Abstract
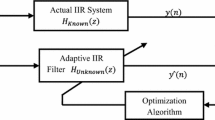
An efficient global adaptive algorithm is required to determine the parameters of infinite impulse response (IIR) filter owing to the error cost surface of adaptive IIR system identification problem being generally nonlinear and non-differentiable. In this paper, a new bio-inspired algorithm, called opposition based hybrid coral reefs optimization algorithm (OHCRO) is applied for the IIR system identification problem. Coral reefs optimization algorithm (CRO) is a novel global algorithm, which mimics the behaviors of corals’ reproduction and coral reef formation. OHCRO is a modified version of CRO, on the one hand utilizing opposition based learning to accelerate global convergence, on the other hand cooperating with rotational direction method to enhance the local search capability. In addition, the Laplace broadcast spawning and power mutation brooding operator are used to maintain the diversity. The simulation studies have been performed for the performance comparison of genetic algorithm, particle swarm optimization and its variants, differential evolution and its variants and the proposed OHCRO for well-known benchmark examples with same order and reduced order filters. Simulation results and comparative studies justify the efficacy of the OHCRO based system identification approach in terms of convergence speed, identified coefficients and fitness values. In conclusion, OHCRO is a promising method for adaptive IIR system identification.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahirwal MK, Kumar A, Singh GK (2014) Adaptive filtering of EEG/ERP through bounded range artificial bee colony (BR-ABC) algorithm. Digit Signal Process 25:164–172
Barreto GA, M Souza LG (2016) Novel approaches for parameter estimation of local linear models for dynamical system identification. Appl Intell 44(1):149–165
Cabrera R, Strohecker T, Rabitz H (2010) The canonical coset decomposition of unitary matrices through householder transformations. J Math Phys 51(8):082,101
Dai C, Chen W, Zhu Y (2010) Seeker optimization algorithm for digital IIR filter design. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 57(5):1710–1718
Deep K, Thakur M (2007) A new crossover operator for real coded genetic algorithms. Appl Math Comput 188(1):895–911
Deep K, Thakur M (2007) A new mutation operator for real coded genetic algorithms. Appl Math Comput 193(1):211–230
Fang W, Sun J, Xu W, Liu J (2006) Analysis of adaptive IIR filter design based on quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization. In: 2006 6Th world congress on intelligent control and automation, vol 1, pp 3396–3400
Ghanbari A, Kazemi SMR, Mehmanpazir F, Nakhostin MM (2013) A cooperative ant colony optimization-genetic algorithm approach for construction of energy demand forecasting knowledge-based expert systems. Knowl-Based Syst 39:194–206
Haykin S (2008) Adaptive filter theory. Pearson Education India
Huang CL, Huang WC, Chang HY, Yeh YC, Tsai CY (2013) Hybridization strategies for continuous ant colony optimization and particle swarm optimization applied to data clustering. Appl Soft Co 13(9):3864–3872
Jiang S, Wang Y, Ji Z (2015) A new design method for adaptive IIR system identification using hybrid particle swarm optimization and gravitational search algorithm. Nonlinear Dyn 79(4):2553–2576
Kang F, Li J, Ma Z (2011) Rosenbrock artificial bee colony algorithm for accurate global optimization of numerical functions. Inform Sci 181(16):3508–3531
Karaboga N (2005) Digital IIR filter design using differential evolution algorithm. In: EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, vol 2005, p 856824
Karaboga N (2009) A new design method based on artificial bee colony algorithm for digital IIR filters. J Frankl Inst 346(4):328–348
Kennedy J, Eberhart R (1995) Particle swarm optimization. In: IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, 1995. Proceedings, vol 4, pp 1942–1948
Kumar M, Aggarwal A, Rawat TK (2016) Bat algorithm: Application to adaptive infinite impulse response system identification. Arab J Sci Eng 41(9):3587–3604
Kumar M, Rawat TK, Aggarwal A (2017) Adaptive infinite impulse response system identification using modified-interior search algorithm with levy flight. ISA T 67:266–279
Li M, Miao C, Leung C (2015) A coral reef algorithm based on learning automata for the coverage control problem of heterogeneous directional sensor networks. Sensor 15(12):30,617–30,635
Lin G, Zhao K, Wan Q (2016) Takagi-sugeno fuzzy model identification using coevolution particle swarm optimization with multi-strategy. Appl Intell 45(1):187–197
Lu Y, Yan D, Levy D (2015) Friction coefficient estimation in servo systems using neural dynamic programming inspired particle swarm search. Appl Intell 43(1):1–14
Ma Q, Cowan CFN (1996) Genetic algorithms applied to the adaptation of IIR filters. Signal Process 48 (2):155–163
Majhi B, Panda G, Choubey A (2008) Efficient scheme of pole-zero system identification using particle swarm optimization technique. In: IEEE Congress on evolutionary computation, CEC 2008, pp 446–451
Mao Y, Ding F, Alsaedi A, Hayat T (2016) Adaptive filtering parameter estimation algorithms for hammerstein nonlinear systems. Signal Process 128:417–425
Ng SC, Leung SH, Chung CY, Luk A, Lau WH (1996) The genetic search approach. a new learning algorithm for adaptive IIR filtering. IEEE Signal Process Mag 13(6):38–46
Panda G, Pradhan PM, Majhi B (2011) IIR system identification using cat swarm optimization. Expert Syst Appl 38(10):12,671–12,683
Parouha RP, Das KN (2016) A robust memory based hybrid differential evolution for continuous optimization problem. Knowl-Based Syst 103:118–131
Rahnamayan S, Tizhoosh HR, Salama MMA (2008) Opposition-based differential evolution. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 12(1):64–79
Rahnamayan S, Tizhoosh HR, Salama MMA (2008) Opposition versus randomness in soft computing techniques. Appl Soft Comput 8(2):906–918
Rashedi E, Nezamabadi-pour H, Saryazdi S (2011) Filter modeling using gravitational search algorithm. Eng Appl Artif Intell 24(1):117–122
Regalia P (1994) Adaptive IIR filtering in signal processing and control, vol 90. CRC Press, New York
Rosenbrock HH (1960) An automatic method for finding the greatest or least value of a function. Comput J 3(3):175–184
Saha SK, Kar R, Mandal D, Ghoshal SP, Mukherjee V (2013) A new design method using opposition-based bat algorithm for IIR system identification problem. Int J Bio-Inspir Comput 5(2):99–132
Saha SK, Kar R, Mandal D, Ghoshal SP (2014) Harmony search algorithm for infinite impulse response system identification. Comput Electr Eng 40(4):1265–1285
Salcedo-Sanz S, Del SJ, Landa-Torres I, Gil-Lpez S, Portilla-Figueras JA (2014) The coral reefs optimization algorithm: a novel metaheuristic for efficiently solving optimization problems. Thescientificworldjo 2014:739,768–739,768
Salcedo-Sanz S, Garcła-dłaz P, Portilla-Figueras JA, Ser JD, Gil-Lpez S (2014) A coral reefs optimization algorithm for optimal mobile network deployment with electromagnetic pollution control criterion. Appl Soft Co 24:239–248
Salcedo-Sanz S, Pastor-Sánchez A, Ser JD, Prieto L, Geem ZW (2015) A coral reefs optimization algorithm with harmony search operators for accurate wind speed prediction. Renew Energ 75:93–101
Salcedo-Sanz S, Camacho-Gómez C, Mallol-Poyato R, Jiménez-Fernández S, Ser JD (2016) A novel coral reefs optimization algorithm with substrate layers for optimal battery scheduling optimization in micro-grids. Soft Co :1–14
Tizhoosh HR (2005) Opposition-based learning: A new scheme for machine intelligence. In: The International Conference on Computational Intelligence for Modelling, Control and Automation, pp 695–701
Tizhoosh HR (2006) Opposition-based reinforcement learning. J Adv Comput Intell Inform 10(4):578–585
Trivedi A, Srinivasan D, Biswas S, Reindl T (2015) Hybridizing genetic algorithm with differential evolution for solving the unit commitment scheduling problem. Swar Evol Comput 23:50–64
Upadhyay P, Kar R, Mandal D, Ghoshal SP (2014) Craziness based particle swarm optimization algorithm for IIR system identification problem. Aeu-int J Electron C 68(5):369–378
Upadhyay P, Kar R, Mandal D, Ghoshal SP, Mukherjee V (2014) A novel design method for optimal IIR system identification using opposition based harmony search algorithm. J Franklin Inst 351(5):2454–2488
Ventresca M, Tizhoosh HR (2006) Improving the convergence of backpropagation by opposite transfer functions. In: International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, IJCNN, p 13
Wang C, Tang T (2014) Several gradient-based iterative estimation algorithms for a class of nonlinear systems using the filtering technique. Nonlinear Dyn 77(3):769–780
Wang J, Shi P, Peng H (2016) Membrane computing model for iir filter design. Inf Sci 329:164–176
Yang Z, Zhang T, Zhang D (2016) A novel algorithm with differential evolution and coral reef optimization for extreme learning machine training. Cogn Neurodyn 10(1):1–11
Yi W, Gao L, Li X, Zhou Y (2015) A new differential evolution algorithm with a hybrid mutation operator and self-adapting control parameters for global optimization problems. Appl Intell 42(4):642–660
Yu X, Liu J, Li H (2009) An adaptive inertia weight particle swarm optimization algorithm for IIR digital filter. In: International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computational Intelligence, pp 114–118
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by Shanghai Astronautical research funding under Grant Nos. USCAST2013-10 and USCAST2016-13 and the research grant (1600158) from Qinghai Province Key Laboratory of Photovoltaic grid connected power generation technology, for which the authors are most grateful.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Yang, B. & Niu, M. Adaptive infinite impulse response system identification using opposition based hybrid coral reefs optimization algorithm. Appl Intell 48, 1689–1706 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-017-1034-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-017-1034-9