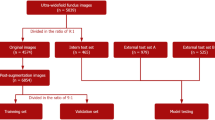
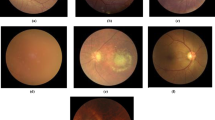
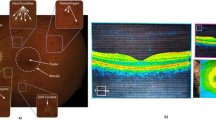
Abstract
Poor eye health is a major public health problem, and the timely detection and diagnosis of fundus abnormalities is important for eye health protection. Traditional imaging models can hinder the comprehensive evaluation of fundus abnormalities due to the use of a narrow field of view. The emerging ultrawide-field (UWF) imaging model surpasses this limitation in a non invasive, wide-view manner and is suitable for fundus observation and screening. Nevertheless, manual screening is labour intensive and subjective, especially in the absence of an ophthalmologist. Therefore, a set of auxiliary screening methods for a fundus screening service using a combination of deep learning and UWF imaging technology, which is designated as DeepUWF-Plus, is proposed. This service includes a subsystem for the screening of fundus, a subsystem for the identification of abnormalities regarding four important fundus locations, and a subsystem for the diagnosis of four retinal diseases that threaten vision. The influence of two-stage and one-stage classification strategies on the prediction performance of the model is experimentally investigated to alleviate severe class imbalance and similarity between classes, and evaluate the effectiveness and reliability of the system. Our experimental results show that DeepUWF-Plus is effective when using the two-stage strategy, especially for identifying signs or symptoms of minor diseases. DeepUWF-Plus can improve the practicality of fundus screening and enable ophthalmologists to provide more comprehensive fundus assessments.










Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
T. I. A. for the Prevention of Blindness (IAPB), Vision 2020. https://www.iapb.org/global-initiatives/vision-2020
Ting DSW, Cheung GCM, Wong TY (2016) Diabetic retinopathy: global prevalence, major risk factors, screening practices and public health challenges: a review. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 44(4):260–277
W. H. Organization, World report on vision. https://www.who.int/publicationsdetail/worldreportonvision
W. H. Organization, Universal eye health: a global action plan 2014-2019. https://www.who.int/blindness/actionplan/en
Li-xin, X. Some suggestions on prevention and treatment of blindness in china. Chin J Ophthalmol Med
M. Y. H., Diabetic retinopathy screening rate of less than 10% in china. Chin J Med Sci 3
The national plan for the prevention of blindness (2012-2015), Chinese Ministry of Health
Zhao J et al (2010) Prevalence of vision impairment in older adults in rural china: the China nine-province survey. Ophthalmology 117(3):409–416
Schmidt-Erfurth U, Sadeghipour A, Gerendas BS, Waldstein SM, Bogunović H (2018) Artificial intelligence in retina. Prog Retin Eye Res 67:1–29
Shi L, Wu H, Dong J, Jiang K, Lu X, Shi J (2015) Telemedicine for detecting diabetic retinopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Ophthalmol 99(6):823–831
He J, Baxter SL, Xu J, Xu J, Zhou X, Zhang K (2019) The practical implementation of artificial intelligence technologies in medicine. Nature Med 25(1):30–36
Bengio Y, Courville A, Vincent P (2013) Representation learning: A review and new perspectives. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(8):1798–1828
LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G (2015) Deep learning. Nature 521(7553):436
Yi Z (2010) Foundations of implementing the competitive layer model by lotka–volterra recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 21(3):494–507
Chen Y, Yi Z (2019) Locality-constrained least squares regression for subspace clustering. Knowl.-Based Syst 163:51–56
Chen D, Davies ME, Golbabaee M Compressive mr fingerprinting reconstruction with neural proximal gradient iterations. arXiv:2006.15271
Liang H, Tsui BY, Ni H, Valentim CC, Baxter SL, Liu G, Cai W, Kermany DS, Sun X, Chen J et al (2019) Evaluation and accurate diagnoses of pediatric diseases using artificial intelligence. Nature Med 25(3):433–438
Li Z, He Y, Keel S, Meng W, Chang RT, He M (2018) Efficacy of a deep learning system for detecting glaucomatous optic neuropathy based on color fundus photographs. Ophthalmology 125 (8):1199–1206
Gargeya R, Leng T (2017) Automated identification of diabetic retinopathy using deep learning. Ophthalmology 124(7):962–969
Pan SJ, Yang Q et al (2010) A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Transactions on knowledge and data engineering 22(10):1345–1359
Michalski RS, A theory and methodology of inductive learning (1983). In: Machine learning. Springer, pp 83–134
Rokach L (2010) Ensemble-based classifiers. Artif Intell Rev 33(1-2):1–39
Polikar R (2006) Ensemble based systems in decision making. IEEE Circ Syst Mag 6(3):21–45
Opitz D, Maclin R (1999) Popular ensemble methods: An empirical study. J Artif Intell Res 11:169–198
Aiello LP, Odia I, Glassman AR, Melia M, Jampol LM, Bressler NM, Kiss S, Silva PS, Wykoff CC, Sun JK (2019) Comparison of early treatment diabetic retinopathy study standard 7-field imaging with ultrawide-field imaging for determining severity of diabetic retinopathy. JAMA Ophthalmol 137 (1):65–73
Silva PS, Cavallerano JD, Sun JK, Noble J, Aiello LM, Aiello LP (2012) Nonmydriatic ultrawide field retinal imaging compared with dilated standard 7-field 35-mm photography and retinal specialist examination for evaluation of diabetic retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 154(3):549–559
Ohsugi H, Tabuchi H, Enno H, Ishitobi N (2017) Accuracy of deep learning, a machine-learning technology, using ultra–wide-field fundus ophthalmoscopy for detecting rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. Sci Rep 7(1):1–4
Nagiel A et al (2016) Ultra-widefield fundus imaging: a review of clinical applications and future trends. Retina 36(4):660–678
Silva PS, Horton MB, Clary D, Lewis DG, Sun JK, Cavallerano JD, Aiello LP (2016) Identification of diabetic retinopathy and ungradable image rate with ultrawide field imaging in a national teleophthalmology program. Ophthalmology 123(6):1360–1367
Abràmoff MD, Lou Y, Erginay A, Clarida W, Amelon R, Folk JC, Niemeijer M (2016) Improved automated detection of diabetic retinopathy on a publicly available dataset through integration of deep learning. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 57(13):5200–5206
Ting DSW, Cheung CY-L, Lim G, Tan GSW, Quang ND, Gan A, Hamzah H, Garcia-Franco R, San Yeo IY, Lee SY et al (2017) Development and validation of a deep learning system for diabetic retinopathy and related eye diseases using retinal images from multiethnic populations with diabetes. Jama 318 (22):2211–2223
Zhang W, Zhong J, Yang S, Gao Z, Hu J, Chen Y, Yi Z (2019) Automated identification and grading system of diabetic retinopathy using deep neural networks. Knowl.-Based Syst 175:12–25
Burlina P, Pacheco KD, Joshi N, Freund DE, Bressler NM (2017) Comparing humans and deep learning performance for grading amd: a study in using universal deep features and transfer learning for automated amd analysis. Comput Biol Med 82:80–86
Raghavendra U, Fujita H, Bhandary SV, Gudigar A, Tan JH, Acharya UR (2018) Deep convolution neural network for accurate diagnosis of glaucoma using digital fundus images. Inform Sci 441:41–49
Asaoka R, Murata H, Iwase A, Araie M (2016) Detecting preperimetric glaucoma with standard automated perimetry using a deep learning classifier. Ophthalmology 123(9):1974–1980
Topol EJ (2019) High-performance medicine: the convergence of human and artificial intelligence. Nature Med 25(1):44
Li Z, Guo C, Nie D, Lin D, Zhu Y, Chen C, Wu X, Xu F, Jin C, Zhang X et al (2020) Deep learning for detecting retinal detachment and discerning macular status using ultra-widefield fundus images. Commun Biol 3(1):1–10
Matsuba S, Tabuchi H, Ohsugi H, Enno H, Ishitobi N, Masumoto H, Kiuchi Y (2018) Accuracy of ultra-wide-field fundus ophthalmoscopy-assisted deep learning, a machine-learning technology, for detecting age-related macular degeneration. Int Ophthalmol 1–7
Nagasato D, Tabuchi H, Ohsugi H, Masumoto H, Enno H, Ishitobi N, Sonobe T, Kameoka M, Niki M, Mitamura Y (2019) Deep-learning classifier with ultrawide-field fundus ophthalmoscopy for detecting branch retinal vein occlusion. Int J Opthalmol 12(1):98–103
Nagasato D, Tabuchi H, Ohsugi H, Masumoto H, Enno H, Ishitobi N, Sonobe T, Kameoka M, Niki M, Hayashi K et al (2018) Deep neural network-based method for detecting central retinal vein occlusion using ultrawide-field fundus ophthalmoscopy. J Ophthalmol
Choi JY, Yoo TK, Seo JG, Kwak J, Um TT, Rim TH (2017) Multi-categorical deep learning neural network to classify retinal images: A pilot study employing small database. PloS One 12(11):e0187336
Fenner BJ, Wong RL, Lam WC, Tan GS, Cheung GC (2018) Advances in retinal imaging and applications in diabetic retinopathy screening: a review. Ophthalmol Ther 7(2):333–346
Lynch SK, Shah A, Folk JC, Wu X, Abramoff MD (2017) Catastrophic failure in image-based convolutional neural network algorithms for detecting diabetic retinopathy. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 58(8):3776–3776
Bagheri N, Wajda B, Calvo C, Durrani A (2016) The Wills eye manual: office and emergency room diagnosis and treatment of eye disease. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Chang JS, Smiddy WE (2014) Cost-effectiveness of retinal detachment repair. Ophthalmology 121(4):946–951
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China under Grant 2018AAA0100201, the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61702349, and the Sichuan Province Science and Technology Support Program 2019YFS0246.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Wei Zhang and Yan Dai are co-first authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Dai, Y., Liu, M. et al. DeepUWF-plus: automatic fundus identification and diagnosis system based on ultrawide-field fundus imaging. Appl Intell 51, 7533–7551 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02242-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02242-4