Abstract
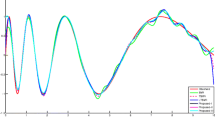
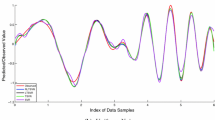
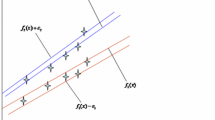
In this paper, we propose a new unconstrained twin support vector regression model in the primal space (UPTSVR). With the addition of a regularization term in the formulation of the problem, the structural risk is minimized. The proposed formulation solves two smaller sized unconstrained minimization problems having continues, piece-wise quadratic objective functions by gradient based iterative methods. However, since their objective functions contain the non-smooth ‘plus’ function, two approaches are taken: (i) replace the non-smooth ‘plus’ function with their smooth approximate functions; (ii) apply a generalized derivative of the non-smooth ‘plus’ function. They lead to five algorithms whose pseudo-codes are also given. Experimental results obtained on a number of interesting synthetic and real-world benchmark datasets using these algorithms in comparison with the standard support vector regression (SVR) and twin SVR (TSVR) clearly demonstrates the effectiveness of the proposed method.




Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Balasundaram S, Gupta D (2014) Training Lagrangian twin support vector regression via unconstrained convex minimization. Knowl-Based Syst 59:85–96
Balasundaram S, Gupta D (2013) On implicit Lagrangian twin support vector regression by Newton method. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems, pp 1–15
Balasundaram S, Tanveer M (2013) On Lagrangian twin support vector regression. Neural Comput Appl 22(Suppl 1):S257– S267
Box GEP, Jenkins GM (1976) Time series analysis: Forecasting and Control. Holden-Day, San Francisco
Brown MPS, Grundy WN, Lin D et al (2000) Knowledge-based analysis of microarray gene expression data using support vector machine. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 97(1):262–267
Chapelle O (2007) Training a support vector machine in primal. Neural Comput 19(5):1155–1178
Chen X, Yang J, Liang J, Ye Q (2012) Smooth twin support vector regression. Neural Comput Appl 21:505–513
Cristianini N, Shawe-Taylor J (2000) An introduction to support vector machines and other kernel based learning method. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Demsar J (2006) Statistical comparisons of classifiers over multiple data sets. J Mach Learn Res 7:1–30
Eubank RL (1999) Nonparametric regression and spline smoothing statistics: Textbooks and monographs, vol 157, 2nd edn. NY, Marcel Dekker
Fung G, Mangasarian OL (2003) Finite Newton method for Lagrangian support vector machine. Neurocomputing 55:39–55
Garcia S, Herrera F (2008) An extension on “Statistical comparisons of classifiers over multiple data sets” for all pairwise comparisons. J Mach Learn Res 9:2677–2694
Gretton A, Doucet A, Herbrich R, Rayner PJW, Scholkopf B (2001) Support vector regression for black-box system identification. In: Proceedings of the 11 th IEEE Workshop on Statistical Signal Processing
Guyon I, Weston J, Barnhill S, Vapnik V (2002) Gene selection for cancer classification using support vector machine. Mach Learn 46:389–422
Hiriart-Urruty J-B, Strodiot JJ, Nguyen VH (1984) Generalized hessian matrix and second-order optimality conditions for problems with C L1 data. Appl Math Opt 11:43–56
Jayadeva, Khemchandani R, Chandra S (2007) Twin support vector machines for pattern classification. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 29(5):905–910
Joachims T, Ndellec C, Rouveriol (1998) Text categorization with support vector machines: learning with many relevant features. In: European Conference on Machine Learning No. 10. Chemnitz, Germany, pp 137–142
Kumar MA, Gopal M (2008) Application of smoothing technique on twin support vector machines. Pattern Recogn Lett 29:1842–1848
Kumar MA, Gopal M (2009) Least squares twin support vector machines for pattern classification. Expert Syst Appl 36:7535–7543
Lee YJ, Mangasarian OL (2001) SSVM: A smooth support vector machine for classification. Comput Opt Appl 20(1):5–22
Lee YJ, Hsieh W-F, Huang C-M (2005) ε-SSVR: A smooth support vector machine for ε-insensitive regression. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 17(5):678–685
Mangasarian OL (2002) A finite Newton method for classification. Opt Methods Softw 17:913–929
Mangasarian OL, Musicant DR (2001) Lagrangian support vector machines. J Mach Learn Res 1:161–177
Mangasarian OL, Wild EW (2006) Multisurface proximal support vector classification via generalized eigenvalues. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 28(1):69–74
Mukherjee S, Osuna E, Girosi F (1997) Nonlinear prediction of chaotic time series using support vector machines. In: NNSP’97: Neural Networks for Signal Processing VII: in Proceedings of IEEE Signal Processing Society Workshop, Amelia Island, FL, USA, pp 511–520
Muller KR, Smola AJ, Ratsch G, Schölkopf B, Kohlmorgen J (1999) Using support vector machines for time series prediction. In: Schölkopf B, Burges CJC, Smola AJ (eds) Advances in Kernel Methods- Support Vector Learning. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, pp 243–254
Murphy PM, Aha DW (1992) UCI repository of machine learning databases. University of California, Irvine. http://www.ics.uci.edu/~mlearn
Osuna E, Freund R, Girosi F (1997) Training support vector machines: An application to face detection. In: Proceedings of Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 130-136
Peng X (2010) TSVR: An efficient twin support vector machine for regression. Neural Netw 23(3):365–372
Peng X (2010) Primal twin support vector regression and its sparse approximation. Neurocomputing 73 (16-18):2846–2858
Peng X (2012) Efficient twin parametric insensitive support vector regression model. Neurocomputing 79:26–38
Shao Y, Zhang C, Wang X, Deng N (2011) Improvements on twin support vector machines. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22(6):962–968
Shao Y, Zhang C, Yang Z, Jing L, Deng N (2012) An ε− twin support vector machine for regression. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s00521-012-00924-3
Sjoberg J, Zhang Q, Ljung L, Berveniste A, Delyon B, Glorennec P, Hjalmarsson H, Juditsky (1995) Nonlinear black-box modeling in system identification: a unified overview. Automatica 31:1691–1724
Souza LGM, Barreto GA (2006) Nonlinear system identification using local ARX models based on the self-organizing map. In: Learning and Nonlinear Models-Revista da Soc Brasileira de Redes Neurals (SBRN), vol 4, no 2, pp 112–123
Van Gestel T, Baesens B, Suykens JAK, De Espinoza M, Baestaens J, Vanthienen De MB (2003) Bankruptcy prediction with least squares support vector machine classifiers. In: Proceedings IEEE Int conf computational intelligence for financial engineering, Hong Kong
Vapnik VN (2000) The nature of statistical learning theory, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Wang XX, Chen S, Lowe D, Harris CJ (2006) Sparse support vector regression based on orthogonal forward selection for generalized kernel model. Neurocomputing 70:462–474
Xu Y, Wang L (2012) A weighted twin support vector regression. Knowl Based Syst 33:92–101
Yang X, Zhang G, Lu J, Ma J (2011) A kernel fuzzy c-means clustering-based fuzzy support vector machine algorithm for classification problems with outliers or noises. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 19(1):105–115
Zhong P, Xu Y, Zhao Y (2012) Training twin support vector regression via linear programming. Neural Comput Appl 21:399–407
Zhao Y, Zhao J, Zhao M (2013) Twin least squares support vector regression. Neurocomputing 118:225–236
Acknowledgments
The authors are extremely thankful to the anonymous reviewers for their comments. Mr.Yogendra Meena acknowledges the financial assistance awarded by Rajiv Gandhi National Fellowship, Government of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balasundaram, S., Meena, Y. Training primal twin support vector regression via unconstrained convex minimization. Appl Intell 44, 931–955 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-015-0731-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-015-0731-5