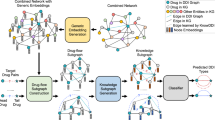
Abstract
Drug repositioning, which recommends approved drugs to potential targets by predicting drug-target interactions (DTIs), can save the cost and shorten the period of drug development. In this work, we propose a novel knowledge graph based deep learning method, named KG-DTI, for DTIs predictions. Specifically, a knowledge graph of 29,607 positive drug-target pairs is constructed by DistMult embedding strategy. A Conv-Conv module is proposed to extract features of drug-target pairs (DTPs), which is followed by a fully connected neural network for DTIs calculation. Data experiments are conducted on randomly chosen 11,840 positive and negative samples. It is obtained that KG-DTI achieves average ACC by 88.0%, F1-Score by 87.7%, AUROC by 94.3% and AUPR by 95% in five-fold cross-validation. In practice, KG-DTI is applied to reposition drugs to Alzheimer’s disease (AD) by Apolipoprotein E target. As results, it is found that seven of the top ten recommended drugs have been used in clinic practice or with literature supported useful to AD. Ligand-target docking results show that the top one recommended drug can dock with Apolipoprotein E significantly, which gives vital hints in repositioning potential drug to AD treatment.











Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Avorn J, (2015) The $2.6 billion pill–Methodologic and policy considerations
Schneider P, Walters WP, Plowright (2019) Rethinking drug design in the artificial intelligence era. Nat Rev Drug Discov:1–12
Kapetanovi I (2008) Computer-aided drug discovery and development: in Silico Chemico-biological approach. Chem Biol Interact 171:165–176
Zanni R, Galvez-Llompart M, Galvez J (2014) Qsar multi-target in drug discovery: a review. Current Computer-Aided Drug Design 10:129–136
Luo Y, Zhao X, Zhou J (2017) A network integration approach for drug-target interaction prediction and computational drug repositioning from heterogeneous information. Nat Commun 8:1–13
Zheng L, Fan J, Mu Y (2019) Onionnet: a multiple-layer intermolecular contact based convolutional neural network for protein-ligand binding affinity prediction. Acs Omega 4:15956–15965
Mohamed SK, Nováček V, Nounu A (2020) Discovering protein drug targets using knowledge graph Embeddings. Bioinformatics 36:603–610
Lin X, Quan Z, Wang Z-J (2020) KGNN: Knowledge Graph Neural Network For Drug-Drug Interaction Prediction
Zeng X, Song X, Ma T, Pan X, Zhou Y, Hou Y, Zhang Z, Li K, Karypis G, Cheng F (2020) Repurpose open data to discover therapeutics for Covid-19 using deep learning. J Proteome Res 19:4624–4636. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.0c00316
Zhang X, Yang Y, Li T, et al. (2020) CMC: a consensus multi-view clustering model for predicting Alzheimer's disease progression[J]. Comput Methods Prog Biomed, 105895
Buza K, Peka L, Koller J (2020) Modified linear regression predicts drug-target interactions accurately[J]. PLoS ONE 15(4):e0230726
Yang B, Yih WT (2014) Embedding entities and relations for learning and inference in knowledge bases. Arxiv Preprint Arxiv 1412:6575
Trouillon T, Welbl J, Riedel S (2016) Complex embedding for simple link prediction, international conference on machine learning, 213–218
Bordes A, Usunier N, Garcia-Duran A (2013) Translating embedding for modeling multi-relational data, Adv Neural Inf Proces Syst 2787–2795
Nickel M, Tresp V, Kriegel HP (2011) A three-way model for collective learning on multi-relational data, in proceeding of ICML, 809–816
Fangping W , Lixiang H , An X, et al. (2018) NeoDTI: neural integration of neighbor information from a heterogeneous network for discovering new drug-target interactions[J]. Bioinformatics
Wishart DS, Feunang YD, Guo AC (2018) Drugbank 5.0: a major update to Drugbank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res 46:D1074–D1082
Szegedy C, Jia Y. (2015) Going deeper with convolutions, in proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 1-9
Ioffe S, Szegedy C (2015) Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. Arxiv Preprint Arxiv 1502:03167
Szegedy C, Vanhoucke V, Ioffe S, (2016) Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision, Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit, 2818-2826
Szegedy C, Ioffe S, Vanhoucke V (2016) Inception-V4, inception-Resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. Arxiv preprint arxiv:1602.07261
Nair V, Hinton GE. (2010) Rectified linear units improve restricted Boltzmann machines, in proceeding of ICML, 326-329
Duchi J, Hazan E, (2011) Adaptive subgradient methods for online learning and stochastic optimization. J Mach Learn Res, 12
Wang S, Liu D, Ding M, Du Z, Zhong Y, Song T, Zhu J, Zhao R (2021) SE-OnionNet: a convolution neural network for protein–ligand binding affinity prediction. Front Genet 11:607824. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.60782
Song T, Zheng P, Dennis Wong ML, Min J, Zeng X (2020) On the computational power of asynchronous axon membrane systems. IEEE Trans Emerg Top Comput Intell 4(5):696–704
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45(1):5–32
Xu H, Gupta V (2015) Zinc affects the proteolytic stability of Apolipoprotein E in an isoform-dependent way. Neurobiol Dis 81:38–48
Cao C, Li Y, Liu H (2014) The potential therapeutic effects of Tec on Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Alzheimer disease 42:973–984
Zhao X, Li S, Gaur U (2020) Artemisinin improved neuronal functions in Alzheimer’s disease animal model 3xtg mice and neuronal cells via stimulating the Erk/Creb signaling pathway. Aging Dis 11:801–819
Wang S, Du Z, Ding M, Zhao R, Rodríguez-Patón A, Song T (2020) LDCNN-DTI: A Novel Light Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Drug-Target Interaction Predictions. BIBM:1132–1136
Song T, Zhong Y, Ding M, Zhao R, Tian Q, Du Z, Liu D, Liu J, Deng Y (2020) Repositioning molecules of Chinese medicine to targets of SARS-Cov-2 by deep learning method. BIBM 2021:2306–2312
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61873280, 61972416), Taishan Scholarship (tsqn201812029), Major projects of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41890851), Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2019MF012), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (19CX05003A-6).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Du, Z., Ding, M. et al. KG-DTI: a knowledge graph based deep learning method for drug-target interaction predictions and Alzheimer’s disease drug repositions. Appl Intell 52, 846–857 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02454-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02454-8