Abstract
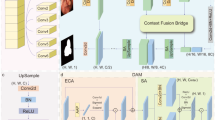
The encoder-decoder CNN architecture has greatly improved CT medical image segmentation, but it encounters a bottleneck due to the loss of details in the encoding process, which limits the accuracy improvement. To address this problem, we propose a multi-scale context-attention network (MC-Net). The key idea is to explore the useful information across multiple scales and the context for the segmentation of objects of medical interest. Through the introduction of multi-scale and context-attention modules, MC-Net gains the ability to extract local and global semantic information around targets. To further improve the segmentation accuracy, we weight the pixels depending on whether they belong to targets. Many experiments on a lung dataset and a bladder dataset demonstrate that the proposed MC-Net outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of accuracy, sensitivity, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve and the Dice score.









Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Soliman A et al (2017) Accurate Lungs Segmentation on CT Chest Images by Adaptive Appearance-Guided Shape Modeling. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 36(1):263–276
Song J et al (2016) Lung Lesion Extraction Using a Toboggan Based Growing Automatic Segmentation Approach. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35(1):337–353
Akter O, Moni MA, Islam MM et al (2020) Lung cancer detection using enhanced segmentation accuracy. Applied https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-02046-y
Jiang J et al (2019) Multiple Resolution Residually Connected Feature Streams for Automatic Lung Tumor Segmentation From CT Images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 38(1):134–144
Fehri H, Gooya A, Lu Y, Meijering E, Johnston SA, Frangi AF (2019) Bayesian Polytrees With Learned Deep Features for Multi- Class Cell Segmentation. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(7):3246– 3260
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox TN (2015) Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Paper presented at International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-assisted Intervention, Springer, pp 234–241
Drozdzal M, Chartrand G, Orontsov EV, Shakeri M, Jorioc LD, Tang A et al (2018) Learning normalized inputs for iterative estimation in medical image segmentation. Med Image Anal 44:1–13
Liskowski P, Krawiec K (2016) Segmenting retinal blood vessels with deep neural networks. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35(11):2369–2380
Ben Abdallah M, Azar A, Guedri H et al (2018) Noise-estimation-based anisotropic diffusion approach for retinal blood vessel segmentation. Neural Comput Appl 29:159–180
Esteva A, Kuprel B, Novoa RA, Ko J, Swetter SM, Blau HM et al (2017) Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature 542(7639):115–118
Pereira S, Pinto A, Alves V, Silva CA (2016) Brain Tumor Segmentation Using Convolutional Neural Networks in MRI Images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35(5):1240–1251
Tuan TM, Ngan TT, Son LH (2016) A novel semi-supervised fuzzy clustering method based on interactive fuzzy satisficing for dental x-ray image segmentation. Appl Intell 45:402–428
Zhang S, You Z, Wu X (2019) Plant disease leaf image segmentation based on superpixel clustering and EM algorithm. Neural Comput Appl 31:1225–1232
Cheng H, Zhang X, Yu J (2016) AC-coefficient histogram-based retrieval for encrypted JPEG images. Multimed Tools Appl 75:13791–13803
Satapathy SC, Sri Madhava Raja N, Rajinikanth V et al (2018) Multi-level image thresholding using Otsu and chaotic bat algorithm. Neural Comput Appl 29:1285–1307
Punarselvam E, Suresh P (2019) Investigation on human lumbar spine MRI image using finite element method and soft computing techniques. Clust Comput 22:13591–13607
Liu L, Chen J, Fieguth P et al (2019) From BoW to CNN: Two Decades of Texture Representation for Texture Classification. Int J Comput Vis 127:74–109
Hannane R, Elboushaki A, Afdel K et al (2016) An efficient method for video shot boundary detection and keyframe extraction using SIFT-point distribution histogram. Int J Multimed Inf Retriev 5:89–104
Chen X, Pan L (2018) A Survey of Graph Cuts/Graph Search Based Medical Image Segmentation. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng 11:112–124
Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T (2015) Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of IEEE Int. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit(CVPR), pp 3431–3440
Chen L, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, Murphy K, Yuille AL (2018) DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 40(4):834–848
Milletari F, Navab N, Ahmadi SA (2016) V-Net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In: 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision(3DV). IEEE, pp 565–571
Zhou Z, Siddiquee MMR, Tajbakhsh N, Liang J (2018) UNet++: A Nested U-Net Architecture for Medical Image Segmentation. In: 4th Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis (DLMIA) Workshop, Granada, DLMIA 2018, LNCS, vol 11045, pp 3–11
Schlemper J, Oktay O, Schaap M, Heinrich M, Kainz B, Glocker B et al (2019) Attention gated networks: Learning to leverage salient regions in medical images. Med Image Anal 53:197–207
Alom MZ, Yakopcic C, Taha TM, Asari VK (2018) Nuclei Segmentation with Recurrent Residual Convolutional Neural Networks based U-Net (R2U-Net). NAECON 2018 - IEEE National Aerospace and Electronics Conference, pp 228–233
Xiao X, Lian S, Luo Z, Li S (2018) Weighted Res-UNet for High-Quality Retina Vessel Segmentation. In: 2018 9th International Conference on Information Technology in Medicine and Education (ITME). IEEE, pp 327–331
Guan S, Khan AA, Sikdar S, Chitnis PV (2020) Fully Dense UNet for 2-D Sparse Photoacoustic Tomography Artifact Removal. IEEE J Biomed Health Inf 24(2):568–576
Ibtehaz N, Rahman MS (2020) MultiResUNet: Rethinking the U-Net Architecture for Multimodal Biomedical Image Segmentation. Neural Netw 121:74–87
Zhao H, Shi J, Qi X, Wang X, Jia J (2019) Pyramid Scene Parsing Network. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, pp 6230– 6239
Chen LC, Zhu Y, Papandreou G, Schroff F, Adam H (2018) Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. In: Ferrari V, Hebert M, Sminchisescu C, Weiss Y (eds), vol 11211. Springer, Cham, pp 833– 851
He K, Gkioxari G, Dollr P, Girshick R (2017) Mask R-CNN. In IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, pp 2980–2988
Szegedy C et al (2015) Going deeper with convolutions. In: 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, pp 1–9
Szegedy C, Vanhoucke V, Ioffe S, Shlens J, Wojna Z (2016) Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, pp 2818–2826
Vo DM, Lee SW (2018) Semantic image segmentation using fully convolutional neural networks with multi-scale images and multi-scale dilated convolutions. Multimed Tools Appl 77:18689– 18707
Jiang Y, Tan N, Peng T, Zhang H (2019) Retinal Vessels Segmentation Based on Dilated Multi-Scale Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Access 7:76342–76352
Liu Y, Xu C, Chen Z et al (2020) Deep Dual-Stream Network with Scale Context Selection Attention Module for Semantic Segmentation. Neural Process Lett 51:2281–2299
Zhu H, Wang B, Zhang X et al (2020) Semantic image segmentation with shared decomposition convolution and boundary reinforcement structure. Appl Intell 50:2676–2689
Gu Z, Cheng J, Fu H, Zhou K, Hao H, Zhao Y et al (2019) CE-Net: context encoder network for 2D medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 38(10):2281–2292
Hu S, Zhang J, Xia Y (2020) Boundary-Aware Network for Kidney Tumor Segmentation. In: Liu M, Yan P, Lian C, Cao X (eds) Machine Learning in Medical Imaging. MLMI 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 12436. Springer, Cham, pp 189–198
Feng S et al (2020) CPFNet: Context Pyramid Fusion Network for Medical Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(10):3008–3018
Zhang J, Xie Y, Wang Y, Xia Y (2020) Inter-slice Context Residual Learning for 3D Medical Image Segmentation. In: IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging(Early Access), pp 1–1
Zhang Q, Jiang Z, Lu Q, Han J, Zeng Z, Gao S, Men A (2020) Split to Be Slim: An Overlooked Redundancy in Vanilla Convolution. In International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence 2020 (IJCAI), Yokohama. arXiv:2006.12085
Szegedy C, Ioffe S, Vanhoucke V, Alemi A (2016) Inception-v4, Inception-ResNet and the Impact of Residual Connections on Learning. arXiv:1602.07261
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 770–778
Xia H, Sun W, Song S et al (2020) Md-Net: Multi-scale Dilated Convolution Network for CT Images Segmentation. In: Neural Process Letters, vol 51. Springer. pp 2915–2927
Lin M, Chen Q, Yan S (2013) Network In Network. arXiv:1312.4400
Wang G et al (2020) A Noise-Robust Framework for Automatic Segmentation of COVID-19 Pneumonia Lesions From CT Images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(8):2653–2663
Sudre CH, Li W, Vercauteren T, Ourselin S, Jorge Cardoso M et al (2017) Generalised Dice Overlap as a Deep Learning Loss Function for Highly Unbalanced Segmentations. In: Cardoso M (ed) Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support. DLMIA 2017, ML-CDS 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 10553. Springer, Cham, pp 240–248
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61762014, in part by the Science and Technology Project of Guangxi under Grant 2018GXNSFAA281351, and in part by the Innovation Project of Guangxi Graduate Education under Grant YCSW2021096.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, H., Ma, M., Li, H. et al. MC-Net: multi-scale context-attention network for medical CT image segmentation. Appl Intell 52, 1508–1519 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02506-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02506-z