Abstract
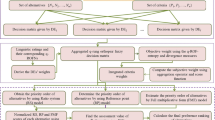
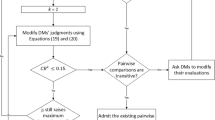
The main purpose of the current study is to explore a novel q-rung orthopair fuzzy score function and extend the measurement of alternatives and ranking according to the compromise solution (MARCOS) method with unknown weight information to the context of q-rung orthopair fuzzy numbers (q-ROFNs). For this, first, the drawbacks of the existing score functions are highlighted via several solid examples. Then, to fill the gaps of the existing ones, a novel score function and its relevant characteristics are delineated. To determine the objective weights of criteria, q-rung orthopair fuzzy criteria importance through intercriteria correlation (CRITIC) method is modeled based on the derived weights of decision-makers (DMs), standard deviation, and correlation coefficient. Following that, the q-rung orthopair fuzzy MARCOS approach is established to cope with multi-criteria group decision-making (MCGDM) problems. Later, a case study of solid waste management is addressed to show the practicality of the presented method. Lastly, the derived results are validated through three phases: two sensitivity analyses, rank reversal phenomena, and comparative analysis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zadeh L (1965) Fuzzy Sets Inf Control 8:338–353
Atanassov K (1986) Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 20(1):87–96
Yager RR (2013) Pythagorean fuzzy subsets. InL 2013 joint IFSA world congress and NAFIPS annual meeting (IFSA/NAFIPS). IEEE, pp 57–61
Yager RR (2013) Pythagorean membership grades in multicriteria decision making. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 22(4):958–965
Bashir Z, Bashir Y, Rashid T, Ali J, Gao W (2019) A novel multi-attribute group decision-making approach in the framework of proportional dual hesitant fuzzy sets. Appl Sci 9(6):1232
Ali J, Bashir Z, Rashid T (2021) Weighted interval-valued dual-hesitant fuzzy sets and its application in teaching quality assessment. Soft Comput 25(5):3503–3530
Atanassov K (1986) Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 20:87–96
Xu Z, Zhao N (2016) Information fusion for intuitionistic fuzzy decision making: an overview. Inf Fusion 28:10–23
Gupta P, Lin CT, Mehlawat MK, Grover N (2015) A new method for intuitionistic fuzzy multiattribute decision making. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst 46(9):1167–1179
Feng F, Fujita H, Ali MI, Yager RR, Liu X (2018) Another view on generalized intuitionistic fuzzy soft sets and related multiattribute decision making methods. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 27(3):474–488
Feng F, Liang M, Fujita H, Yager RR, Liu X (2019) Lexicographic orders of intuitionistic fuzzy values and their relationships. Mathematics 7(2):166
Ma Z, Xu Z (2016) Symmetric pythagorean fuzzy weighted geometric/averaging operators and their application in multicriteria decision-making problems. Int J Intell Syst 31(12):1198–1219
Huang C, Lin M, Xu Z (2020) Pythagorean fuzzy MULTIMOORA method based on distance measure and score function: its application in multicriteria decision making process. Knowl Inf Syst 62(11):4373–4406
Garg H (2018) Some methods for strategic decision-making problems with immediate probabilities in pythagorean fuzzy environment. Int J Intell Syst 33(4):687–712
Han Q, Li W, Lu Y, Zheng M, Quan W, Song Y (2019) TOPSIS Method based on novel entropy and distance measure for linguistic pythagorean fuzzy sets with their application in multiple attribute decision making. IEEE Access 8:14401–14412
Lang G, Miao D, Fujita H (2019) Three-way group conflict analysis based on Pythagorean fuzzy set theory. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 28(3):447–461
Qiang Z, JunHua H, An L, GuoMing C, QiMin Y (2020) New ranking methods of intuitionistic fuzzy numbers and Pythagorean fuzzy numbers. In: 2020 Chinese Control And Decision Conference (CCDC). IEEE, pp 4661–4666
Yager RR (2016) Generalized orthopair fuzzy sets. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 25(5):1222–1230
Peng X, Dai J, Garg H (2018) Exponential operation and aggregation operator for q-rung orthopair fuzzy set and their decision-making method with a new score function. Int J Intell Syst 33(11):2255–2282
Shu X, Ai Z, Xu Z, Ye J (2019) Integrations of q-rung orthopair fuzzy continuous information. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 27(10):1974–1985
Ai Z, Xu Z, Yager RR, Ye J (2021) q-rung orthopair fuzzy integrals in the frame of continuous Archimedean t-norms and t-conorms and their application. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 29(5):996–1007
Gao J, Liang Z, Shang J, Xu Z (2018) Continuities, derivatives, and differentials of q-rung orthopair fuzzy functions. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 27(8):1687–1699
Liu Z, Liu P, Liang X (2018) Multiple attribute decision-making method for dealing with heterogeneous relationship among attributes and unknown attribute weight information under q-rung orthopair fuzzy environment. Int J Intell Syst 33(9):1900–1928
Liu P, Wang P (2018) Some q-rung orthopair fuzzy aggregation operators and their applications to multiple-attribute decision making. Int J Intell Syst 33(2):259–280
Wei G, Gao H, Wei Y (2018) Some q-rung orthopair fuzzy heronian mean operators in multiple attribute decision making. Int J Intell Syst 33(7):1426–1458
Aydemir SB, Gündüz SY (2020) Extension of multi-Moora method with some q-rung orthopair fuzzy Dombi prioritized weighted aggregation operators for multi-attribute decision making. Soft Comput 24(24):18545–18563
Peng X, Krishankumar R, Ravichandran K S (2019) Generalized orthopair fuzzy weighted distance-based approximation (WDBA) algorithm in emergency decision-making. Int J Intell Syst 34(10):2364–2402
Peng X, Dai J (2019) Research on the assessment of classroom teaching quality with q-rung orthopair fuzzy information based on multiparametric similarity measure and combinative distance-based assessment. Int J Intell Syst 34(7):1588–1630
Mi X, Li J, Liao H, Zavadskas EK, Al-Barakati A, Barnawi A, Herrera-Viedma E (2019) Hospitality brand management by a score-based q-rung ortho pair fuzzy VIKOR method integrated with the best worst method. Econ Res-Ekon Istraz 32(1):3266–3295
Xing Y, Zhang R, Zhou Z, Wang J (2019) Some q-rung orthopair fuzzy point weighted aggregation operators for multi-attribute decision making. Soft Comput 23(22):11627–11649
Peng X, Huang H (2020) Fuzzy decision making method based on CoCoSo with critic for financial risk evaluation. Technol Econ Dev Econ 26(4):695–724
Li H, Yin S, Yang Y (2019) Some preference relations based on q-rung orthopair fuzzy sets. Int J Intell Syst 34(11):2920–2936
Rani P, Mishra AR (2020) Multi-criteria weighted aggregated sum product assessment framework for fuel technology selection using q-rung orthopair fuzzy sets. Sustain Prod Consum 24:90–104
Stević ž, Pamučar D, Puška A, Chatterjee P (2020) Sustainable supplier selection in healthcare industries using a new MCDM method: Measurement of alternatives and ranking according to compromise solution (MARCOS). Comput Ind Eng 140:106231
Stanković M, Stević ž, Das DK, Subotić M, Pamučar D (2020) A new fuzzy MARCOS method for road traffic risk analysis. Mathematics 8(3):457
Puška A, Stojanović I, Maksimović A, Osmanović N (2020) Project management software evaluation by using the measurement of alternatives and ranking according to compromise solution (MARCOS) method. Oper Res Eng Sci Theory Appl 3(1):89–102
Badi I, Pamucar D (2020) Supplier selection for steelmaking company by using combined grey-MARCOS methods. Decis Mak Appl Manag Eng 3(2):37–48
Simić V, Soušek R, Jovčić S (2020) Picture fuzzy mcdm approach for risk assessment of railway infrastructure. Mathematics 8(12):2259
Torkayesh AE, Zolfani SH, Kahvand M, Khazaelpour P (2021) Landfill location selection for healthcare waste of urban areas using hybrid BWM-grey MARCOS model based on GIS. Sustain Cities Soc 67:102712
Ecer F, Pamucar D (2021) MARCOS Technique under intuitionistic fuzzy environment for determining the COVID-19 pandemic performance of insurance companies in terms of healthcare services. Appl Soft Comput 104:107199
Peng X, Liu L (2019) Information measures for q-rung orthopair fuzzy sets. Int J Intell Syst 34(8):1795–1834
Wang JQ, Li KJ, Zhang HY (2012) Interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy multi-criteria decision-making approach based on prospect score function. Knowl-Based Syst 27:119–125
Diakoulaki D, Mavrotas G, Papayannakis L (1995) Determining objective weights in multiple criteria problems: The CRITIC method. Comput Oper Res 22(7):763–770
Guan N, Liu T, Zhang Y, Tao D, Davis LS (2017) Truncated cauchy non-negative matrix factorization. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 41(1):246–259
Shen X, Zhang X, Lan L, Liao Q, Luo Z (2019) Another robust NMF: Rethinking the hyperbolic tangent function and locality constraint. IEEE Access 7:31089–31102
Jara-Samaniego J, Pérez-Murcia M, Bustamante M, Pérez-Espinosa A, Paredes C, López M, López-Lluch D, Gavilanes-Terán I, Moral R (2017) Composting as sustainable strategy for municipal solid waste management in the chimborazo region, ecuador: Suitability of the obtained composts for seedling production. J Clean Prod 141:1349–1358
Abdel-Shafy HI, Mansour MS (2018) Solid waste issue: sources, composition, disposal, recycling, and valorization. Egypt J Pet 27(4):1275–1290
Javaheri H, Nasrabadi T, Jafarian M, Rowshan G, Khoshnam H (2006) Site selection of municipal solid waste landfills using analytical hierarchy process method in a geographical information technology environment in giroft. J Environ Health Sci Eng 3(3):177–184
Sumathi V, Natesan U, Sarkar C (2008) GIS-Based approach for optimized siting of municipal solid waste landfill. Waste Manage 28(11):2146–2160
Eiselt HA, Marianov V (2015) Location modeling for municipal solid waste facilities. Comput Oper Res 62:305–315
Vučijak B, Kurtagić SM, Silajdžić I (2016) Multicriteria decision making in selecting best solid waste management scenario: a municipal case study from bosnia and herzegovina. J Clean Prod 130:166–174
Rezaei J (2015) Best-worst multi-criteria decision-making method. Omega 53:49–57
Pamučar D, Gigović L, Bajić Z, Janošević M (2017) Location selection for wind farms using GIS multi-criteria hybrid model: an approach based on fuzzy and rough numbers. Sustainability 9(8):1315
Hafezalkotob A, Hafezalkotob A (2017) A novel approach for combination of individual and group decisions based on fuzzy best-worst method. Appl Soft Comput 59:316–325
Ren J, Liang H, Chan FT (2017) Urban sewage sludge, sustainability, and transition for eco-city: Multi-criteria sustainability assessment of technologies based on best-worst method. Technol Forecast Soc Change 116:29–39
Zhao H, Guo S, Zhao H (2018) Comprehensive benefit evaluation of eco-industrial parks by employing the best-worst method based on circular economy and sustainability. Environ Dev Sustain 20(3):1229–1253
Liu HC, You JX, Lu C, Shan MM (2014) Application of interval 2-tuple linguistic multimoora method for health-care waste treatment technology evaluation and selection. Waste Manage 34(11):2355–2364
Kabak M, Erbaṡ M, Ċetinkaya C, Özceylan E (2018) A gis-based mcdm approach for the evaluation of bike-share stations. J Clean Prod 201:49–60
Hariz HA, Dönmez CÇ, Sennaroglu B (2017) Siting of a central healthcare waste incinerator using GIS-based multi-criteria decision analysis. J Clean Prod 166:1031–1042
Kaya SK (2020) Evaluation of the effect of covid-19 on countries’ sustainable development level: a comparative MCDM framework. Oper Res Eng Sci Theory Appl 3(3):101–122
Zolfani S, Yazdani M, Pamucar D, Zarate P (2020) A VIKOR and TOPSIS focused reanalysis of the madm methods based on logarithmic normalization. FU Mech Eng 18(3):341–355
Kirkwood CW (1998) Strategic decision making multiobjective decision analysis with spreadsheets. J Oper Res Soc 49(1):96–97
Kahraman YR (2002) Robust sensitivity analysis for multi-attribute deterministic hierarchical value models. AIR FORCE INST OF TECH WRIGHT-PATTERSONAFB OH
Spearman C (1961) The proof and measurement of association between two things. Am J Psychol 100(3/4):441–471
Liao H, Zhang H, Zhang C, Wu X, Mardani A, Al-Barakati A (2020) A q-rung orthopair fuzzy GLDS method for investment evaluation of BE angel capital in China. Technol Econ Dev Econ 26(1):103–134
Alkan N, Kahraman C (2021) Evaluation of government strategies against COVID-19 pandemic using q-rung orthopair fuzzy TOPSIS method. Appl Soft Comput 110:107653
Krishankumar R, Nimmagadda SS, Rani P, Mishra AR, Ravichandran K, Gandomi AH (2021) Solving renewable energy source selection problems using a q-rung orthopair fuzzy-based integrated decision-making approach. J Clean Prod 279:123329
Liu P, Liu P, Wang P, Zhu B (2019) An extended multiple attribute group decision making method based on q-rung orthopair fuzzy numbers. IEEE Access 7:162050–162061
Ching LH, Yoon P (1981) Multiple attribute decision making. In: Lect Notes Econ Math Syst
Petković D, Madić M, Radovanović M, Gečevska V (2017) Application of the performance selection index method for solving machining MCDM problems. FU Mech Eng 15(1):97–106
Opricovic S, Tzeng GH (2004) Compromise solution by mcdm methods: a comparative analysis of VIKOR and TOPSIS. Eur J Oper Res 156(2):445–455
Li H, Lv L, Li F, Wang L, Xia Q (2020) A novel approach to emergency risk assessment using FMEA with extended MULTIMOORA method under interval-valued Pythagorean fuzzy environment. Int J Intell Comput Cybern 13(1):41– 65
Luo D, Wang X (2012) The multi-attribute grey target decision method for attribute value within three-parameter interval grey number. Appl Math Model 36(5):1957–1963
Grabisch M, Sugeno M, Murofushi T (2000) Fuzzy measures and integrals: theory and applications. Physica, Heidelberg
Dong Y, Zhang H, Herrera-Viedma E (2016) Integrating experts’ weights generated dynamically into the consensus reaching process and its applications in managing non-cooperative behaviors. Decis Support Syst 84:1–15
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, J. A q-rung orthopair fuzzy MARCOS method using novel score function and its application to solid waste management. Appl Intell 52, 8770–8792 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02921-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02921-2