Abstract
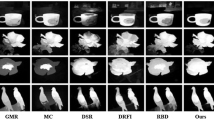
The visual saliency detection consists in determining the relevant visual information in a scene to segment it from the background. This paper proposes visual saliency detection in a rule-based approach using the image similarity cue to improve saliency detection performance. Our system induces rules for saliency detection, and for a given input image, determines the subset of rules to be used from a set of candidate rules. The proposed approach consists of two main stages: training and testing. Firstly, during the training stage, our system learns an ensemble of rough-set-based rules by combining knowledge extracted from outputs of four state-of-the-art saliency models. Secondly, our system determines the most suitable subset of induced rules for binary detection of pixels of a salient object in an image. The decision of the best subset of rules is based on the image similarity cue. The binary determination of saliency in the output image, exempts us from performing a post-processing stage as is needed in most saliency approaches. The proposed method is evaluated quantitatively on three challenging databases designed for the saliency detection task. The results obtained from the performed experiments indicate that the proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches used for comparison.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Itti L, Koch C (2000) A saliency-based search mechanism for overt and covert shifts of visual attention. Vision Res 40(10):1489–1506
Achanta R, Hemami S, Estrada F, Susstrunk S (2009) Frequency-tuned salient region detection. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (CVPR), pp 1597–1604
Ren Z, Gao S, Chia L, Tsang IW (2014) Region-based saliency detection and its application in object recognition. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 24(5):769–779
Gao D, Han S, Vasconcelos N (2009) Discriminant saliency, the detection of suspicious coincidences, and applications to visual recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 31(6):989–1005
Wang Q, Yuan Y, Yan P (2013) Visual saliency by selective contrast. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 23(7):1150–1155
Chang C, Siagian C, Itti L (2010) Mobile robot vision navigation & localization using gist and saliency. In: 2010 IEEE Int. Conf. Intell. Robot. Syst., pp 4147–4154
Harding P, Robertson NM (2013) Visual saliency from image features with application to compression. Cogn Comput 5(1):76–98
Treisman AM, Gelade G (1980) A feature-integration theory of attention. Cogn Psychol 12(1):97–136
Frintrop S, Klodt M, Rome E (2007) A real-time visual attention system using integral images. In: Proc. 5th Int. Conf. Comput. Vis. Syst. (ICVS), pp 1–10
Frintrop S, Werner T, Garcia GM (2015) Traditional saliency reloaded: a good old model in new shape. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (CVPR), pp 82–90
Le Meur O, Le Callet P, Barba D, Thoreau D (2006) A coherent computational approach to model the bottom-up visual attention. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 28:802–817
Goferman S, Zelnik-Manor L, Tal A (2012) Context-aware saliency detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Intell 34(10):1915–1926
Cheng M-M, Mitra NJ, Huang X, Torr PHS, Hu S-M (2015) Global contrast based salient region detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Intell 37(3):569–582
Perazzi F, Krahenbuhl P, Pritch Y, Hornung A (2012) Saliency filters: Contrast based filtering for salient region detection. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (CVPR), pp 733–740
Zhang J, Sclaroff S, Lin Z, Shen X, Price B, Mech R (2015) Minimum barrier salient object detection at 80 fps. In: Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Comput. Vis. (ICCV), pp 1404–1412
Huang X, Zhang. Y-J (2017) 300-FPS salient object detection via minimum directional contrast. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(9):4243–4254
Itti L, Koch C (2001) Computational modelling of visual attention. Nature Rev Neurosci 2(3):194–203
Bylinskii Z, Judd T, Oliva A, Torralba A, Durand F (2016) What do different evaluation metrics tell us about saliency models?
Mai L, Niu Y, Liu F (2013) Saliency aggregation: A data-driven approach. In: IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (CVPR), pp 1131–1138
Borji A, Sihite DN, Itti L (2012) Salient object detection: a benchmark. In: Proc. European Conf. Comput. Vis. (ECCV), pp 414–429
Zhou X, Liu Z, Sun G, Wang X (2017) Adaptive saliency fusion based on quality assessment. Multimedia Tools Appl 76(22):23187–23211
Lopez-Alanis A, Lizarraga-Morales RA, Sanchez-Yanez RE, Martinez-Rodriguez DE, Contreras-Cruz MA (2019) Visual saliency detection using a rule-based aggregation approach. Appl. Sci 9(10)
Nguyen TV, Kankanhalli M (2017) As-similar-as-possible saliency fusion. Multimedia Tools Appl 76 (8):10501–10519
Le Meur O, Liu Z (2014) Saliency aggregation: Does unity make strength? In: Proc. 12th Asia Conf. Comput. Vis. (ACCV), pp 18–32
Liu N, Han J (2016) Dhsnet: Deep hierarchical saliency network for salient object detection. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (CVPR), pp 678–686
Hu P, Shuai B, Liu J, Wang G (2017) Deep level sets for salient object detection. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (CVPR), pp 540–549
Li H, Chen J, Lu H, Chi Z (2017) Cnn for saliency detection with low-level feature integration. Neurocomputing 226:212–220
Mu N, Xu X, Zhang X, Zhang H (2018) Salient object detection using a covariance-based cnn model in low-contrast images. Neural Comput Appl 29(8):181–192
Chen S, Wang B, Tan X, Hu X (2018) Embedding attention and residual network for accurate salient object detection. IEEE Trans. on Cybern, pp 1–13
Stefanowski J (2007) On combined classifiers, rule induction and rough sets. Trans on Rough Sets VI: LNCS 4374:329–350
Borji A, Cheng MM, Jiang H, Li J (2015) Salient object detection: a benchmark. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(12):5706–5722
Borji A, Cheng M-M, Jiang H, Li J (2014) Salient object detection: a survey. arXiv:1411.5878
Pawlak Z (1982) Rough sets. Int J Comput Inform Sci 11(5):341–356
Stefanowski J (1998) On rough set based approaches to induction of decision rules. Rough Sets in Knowledge Discovery 1(1):500–529
Stepaniuk J (2000) Knowledge discovery by application of rough set models, pp 137–233
Grzymala-Busse JW, Stefanowski J (2001) Three discretization methods for rule induction. Int J Intell Syst 16(1):29–38
Hall M, Frank E, Holmes G, Pfahringer B, Reutemann P, Witten IH (2009) The weka data mining software: an update. ACM SIGKDD Explorations Newslett 11(1):10–18
Sandler M, Howard A, Zhu M, Zhmoginov A, Chen L (2018) Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 4510–4520
Bianco S, Cadene R, Celona L, Napoletano P (2018) Benchmark analysis of representative deep neural network architectures. IEEE Access 6:64270–64277
Chollet F, et al. (2015) Keras. https://keras.io
Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, Li L, Li Kai, Li Fei-Fei. (2009) Imagenet A large-scale hierarchical image database. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (CVPR), pp 248–255
Wang Y, Feng H-Y (2015) Outlier detection for scanned point clouds using majority voting. Comput Aided Design 62:31–43
Lam L, Suen SY (1997) Application of majority voting to pattern recognition: an analysis of its behavior and performance. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern A., Syst Human 27(5):553–568. https://doi.org/10.1109/3468.618255
Shi J, Yan Q, Xu L, Jia J (2016) Hierarchical image saliency detection on extended cssd. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 38(4):717–729
Batra D, Kowdle A, Parikh D, Luo J, Chen T (2010) iCoseg: Interactive co-segmentation with intelligent scribble guidance. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (CVPR), pp 3169–3176
Jiang H, Wang J, Yuan Z, Wu Y, Zheng N, Li S (2013) Salient object detection: a discriminative regional feature integration approach. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (CVPR), pp 2083–2090
Dembczynski KJ, Waegeman W, Cheng W, Hüllermeier E (2011) An exact algorithm for f-measure maximization. In Proc. Adv. Neural Inf. Process Syst., pp 1404–1412
Liu T, Yuan Z, Sun J, Wang J, Zheng N, Tang X, Shum H (2011) Learning to detect a salient object. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 33(2):353–367
Acknowledgements
Alberto Lopez-Alanis and Marco A.Contreras-Cruz would like to acknowledge CONACYT for the financial support through the educational scholarships with numbers 718822 and 568675, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lopez-Alanis, A., Lizarraga-Morales, R.A., Contreras-Cruz, M.A. et al. Rule-based aggregation driven by similar images for visual saliency detection. Appl Intell 50, 1745–1762 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-019-01582-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-019-01582-6