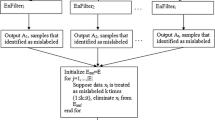
Abstract
This paper presents a new approach for identifying and eliminating mislabeled training instances for supervised learning algorithms. The novelty of this approach lies in the using of unlabeled instances to aid the detection of mislabeled training instances. This is in contrast with existing methods which rely upon only the labeled training instances. Our approach is straightforward and can be applied to many existing noise detection methods with only marginal modifications on them as required. To assess the benefit of our approach, we choose two popular noise detection methods: majority filtering (MF) and consensus filtering (CF). MFAUD/CFAUD is the new proposed variant of MF/CF which relies on our approach and denotes majority/consensus filtering with the aid of unlabeled data. Empirical study validates the superiority of our approach and shows that MFAUD and CFAUD can significantly improve the performances of MF and CF under different noise ratios and labeled ratios. In addition, the improvement is more remarkable when the noise ratio is greater.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Mingers J (1989) An empirical comparison of pruning methods for decision tree induction. Mach Learn 4(2):227–243
Quinlan JR (1993) C4.5: programs for machine learning. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco
Gamberger D, Lavrac N, Dzeroski S (2000) Noise detection and elimination in data proprocessing: Experiments in medical domains. Appl Artif Intell 14(2):205–223
Quinlan JR (1986) Induction of decision trees. Mach Learn 1(1):81–106
Guyon I, Matic N, Vapnik V (1996) Discovering information patterns and data cleaning. In: Advances in knowledge discovery and data mining. AAAI/MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 181–203
Gamberger D, Lavrac N, Groselj C (1999) Experiments with noise filtering in a medical domain. In: Proceedings of 16th international conference on machine learning, pp 143–151
Brodley CE, Friedl MA (1996) Identifying and eliminating mislabeled training instances. In: Proceedings of 13th national conference on artificial intelligence, pp 799–805
Brodley CE, Friedl MA (1999) Identifying mislabeled training data. J Artif Intell Res 11:131–167
Wilson D (1972) Asymptotic properties of nearest neighbor rules using edited data. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 2:408–421
Aha D, Kibler D, Albert M (1991) Instance-based learning algorithms. Mach Learn 6(1):37–66
Riloff E, Wiebe J, Wilson T (2003) Learning subjective nouns using extraction pattern bootstrapping. In: Proceedings of the 7th conference on natural language learning, pp 25–32
Blum A, Mitchell T (1998) Combining labeled and unlabeled data with co-training. In: Proceedings of 11th annual conference on computational learning theory, pp 92–100
UCI KDD archive. http://kdd.ics.uci.edu
Keerthi S, Shevade S, Bhattacharyya C, Murthy K (2001) Improvements to Platt’s SMO algorithm for SVM classifier design. Neural Comput 13(3):637–649
John G, Leonard E (1995) An instance-based learner using an entropic distance measure. In: Proceedings of the 12th international conference on machine learning, pp 108–114
Angluin D, Laird P (1988) Learning from noisy examples. Mach Learn 2(2):343–370
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research was done when Dr. Donghai Guan worked in Ubiquitous Computing Lab, Kyung Hee University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, D., Yuan, W., Lee, YK. et al. Identifying mislabeled training data with the aid of unlabeled data. Appl Intell 35, 345–358 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-010-0225-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-010-0225-4