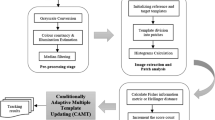
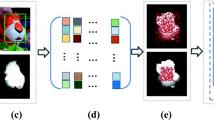
Abstract
Arbitrary object tracking is a challenging task in computer vision, as many factors affecting the target representation must be considered. A target template based on only the global appearance or on only the local appearance is unable to capture the discriminating information required for the robust performance of a tracker. In this paper, the target appearance is represented using a hybrid of global and local appearances along with a framework to exploit the Integral Channel Features (ICF). The proposed hybrid approach achieves fusion of the conventional global and patch-based approaches for target representation to synergize the advantages of both approaches. The ICF approach under the hybrid approach integrates heterogeneous sources of information of the target and provides feature strength to the hybrid template. The use of ICF also expedites the extraction of the structural and color features from video frames as the features are collected over multiple channels. The target appearance representation is updated based on only samples with appearances similar to the target appearance using clustering and vector quantization. These factors offer the proposed algorithm robustness to occlusion, illumination changes, and in-plane rotation. Further experimentation analyzes the effects of a change in the scale of the bounding box on the tracking performance of the proposed algorithm. The proposed approach outperforms all the state-of-the-art algorithms in all considered scenarios.






Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Smeulders AW, Chu DM, Cucchiara R, Calderara S, Dehghan A, Shah M (2014) Visual tracking: an experimental survey. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 36(7):1442–1468
Yang H, Shao L, Zheng F, Wang L, Song Z (2011) Recent advances and trends in visual tracking: a review. Neurocomputing 74(18):3823–3831
Briechle K, Hanebeck UD (2001) Template matching using fast normalized cross correlation 95–102
Xue M, Haibin L (2009) Robust visual tracking using l1 minimization. In: IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV). Kyoto, Japan, pp 1436–1443
Xue M, Haibin L, Yi W, Blasch E, Li B (2011) Minimum error bounded efficient l1 tracker with occlusion detection. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). Colorado, pp 1257–1264
Kalal Z, Matas J, Mikolajczyk K (2010) Pn learning: bootstrapping binary classifiers by structural constraints. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). San Francisco, pp 49–56
Wang Q, Chen F, Xu W, Yang M-H (2012) Object tracking via partial least squares analysis. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(10):4454–4465
Zhou T, He X, Xie K, Fu K, Zhang J, Yang J (2015) Robust visual tracking via efficient manifold ranking with low-dimensional compressive features. Pattern Recogn 48(8):2459–2473
Yuan Y, Huan Y, Yuming F, Weisi L (2015) Visual object tracking by structure complexity coefficients. IEEE Trans Multimed 17(8):1125–1136
Adam A, Rivlin E, Shimshoni I (2006) Robust fragments-based tracking using the integral histogram. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). New York, pp 798–805
Junseok K, Kyoung Mu L (2009) Tracking of a non-rigid object via patch-based dynamic appearance modeling and adaptive Basin Hopping Monte Carlo sampling. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). Miami, pp 1208–1215
Cehovin L, Kristan M, Leonardis A (2011) An adaptive coupled-layer visual model for robust visual tracking. In: IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV). Barcelona, pp 1363–1370
Oron S, Bar-Hillel A, Levi D, Avidan S (2012) Locally orderless tracking. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). Rhode Island, pp 1940–1947
Shu W, Huchuan L, Fan Y, Ming-Hsuan Y (2011) Superpixel tracking. In: IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), Barcelona, pp 1323–1330
Weiming H, Xi L, Wenhan L, Xiaoqin Z, Maybank S, Zhongfei Z (2012) Single and multiple object tracking using log-Euclidean Riemannian subspace and block-division appearance model. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 34(12):2420–2440
Jia X, Lu H, Yang M-H (2012) Visual tracking via adaptive structural local sparse appearance model. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). Providence, pp 1822–1829
Babenko B, Yang M-H, Belongie S (2011) Robust object tracking with online multiple instance learning. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 33(8):1619–1632
Zhang K, Zhang L, Liu Q, Zhang D, Yang M-H (2014) Fast visual tracking via dense spatio-temporal context learning. In: European conference on computer vision. Zurich, pp 127–141
Zhu Q, Yeh M-C, Cheng K-T, Avidan S (2006) Fast human detection using a cascade of histograms of oriented gradients. In: IEEe conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). New York, pp 1491–1498
Laptev I (2006) Improvements of object detection using boosted histograms. In: British machine vision conference (BMVC). Edinburgh, pp 949–958
Dollár P, Tu Z, Perona P, Belongie S (2009) Integral channel features. In: British machine vision conference (BMVC). Londan, p 5
Henriques JF, Caseiro R, Martins P, Batista J (2015) High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 37(3):583–596
Kalal Z, Mikolajczyk K, Matas J (2012) Tracking-Learning-Detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 34(7):1409–1422
Hare S, Saffari A, Torr PH (2011) Struck: structured output tracking with kernels. In: IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), Barcelona, pp 263–270
Ross D, Lim J, Lin R-S, Yang M-H (2008) Incremental learning for robust visual tracking. Int J Comput Vis 77(1–3):125–141
Jepson AD, Fleet DJ, El-Maraghi TF (2003) Robust online appearance models for visual tracking. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 25(10):1296–1311
Kwon J, Lee K M (2010) Visual tracking decomposition. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). San Francisco, pp 1269–1276
Avidan S (2007) Ensemble tracking. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 29(2):261–271
Grabner H, Bischof H (2006) On-line boosting and vision. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). New York, pp 260–267
Baker S, Matthews I (2004) Lucas-Kanade 20 years on: a unifying framework. Int J Comput Vis 56 (3):221–255
Shu G, Dehghan A, Oreifej O, Hand E, Shah M (2012) Part-based multiple-person tracking with partial occlusion handling. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). Rhode Island, pp 1815–1821
Lin Z, Davis LS, Doermann D, DeMenthon D (2007) Hierarchical part-template matching for human detection and segmentation. In: IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), Rio de Janeiro, pp 1–8
Porikli F (2005) Integral histogram: a fast way to extract histograms in cartesian spaces. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). San Dieg, pp 829–836
Li X R, Jilkov VP (2000) Survey of maneuvering target tracking: dynamic models. In: Proceedings of SPIE conference on signal and data processing of small targets. Orlando, pp 212–235
Wu Y, Lim J, Yang M-H (2013) Online object tracking: a benchmark. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). Portland, pp 2411–2418
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parate, M.R., Satpute, V.R. & Bhurchandi, K.M. Global-patch-hybrid template-based arbitrary object tracking with integral channel features. Appl Intell 48, 300–314 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-017-0974-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-017-0974-4