Abstract
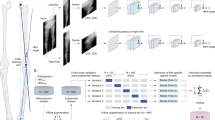
The human lower limb mechanical axis is the most basic and essential diagnosis reference in clinical orthopedics. Orthopedists diagnose the varus or valgus knee according to the status of the lower limb mechanical axis. The conventional method used in this task relies on manual measurement, which is time-consuming and has operational differences. Given the above reason, in this work, we focus on designing a deep learning algorithm to address this problem and present a novel convolutional neural network architecture for mechanical axis detection. After the mechanical axis is detected, HKAA (Hip-Knee-Ankle Angle), which is a medical index, can be calculated automatically to assist in the medical diagnosis. We locate the mechanical axis by detecting both ends’ key points. Then we apply the detected key points to implement the patella misalignment detection for auxiliary radiography imaging. The mechanical axis key points detection network is based on the stacked hourglass module and adopts the deformable convolution for modeling the geometric features. Besides, we introduce an offset branch to reduce the systematic error. Then a detector trained in a semi-supervised strategy is applied for patella detection. The horizontal deviation of the patella from the knee center reflects the alignment of the patella. We use 879 collected radiographs (X-ray images) to train the key point detection model and other 98 radiographs perform as the validation set in this study. The proposed model achieves an accuracy of 83.0% for key points and reaches 61.1 mAP in patella detection. This model achieves excellent performance in human lower limb mechanical axis and patella detection.










Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Acharya UR, Fujita H, Oh SL, Hagiwara Y, Tan JH, Adam M, San Tan R (2019) Deep convolutional neural network for the automated diagnosis of congestive heart failure using ecg signals. Appl Intell 49 (1):16–27
Artacho B, Savakis A (2020) Unipose: Unified human pose estimation in single images and videos. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). pp 7033–7042. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00706
Belagiannis V, Zisserman A (2017) Recurrent human pose estimation. In: 2017 12th IEEE International conference on automatic face & gesture recognition (FG 2017). IEEE, pp 468–475
Cai Z, Vasconcelos N (2018) Cascade r-cnn: Delving into high quality object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 6154–6162
Cerejo R, Dunlop DD, Cahue S, Channin DS, Song J, Sharma L (2002) The influence of alignment on risk of knee osteoarthritis progression according to baseline stage of disease. Arthritis Rheum 46 (10):2632–2636
Chen H, Sun K, Tian Z, Shen C, Huang Y, Yan Y (2020) Blendmask: Top-down meets bottom-up for instance segmentation. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00860, pp 8570–8578
Chen L, Papandreou G, Schroff F, Adam H (2017) Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. Comput Vis Pattern Recognit
Cheng B, Xiao B, Wang J, Shi H, Zhang L (2020) Higherhrnet: Scale-aware representation learning for bottom-up human pose estimation. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR)
Chollet F (2017) Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 1251–1258
Chu X, Yang W, Ouyang W, Ma C, Yuille AL, Wang X (2017) Multi-context attention for human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 1831–1840
Dai J, Qi H, Xiong Y, Li Y, Zhang G, Hu H, Wei Y (2017) Deformable convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. pp 764– 773
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 770–778
He K, Gkioxari G, Dollár P, Girshick R (2017) Mask r-cnn. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 2961–2969
Huang G, Liu Z, Van Der Maaten L, Weinberger KQ (2017) Densely connected convolutional networks. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 2261–2269
Huang J, Zhu Z, Guo F, Huang G (2020) The devil is in the details: Delving into unbiased data processing for human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 5700–5709
Ke L, Chang MC, Qi H, Lyu S (2018) Multi-scale structure-aware network for human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 713–728
Lin TY, Goyal P, Girshick R, He K, Dollár P (2017) Focal loss for dense object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. pp 2980–2988
Newell A, Yang K, Deng J (2016) Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 483–499
Nguyen TP, Chae DS, Park SJ, Kang KY, Lee WS, Yoon J (2020) Intelligent analysis of coronal alignment in lower limbs based on radiographic image with convolutional neural network. Comput Biol Med 120:103732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.103732, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0010482520301153
Rajpurkar P, Irvin J, Bagul A, Ding D, Duan T, Mehta H, Yang B, Zhu K, Laird D, Ball RL et al (2017) Mura: Large dataset for abnormality detection in musculoskeletal radiographs. Med Phys
Ren S, He K, Girshick R, Sun J (2015) Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: Advances in neural information processing systems. pp 91–99
Rieke N, Hancox J, Li W, Milletari F, Roth HR, Albarqouni S, Bakas S, Galtier MN, Landman BA, Maier-Hein K et al (2020) The future of digital health with federated learning. NPJ Digit Med 3(1):1–7
Sharma L, Song J, Felson DT, Cahue S, Shamiyeh E, Dunlop DD (2001) The role of knee alignment in disease progression and functional decline in knee osteoarthritis. JAMA 286(2):188–195
Sun K, Xiao B, Liu D, Wang J (2019) Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 5693–5703
Szegedy C, Vanhoucke V, Ioffe S, Shlens J, Wojna Z (2016) Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 2818–2826
Tang W, Yu P, Wu Y (2018) Deeply learned compositional models for human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the european conference on computer vision (ECCV). pp 190–206
Tian Y, Zitnick CL, Narasimhan SG (2012) Exploring the spatial hierarchy of mixture models for human pose estimation. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 256–269
Tian Z, Shen C, Chen H, He T (2019) Fcos: Fully convolutional one-stage object detection. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision (ICCV). pp 9626–9635. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00972
Tompson JJ, Jain A, LeCun Y, Bregler C (2014) Joint training of a convolutional network and a graphical model for human pose estimation. In: Advances in neural information processing systems. pp 1799–1807
Turkoglu M (2020) Covidetectionet: Covid-19 diagnosis system based on x-ray images using features selected from pre-learned deep features ensemble. Appl Intell :1–14
Wang Q, Guo G (2019) Ls-cnn: Characterizing local patches at multiple scales for face recognition. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 15:1640–1653
Wang Q, Wu T, Zheng H, Guo G (2020) Hierarchical pyramid diverse attention networks for face recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 8326–8335
Wang W, Charkborty G (2020) Automatic prognosis of lung cancer using heterogeneous deep learning models for nodule detection and eliciting its morphological features. Appl Intell :1–14
Wei SE, Ramakrishna V, Kanade T, Sheikh Y (2016) Convolutional pose machines. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 4724–4732
Wu X, Zhong M, Guo Y, Fujita H (2020) The assessment of small bowel motility with attentive deformable neural network. Inf Sci 508:22–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.08.059, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0020025519308084
Xiao J, Li H, Qu G, Fujita H, Cao Y, Zhu J, Huang C (2021) Hope: heatmap and offset for pose estimation. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput :1–13
Xie Q, Luong MT, Hovy E, Le QV (2020) Self-training with noisy student improves imagenet classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 10687–10698
Xie S, Girshick R, Dollár P, Tu Z, He K (2017) Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 1492–1500
Yang Y, Ramanan D (2012) Articulated human detection with flexible mixtures of parts. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(12):2878–2890
Zhang H, Chang H, Ma B, Wang N, Chen X (2020) Dynamic R-CNN: towards high quality object detection via dynamic training. arXiv:2004.06002
Zhu K, Jiang X, Fang Z, Gao Y, Fujita H, Hwang JN (2021) Photometric transfer for direct visual odometry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2020.106671, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0950705120308005, vol 213, p 106671
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grant No.62073237. Thanks for the data support of Linyi’s People Hospital. Thanks for the valuable comments from the editor-in-chief and three anonymous reviewers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
There is no conflict of interest nor any competing interest about this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Zhang, G., Guan, B. et al. Detection of human lower limb mechanical axis key points and its application on patella misalignment detection. Appl Intell 52, 5385–5399 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02718-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02718-3