217-6
Zhang, Y., Chen, M., Huang, D., Wu, D., & Li, Y. (2017b). iDoctor: Personalized and professionalized medical recommendations based on hybrid matrix factorization. Future Generation Computer Systems, 66, 30–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2015.12.001
Zhang, H., Ji, P., Wang, J., & Chen, X. (2017a). A novel decision support model for satisfactory restaurants utilizing social information: A case study of TripAdvisor.com. Tourism Management, 59, 281–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2016.08.010
Zhao, M., Li, L., & Xu, Z. (2021). Study on hotel selection method based on integrating online ratings and reviews from multi-websites. Information Sciences, 572, 460–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2021.05.042
Zhao, M., Shen, X., Liao, H., & Cai, M. (2022). Selecting products through text reviews: An MCDM method incorporating personalized heuristic judgments in the prospect theory. Fuzzy Optimization and Decision Making, 21(1), 21–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10700-021-09359-8
Zhang, D., Wu, C., & Liu, J. (2020). Ranking products with online reviews: A novel method based on hesitant fuzzy set and sentiment word framework. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 71(3), 528–542. https://doi.org/10.1080/01605682.2018.1557021
Zhang, X., & Xing, X. (2017). Probabilistic linguistic VIKOR method to evaluate green supply chain initiatives. Sustainability, 9(7), 1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9071231
Zhang, Y., Xu, Z., Wang, H., & Liao, H. (2016). Consistency-based risk assess- ment with probabilistic linguistic preference relation. Applied Soft Computing, 49, 817–833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2016.08.045
Zhang, C., Zhang, H., & Wang, J. (2018). Personalized restaurant recommendation method combining group correlations and customer preferences. Information Sciences, 454, 128–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2018.04.061
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Major Research Program Integration Project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 91846301) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 71971223).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors confirm that there is no conflict of interest for this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Wang, H. & Li, X. Doctor recommendation under probabilistic linguistic environment considering patient’s risk preference. Ann Oper Res 341, 555–581 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-022-04843-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-022-04843-9