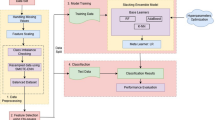
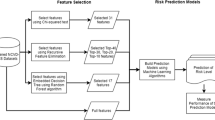
Abstract
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is one of the most lethal diseases which is major cause of deaths around the globe. CAD is among such diseases with mortality rate approximately 7 million per annum. Though, early detection, prognostication and timely diagnosis can help in mortality rate reduction. Conventional CAD detection systems are cumbersome and expensive. Moreover, scarcity or uneven distribution of radiologists in different geographical locations is a hindrance in early diagnosis. Therefore, this is the time when researchers and doctors are collaboratively looking forward for developing a computational intelligence system in the area of medical imaging systems for prognostication, identification, treatment and disease diagnosis. To support the vision of researchers, a computational intelligence system for coronary artery disease diagnosis, C-CADZ, has been proposed. To validate the model, C-CADZ, the dataset namely, Z-Alizadeh Sani CAD dataset from UCI repository is considered. C-CADZ utilizes the fixed analysis of mixed data (FAMD) for feature extraction. FAMD extracts 96 features. In order to retrieve significant features, nature-inspired algorithms are utilized. C-CADZ implemented Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique (SMOTE) to handle class-imbalanced data as machine learning (ML) predictive models are built to handle class-balanced datasets. Z-Score normalization technique is used for normalizing the dataset. Furthermore, C-CADZ is trained using ML classifiers, Random Forest (RF) and Extra Trees (ET) and validated using holdout validation scheme with hold-out ratio 3 : 1. Experimentation results show that C-CADZ outperforms state-of-the-art methods of last decades in terms of accuracy. C-CADZ has gained an increase in accuracy from state-of-the-art methods published in 2020 by 5.17% with performance metric 〈Acc, Sens, Spec〉≡〈97.37, 98.15, 95.45〉. The performance analysis shows that achieving highest accuracy and the stable nature of boxplot and ROC-AUC curve of RF-ET makes it suitable for heart disease prediction.














Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
The henry j (2019) kaiser family foundation, snapshots: Comparing projected growth in health care expenditures and the economy. Accessed on : July 25, 2019. Kff.org
World health organization (2019) WHO. Accessed on : July 25, 2019. https://www.who.int
WHO (2019) The top 10 causes of death. Accessed on : July 25, 2019. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death
WHO (2019) Global health observatory (GHO) data. Accessed on : July 25, 2019. https://www.who.int/gho/mortality_burden_disease/causes_death/top_10/en/
European coordination committee of the radiological, electromedical, and healthcare it industry: Medical imaging equipment age profile and density. Accessed on : July 25, 2019. http://www.cocir.org/uploads/media/16052_COC_AGE_PROFILE_web_01.pdf
Organisation for economic co-operation and development (OECD): Medical technologies, in health at a glance 2015. Accessed on : July 25, 2019. http://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/social-issues-migration-health/health-at-a-glance-2015/medical-technologies_health_glance-2015-31-en
Tirkes T, Hollar MA, Tann M, Kohli MD, Akisik F, Sandrasegaran K (2013) Response criteria in oncologic imaging: Review of traditional and new criteria. RadioGraphics 33(5):1323–1341. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.335125214
Torrisi JM, Schwartz LH, Gollub MJ, Ginsberg MS, Bosl GJ, Hricak H (2011) CT findings of chemotherapy-induced toxicity: What radiologists need to know about the clinical and radiologic manifestations of chemotherapy toxicity. Radiology 258(1):41–56. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.10092129
Computer learns to detect skin cancer more accurately than doctors. accessed on : July 25, 2019. https://www.theguardian.com/society/2018/may/29/skin-cancer-computer-learns-to-detect-skin-cancer-more-accurately-than-a-doctor/
Google’s lung cancer detection AI outperforms 6 human radiologists. Accessed on : July 25, 2019. https://venturebeat.com/2019/05/20/googles-lung-cancer-detection-ai-outperforms-6-human-radiologists/
Google AI better than doctors at detecting breast cancer. Accessed on : July 25, 2019. https://www.sciencefocus.com/news/google-ai-better-than-doctors-at-detecting-breast-cancer/
Davie AP, Francis CM, Love MP, Caruana L, Starkey IR, Shaw TRD, Sutherland GR, McMurray JJV (1996) Value of the electrocardiogram in identifying heart failure due to left ventricular systolic dysfunction. BMJ: Bri Med J 312(7025):222–222
Marinho LB, deM.M.Nascimento N, Souza J WM, Gurgel MV, Filho] P PR, [de Albuquerque] V HC (2019) A novel electrocardiogram feature extraction approach for cardiac arrhythmia classification. Fut Gener Comput Syst 97:564–577
Deng S-W, Han J-Q (2016) Towards heart sound classification without segmentation via autocorrelation feature and diffusion maps. Fut Gener Comput Syst 60:13–21
Leung DY, Davidson PM, Cranney GB, Walsh WF (1997) Thromboembolic risks of left atrial thrombus detected by transesophageal echocardiogram. Am J Cardiol 79(5):626–629
Wyman RM, Safian RD, Portway V, Skillman JJ, McKAY RG, Baim DS (1988) Current complications of diagnostic and therapeutic cardiac catheterization. J Am Coll Cardiol 12(6):1400–1406
Rajkumar G, Jayabharathy R, Narasimhan K, Raju N, Easwaran M, Elamaran V, Ramirez-Gonzalez G, Burbano-Fernandez M (2019) Spectral and snr improvement analysis of normal and abnormal heart sound signals using different windows. Fut Gener Comput Syst 92:438–443
Dongdong J, Arunkumar N, Wenyu Z, Beibei L, Xinlei Z, Guangjian Z (2019) Semantic clustering fuzzy C means spectral model based comparative analysis of cardiac color ultrasound and electrocardiogram in patients with left ventricular heart failure and cardiomyopathy. Fut Gener Comput Syst 92:324–328
Brenner DJ, Hall EJ (2007) Computed tomography–an increasing source of radiation exposure. N. Engl. J. Med. 357(22):2277–2284
Nandalur KR, Dwamena BA, Choudhri AF, Nandalur MR, Carlos RC (2007) Diagnostic performance of stress cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in the detection of coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 50(14):1343–1353
Kuchar DL, Thorburn CW, Sammel NL (1987) Prediction of serious arrhythmic events after myocardial infarction: signal-averaged electrocardiogram, Holter monitoring and radionuclide ventriculography. J Am Coll Cardiol 9(3):531–538
Rajpal S, Alshawabkeh L, Opotowsky AR (2017) Current role of blood and urine biomarkers in the clinical care of adults with congenital heart disease. Cur Cardiol Rep 19(6):50
Alizadehsani R, Hosseini MJ, Khosravi A, Khozeimeh F, Roshanzamir M, Sarrafzadegan N, Nahavandi S (2018) Non-invasive detection of coronary artery disease in high-risk patients based on the stenosis prediction of separate coronary arteries. Comput Methods Program Biomed 162:119–127
Uci machine learning repository, center for machine learning and intelligent systems (2017). Accessed on : Feb 2, 2020. https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/00412/
Joloudari JH, Joloudari EH, Saadatfar H, GhasemiGol M, Razavi SM, Mosavi A, Nabipour N, Shamshirband S, Nadai L (2020) Coronary artery disease diagnosis; ranking the significant features using a random trees model. Int J Environ Rese Publ Health 17(3):731
Alizadehsani R, Habibi J, Sani ZA, Mashayekhi H, Boghrati R, Ghandeharioun A, Bahadorian B (2012) Diagnosis of Coronary Artery Disease Using Data mining based on Lab Data and Echo Features. J Med Bioeng 1(1)
Alizadehsani R, Hosseini MJ, Boghrati R, Ghandeharioun A, Khozeimeh F, Sani ZA (2012) Exerting Cost-Sensitive and Feature Creation Algorithms for Coronary Artery Disease Diagnosis. Int J Know Dis Bioinfo (IJKDB) 3(1):59–79
Alizadehsani R, Hosseini MJ, Sani ZA, Ghandeharioun A, Boghrati R (2012) Diagnosis of coronary artery disease using cost-sensitive algorithms. In: IEEE 12th Int. Conf. Data Mining Workshops. IEEE, pp 9–16
Alizadehsani R, Habibi J, Hosseini MJ, Boghrati R, Ghandeharioun A, Bahadorian B, Sani ZA (2012) Diagnosis of coronary artery disease using data mining techniques based on symptoms and ecg features. Eur J Sci Res 82(4):542–553
Alizadehsani R, Habibi J, Sani ZA, Mashayekhi H, Boghrati R, Ghandeharioun A, Khozeimeh F, Alizadeh-Sani F (2013) Diagnosing coronary artery disease via data mining algorithms by considering laboratory and echocardiography features. Res Cardiov Med 2(3):133
Alizadehsani R, Habibi J, Hosseini MJ, Mashayekhi H, Boghrati R, Ghandeharioun A, Bahadorian B, Sani ZA (2013) A data mining approach for diagnosis of coronary artery disease. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 111(1):52–61
Alizadehsani R, Zangooei MH, Hosseini MJ, Habibi J, Khosravi A, Roshanzamir M, Khozeimeh F, Sarrafzadegan N, Nahavandi S (2016) Coronary artery disease detection using computational intelligence methods. Know Based Sys 109:187–197
Arabasadi Z, Alizadehsani R, Roshanzamir M, Moosaei H, Yarifard AA (2017) Computer aided decision making for heart disease detection using hybrid neural network-Genetic algorithm. Comput Methods Program Biomed 141:19–26
Nasarian E, Abdar M, Fahami MA, Alizadehsani R, Hussain S, Basiri ME, Zomorodi-Moghadam M, Zhou X, Pławiak P, Acharya UR et al (2020) Association between work-related features and coronary artery disease: a heterogeneous hybrid feature selection integrated with balancing approach. Pattern Recognition Letters
Abdar M, Ksiazek W, Acharya UR, Tan R-S, Makarenkov V, Plawiak P (2019) A new machine learning technique for an accurate diagnosis of coronary artery disease. Comput Methods Program Biomed 179:104992
Yadav C, Lade S, Suman MK (2014) Predictive analysis for the diagnosis of coronary artery disease using association rule mining. Int J Comp Appl 87(4)
Kolukısa B, Hacılar H, Kuş M, Bakır-Güngör B, Aral A, Güngör VC (2019) Diagnosis of coronary heart disease via classification algorithms and a new feature selection methodology. Int J Data Min Sci 1(1):8–15
Gokulnath CB, Shantharajah SP (2019) An optimized feature selection based on genetic approach and support vector machine for heart disease. Clust Comput 22(6):14777–14787
Jayaraman V, Sultana HP (2019) Artificial gravitational cuckoo search algorithm along with particle bee optimized associative memory neural network for feature selection in heart disease classification. J Ambient Intell Hum Comput:1–10
Harimoorthy K, Thangavelu M (2020) Multi-disease prediction model using improved svm-radial bias technique in healthcare monitoring system. J Ambient Intell Hum Comput:1–9
Sowmiya C, Sumitra P (2020) A hybrid approach for mortality prediction for heart patients using aco-hknn. J Ambient Intell Hum Comput
Selvi RT, Muthulakshmi I (2020) An optimal artificial neural network based big data application for heart disease diagnosis and classification model. J Ambient Intell Hum Comput:1–11
Paul AK, Shill PC, Rabin M RI, Murase K (2018) Adaptive weighted fuzzy rule-based system for the risk level assessment of heart disease. Appl Intell 48(7):1739–1756
Ahmed H, Younis EMG, Hendawi A, Ali AA (2020) Heart disease identification from patients social posts, machine learning solution on spark. Futur Gener Comput Syst 111:714–722
Nilashi M, Ahmadi H, Manaf AA, Rashid TA, Samad S, Shahmoradi L, Aljojo N, Akbari E (2020) Coronary heart disease diagnosis through self-organizing map and fuzzy support vector machine with incremental updates. Int J Fuzzy Syste:1–13
Ghiasi MM, Zendehboudi S, Mohsenipour AA (2020) Decision tree based diagnosis of coronary artery disease: Cart model. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 192:105400
Ashish L, Kumar S, Yeligeti S (2021) Ischemic heart disease detection using support vector machine and extreme gradient boosting method. Materials Today: Proceedings
Velusamy D, Ramasamy K (2021) Ensemble of heterogeneous classifiers for diagnosis and prediction of coronary artery disease with reduced feature subset. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 198:105770
Sani Z-A (2019) Z-alizadeh sani data set, uci machine learning repository, center for machine learning and intelligent systems, 2017; Accessed on : July 25, 2019. https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Z-Alizadeh+Sani
López-Sendón J (2011) The heart failure epidemic. Medicographia 33:363–369
Allen LA et al (2012) Decision making in advanced heart failure. Circulation 125(15):1928–1952
Pagès J (2014) Multiple factor analysis by example using r. CRC Press
Houck CR, Joines J, Kay MG (1995) A genetic algorithm for function optimization: a matlab implementation. Ncsu-ie tr 95(09):1–10
Schmitt LM (2001) Theory of genetic algorithms. Theor Comput Sci 259 (1):1–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3975(00)00406-0, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304397500004060
El-Maleh AH, Sheikh AT, Sait SM (2013) Binary particle swarm optimization (bpso) based state assignment for area minimization of sequential circuits. Appl Soft Comput 13(12):4832–4840
Rodrigues D, Pereira L AM, Almeida T NS, Papa JP, Souza AN, Ramos C CO, Yang X (2013) Bcs: A binary cuckoo search algorithm for feature selection. In: 2013 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), pp 465–468
Yang X-S (2009) Firefly algorithms for multimodal optimization. In: International symposium on stochastic algorithms. Springer, pp 169–178
Palit S, Sinha SN, Molla MA, Khanra A, Kule M (2011) A cryptanalytic attack on the knapsack cryptosystem using binary firefly algorithm. In: 2011 2nd International conference on computer and communication technology (ICCCT-2011). IEEE, pp 428–432
Nakamura RYM, Pereira LAM, Costa KA, Rodrigues D, Papa JP, Yang X-S (2012) Bba: a binary bat algorithm for feature selection. In: 2012 25th SIBGRAPI conference on graphics, Patterns and Images. IEEE, pp 291–297
Rashedi E, Nezamabadi-Pour H, Saryazdi S (2010) Bgsa: binary gravitational search algorithm. Nat Comput 9(3):727–745
Mafarja MM, Eleyan D, Jaber I, Hammouri A, Mirjalili S (2017) Binary dragonfly algorithm for feature selection. In: 2017 International Conference on New Trends in Computing Sciences (ICTCS). IEEE, pp 12–17
Griffin DR, Webster FA, Michael CR (1960) The echolocation of flying insects by bats. Anim Behav 8(3):141–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-3472(60)90022-1
Metzner W (1991) Echolocation behaviour in bats. Sci Prog:453–465
Schnitzler HU, Kalko E KV (2001) Echolocation by Insect Eating Bats: We define four distinct functional groups of bats and find differences in signal structure that correlate with the typical echolocation tasks faced by each group. Bioscience 51(7):557–569. https://doi.org/10.1641/0006-3568(2001)051[0557:EBIEB]2.0.CO;2
Yang X-S (2011) Bat algorithm for multi-objective optimisation. Int J Bio-Inspir Comput 3 (5):267–274
Yang X-S, Deb S (2009) Cuckoo search via lévy flights. In: 2009 World congress on nature & biologically inspired computing (NaBIC). IEEE, pp 210–214
Kennedy J, Eberhart R (1995) Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of ICNN’95-International Conference on Neural Networks, vol 4. IEEE, pp 1942–1948
Chawla NV, Bowyer KW, Hall LO, Kegelmeyer WP (2002) Smote: synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J Artif Intell Res 16:321–357
Bowyer KW, Chawla NV, Hall LO, Kegelmeyer WP (2011) SMOTE: synthetic minority over-sampling technique. CoRR, arXiv:1106.1813
Han H, Wang W-Y, Mao B-H (2005) Borderline-smote: A new over-sampling method in imbalanced data sets learning. In: Advances in Intelligent Computing. Springer, Berlin, pp 878–887
M. NH, W. CE, Katsuari K (2009) Borderline over-sampling for imbalanced data classification. In: 5th international workshop on computational intelligence & applications ieee smc hiroshima chapter :IWCIA, pp 24–29
Haibo He, Yang Bai, Garcia EA, Shutao Li (2008) Adasyn: Adaptive synthetic sampling approach for imbalanced learning. In: IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence), pp 1322–1328
Gupta A, Kumar R, Singh Arora H, Raman B (2020) Mifh: A machine intelligence framework for heart disease diagnosis. IEEE Access 8:14659–14674. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2962755
Zweig MH, Campbell G (1993) Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) plots: a fundamental evaluation tool in clinical medicine. Clin Chem 39(4):561–577
Qin C-J, Guan Q, Wang X-P (2017) Application of ensemble algorithm integrating multiple criteria feature selection in coronary heart disease detection. Biomed Eng Appl Basis Commun 29(06):1750043
Khan Y, Qamar U, Asad M, Zeb B (2019) Applying feature selection and weight optimization techniques to enhance artificial neural network for heart disease diagnosis. In: Proc. SAI Intelligent Systems Conf. Springer, pp 340–351
Abdar M, Acharya UR, Sarrafzadegan N, Makarenkov V (2019) Ne−nu −svc: A new nested ensemble clinical decision support system for effective diagnosis of coronary artery disease. IEEE Access 7:167605–167620
Funding
There is no funding provided in the course of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. All the database is acquired from the public logging system (Internet source) whose appropriate references are added in the sections above.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The authors Ankur Gupta and Rahul Kumar contributed equally in this manuscript
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, A., Kumar, R., Arora, H.S. et al. C-CADZ: computational intelligence system for coronary artery disease detection using Z-Alizadeh Sani dataset. Appl Intell 52, 2436–2464 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02467-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02467-3