Abstract
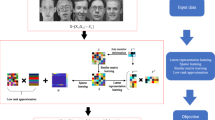
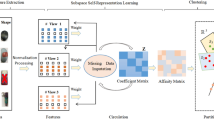
The kernel subspace clustering algorithm aims to tackle the nonlinear subspace model. The block diagonal representation subspace clustering has a more promising capability in pursuing the k-block diagonal matrix. Therefore, the low-rankness and the adaptivity of the kernel subspace clustering can boost the clustering performance, so an adaptive low-rank kernel block diagonal representation (ALKBDR) subspace clustering algorithm is put forward in this work. On the one hand, for the nonlinear nature of the practical visual data, a kernel block diagonal representation (KBDR) subspace clustering algorithm is put forward. The proposed KBDR algorithm first maps the original input space into the kernel Hilbert space which is linearly separable, and next applies the spectral clustering on the feature space. On the other hand, the ALKBDR algorithm uses the adaptive kernel matrix and makes the feature space low-rank to further promote the clustering performance. The experimental results on the Extended Yale B database and the ORL dataset have proved the excellent quality of the proposed KBDR and ALKBDR algorithm in comparison with other advanced subspace clustering algorithms that also are tested in this paper.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barik L (2020) Data mining approach for digital forensics task with deep learning techniques. Int J Adv Appl Sci 7(5):56–65
Cai S S, Zhang J (2020) Exploration of credit risk of P2P platform based on data mining technology. J Comput Appl Math:372
Elhamifar E, Vidal R (2009) Sparse subspace clustering. IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recogn:2790–2797
Elhamifar E, Vidal R (2013) Sparse subspace clustering: algorithm, theory, and applications. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(11):2765–2781
Elhamifar E, Vidal R (2010) Clustering disjoint subspaces via sparse representation. IEEE Int Conf Acoust Speech Signal Process:1926–1929
You C, Robinson D, Vidal R (2016) Scalable sparse subspace clustering by orthogonal matching pursuit. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit:3918–3927
Dyer E L, Studer C, Baraniuk R G (2013) Subspace clustering with dense representations. IEEE Int Conf Acoust Speech Signal Process:3258–3262
Ji P, Salzmann M, Li H (2014) Efficient dense subspace clustering. IEEE Winter Conf Appl Comput Vis:461–468
Favar P, Vidal R, Ravichandran A (2011) A closed form solution to robust subspace estimation and clustering. IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recogn:1801–1807
Vidal R, Favaro P (2014) Low rank subspace clustering (LRSC). Pattern Recogn Lett:47–61
Lu C Y, Min H, Zhao Z Q, Zhu L, Huang D S, Yan S (2012) Robust and efficient subspace segmentation via least squares regression. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, Berlin, pp 347–360
Bin C, Jianchao Y, Shuicheng Y, Yun F, Huang T S (2010) Learning with ℓ1-graph for image analysis. IEEE Trans Image Process 19(4):858–866
Liu G, Lin Z, Yu Y (2010) Robust subspace segmentation by low-rank representation. Proc 27th Int Conf Mach Learn:663–670
Liu G, Lin Z, Yan S, Sun J, Yu Y, Ma Y (2013) Robust recovery of subspace structures by low-rank representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(1):171–184
Chen Y, Li C G, You C (2020) Stochastic sparse subspace clustering. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recogn:4155–4164
Xu J, Xu K, Chen K, Ruan J S (2015) Reweighted sparse subspace clustering. Comput Vis Image Underst 138:25–37
Dong W, Wu X J, Kittler J (2019) Sparse subspace clustering via smoothed ℓp minimization. Pattern Recognit Lett 125:206–211
Dong W, Wu X J (2019) Robust affine subspace clustering via smoothed ℓ0-norm. Neural Process Lett 50(1):785–797
Lu C, Feng J, Lin Z, Yan S (2013) Correlation adaptive subspace segmentation by trace lasso. Proc IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis:1345–1352
Li C G, You C, Vidal R (2017) Structured sparse subspace clustering: a joint affinity learning and subspace clustering framework. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(6):2988–3001
Li C G, Vidal R (2015) Structured sparse subspace clustering: a unified optimization framework. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recogn:277–286
Li C G, Vidal R (2016) A structured sparse plus structured low-rank framework for subspace clustering and completion. IEEE Trans Signal Process 64(24):6557–6570
Patel V M, Vidal R (2014) Kernel sparse subspace clustering. IEEE Int Conf Image Process:2849–2853
Patel V M, Nguyen H V, Vidal R (2015) Latent space sparse and low-rank subspace clustering. IEEE J Sel Top Signal Process 9(4):691–701
Patel V M, Nguyen H V, Vidal R (2013) Latent space sparse subspace clustering. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision
Ji P, Reid I, Garg R, et al. (2017) Adaptive low-rank kernel subspace clustering. arXiv:1707.04974v4
Xiao S, Tan M, Xu D, et al. (2016) Robust kernel low-rank representation. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 27(11):2268–2281
Hu W B, Wu X J (2020) Multi-geometric sparse subspace clustering. Neural Process Lett:11
Peng C, Kang Z, Xu F, Chen Y, Cheng Q (2017) Image projection ridge regression for subspace clustering. IEEE Signal Process Lett 24(7):991–995
Peng C, Zhang Q, Kang Z, Chen C, Cheng Q (2020) Kernel two-dimensional ridge regression for subspace clustering. Pattern Recogn:107749
Zhen L, Peng D, Wang W, Yao X (2020) Kernel truncated regression representation for robust subspace clustering. Information Sciences
Li Z, Liu J, Yang Y, Zhou X, Lu H (2014) Clustering-guided sparse structural learning for unsupervised feature selection. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 26(9):2138–2150
Chen H, Wang W, Feng X (2018) Structured sparse subspace clustering with within-cluster grouping. Pattern Recognit 83:107–118
Chen H, Wang W, Feng X, He R (2018) Discriminative and coherent subspace clustering. Neurocomputing 284:177–186
Lu C, Feng J, Lin Z, Mei T, Yan S (2019) Subspace clustering by block diagonal representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 41(2):487–501
Zhang Z, Xu Y, Shao L, Yang J (2018) Discriminative block-diagonal representation learning for image recognition. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 29(7):3111–3125
Xie X, Guo X, Liu G, Wang J (2018) Implicit block diagonal low-rank representation. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(1):477– 489
Wang L, Huang J, Yin M, Cai R, Hao Z (2020) Block diagonal representation learning for robust subspace clustering. Inf Ences:526
Georghiades A S, Belhumeur P N, Kriegman D J (2001) From few to many: illumination cone models for face recognition under variable lighting and pose. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 6:643–660
Samaria F S, Harter A C (1994) Parameterisation of a stochastic model for human face identification. In: Proceedings of 1994, IEEE workshop on applications of computer vision. IEEE, pp 138–142
Ji P, Zhang T, Li H, Salzmann M (2017) Deep subspace clustering networks. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst:24–33
Lin Z, Chen M, Wu L, Ma Y (2010) The augmented lagrange multiplier method for exact recovery of corrupted low-rank matrices. arXiv:1009.5055
Liu M, Wang Y, Sun J, Ji Z (2020) Structured block diagonal representation for subspace clustering. Appl Intell 50(8):2523–2536
Liu X, Zhu X, Li M, et al. (2019) Multiple kernel k-means with incomplete kernels. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 42(5):1191–1204
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Project Number: 2018YFB1701903) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project Numbers: 61973138, 61672263).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Wang, Y., Sun, J. et al. Adaptive low-rank kernel block diagonal representation subspace clustering. Appl Intell 52, 2301–2316 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02396-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02396-1