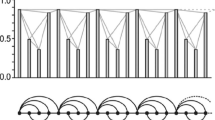
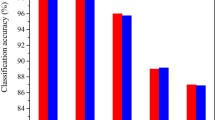
Abstract
Combining basic probability assignments (BPAs) with time series is common in real-life cases. Therefore, a new evidence fusion approach based on belief entropy and a visibility graph (BE-VG) is proposed. The approach converts a time-series BPA into a weighted visibility graph (WVG). In addition, some numerical examples are illustrated to illustrate the efficiency and applicability of the proposed method. Finally, to demonstrate the effect of the BE-VG method, the proposed method is applied to electroencephalogram (EEG) dynamic fusion. Experimentally, the results indicate that the BE-VG method is effective and accurate in conducting EEG signal fusion.









Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
For two matrices A and B of the same dimension m × n, the Hadamard product A ∘ B is a matrix of the same dimension as the operands, with elements given by (A ∘ B)ij = (A)ij(B)ij.
References
Cao Z, Ding W, Wang YK, Hussain F, Al-Jumaily A, Lin CT (2020) Effects of repetitive SSVEPs on EEG complexity using multiscale inherent fuzzy entropy. Neurocomputing 389:198–206
Cao Z, Lin C, Lai K, Ko L, King J, Liao K, Fuh J, Wang S (2020) Extraction of SSVEPs-based inherent fuzzy entropy using a wearable headband EEG in migraine patients. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 28(1):14–27
Chang L, Zhang L, Fu C, Chen YW (2021) Transparent digital twin for output control using belief rule base. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2021.3063285
Chen D, Xie H (2021) Fire safety evaluation for scenic spots: An evidential best-worst method. Journal of Mathematics 2021, https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5592,150
Chen L, Deng Y, Cheong KH (2021) Probability transformation of mass function: a weighted network method based on the ordered visibility graph. Eng Appl Artif Intell 105(104):438
Dempster AP (1967) Upper and lower probabilities induced by a multivalued mapping. Ann Math Stat 325–339
Deng J, Deng Y, Cheong KH (2021) Combining conflicting evidence based on pearson correlation coefficient and weighted graph. International Journal of Intelligent Systems https://doi.org/10.1002/int.22593
Deng X, Jiang W (2019) On the negation of a Dempster-Shafer belief structure based on maximum uncertainty allocation. Inf Sci 516:346–352
Deng Y (2020) Information volume of mass function. Int J Comput Commun Control 15(6):3983
Ding R, Palomares I, Wang X, Yang G, Liu B, Dong Y, Herrera-Viedma E, Herrera F (2020) Large-scale decision-making: characterization, taxonomy, challenges and future directions from an artificial intelligence and applications perspective. Inform Fusion 59:84–102
Fei L, Lu J, Feng Y (2020) An extended best-worst multi-criteria decision-making method by belief functions and its applications in hospital service evaluation. Comput Indust Eng 142(106):355
Feng F, Cho J, Pedrycz W, Fujita H, Herawan T (2016) Soft set based association rule mining. Knowl-Based Syst 111:268– 282
Fu C, Xue M, Xu D, Yang S (2019) Selecting strategic partner for tax information systems based on weight learning with belief structures. Int J Approx Reason 105:66–84
Fujita H, Cimr D (2019) Decision support system for arrhythmia prediction using convolutional neural network structure without preprocessing. Appl Intell 49:3383–3391
Fujita H, Gaeta A, Loia V, Orciuoli F (2019) Improving awareness in early stages of security analysis: A zone partition method based on GrC. Appl Intell 49:1063–1077
Fujita H, Gaeta A, Loia V, Orciuoli F (2020) Hypotheses analysis and assessment in counterterrorism activities: a method based on OWA and fuzzy probabilistic rough sets. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 28 (5):831–845
Fujita H, Ko YC (2020) A heuristic representation learning based on evidential memberships: Case study of UCI-SPECTF. Int J Approx Reason 120:125–137
Gao X, Su X, Qian H, Pan X (2021) Dependence assessment in Human Reliability Analysis under uncertain and dynamic situations. Nuclear Engineering and Technology
Garg H, Chen S (2020) Multiattribute group decision making based on neutrality aggregation operators of q-rung orthopair fuzzy sets. Inf Sci 517:427–447
Greff K, Srivastava RK, Koutnik J, Steunebrink BR, Schmidhuber J (2017) LSTM: A search space odyssey. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 28(10):2222–2232
Jiang W, Cao Y, Deng X (2020) A novel Z-network model based on Bayesian network and Z-number. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 28(8):1585–1599
Kang B, Zhang P, Gao Z, Chhipi-Shrestha G, Hewage K, Sadiq R (2019) Environmental assessment under uncertainty using Dempster-Shafer theory and Z-numbers. J Ambient Intell Humanized Comput 11:2041–2060
Lacasa L, Just W (2018) Visibility graphs and symbolic dynamics. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena 35–44
Lacasa L, Luque B, Ballesteros F, Luque J, Nuno JC (2008) From time series to complex networks: The visibility graph. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(13):4972
Lai JW, Chang J, Ang L, Cheong KH (2020) Multi-level information fusion to alleviate network congestion. Inform Fusion 63:248–255
Liao H, Ren Z, Fang R (2020) A Deng-entropy-based evidential reasoning approach for multi-expert multi-criterion decision-making with uncertainty. Int J Comput Intell Syst 13(1):1281–1294
Liu F, Wang Z, Deng Y (2020) GMM: A generalized mechanics model for identifying the importance of nodes in complex networks. Knowl-Based Syst 193(105):464
Liu G, Xiao F (2019) A data-driven dynamic data fusion method based on visibility graph and evidence theory. IEEE Access 7:104,443–104,452
Liu P, Zhang X, Pedrycz W (2020) A consensus model for hesitant fuzzy linguistic group decision-making in the framework of Dempster–Shafer evidence theory. Knowl-Based Syst 212(106):559
Liu Q, Tian Y, Kang B (2019) Derive knowledge of Z-number from the perspective of Dempster-Shafer evidence theory. Eng Appl Artif Intell 85:754–764
Liu Z, Li G, Mercier G, He Y, Pan Q (2017) Change detection in heterogenous remote sensing images via homogeneous pixel transformation. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(4):1822– 1834
Liu Z, Pan Q, Dezert J, Han JW, He Y (2018) Classifier fusion with contextual reliability evaluation. IEEE Trans Cybern 48(5):1605–1618
Long H, Peng Z, Deng Y (2021) A new structure of the focal element in object recognition. International Journal of Intelligent Systems https://doi.org/10.1002/int.2267
Meng D, Xie T, Wu P, He C, Hu Z, Lv Z (2021) An uncertainty-based design optimization strategy with random and interval variables for multidisciplinary engineering systems. In: Structures, vol 32. Elsevier, pp 997–1004
Meng D, Xie T, Wu P, Zhu SP, Hu Z, Li Y (2020) Uncertainty-based design and optimization using first order saddle point approximation method for multidisciplinary engineering systems. ASCE-ASME Journal of Risk and Uncertainty in Engineering Systems Part A: Civil Engineering 6(3):04020,028
Shafer G (1976) A mathematical theory of evidence, vol 42. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Shang QY, Deng Y, Cheong KH (2021) Identifying influential nodes in complex networks: Effective distance gravity model. Inf Sci 577:162–179
Smets P (2007) Analyzing the combination of conflicting belief functions. Inform Fusion 8 (4):387–412
Song Y, Deng Y (2021) Entropic explanation of power set. Int J Comput Commun Control 16(4):4413. https://doi.org/10.15837/ijccc.2021.4.4413
Song Y, Fu Q, Wang Y, Wang X (2019) Divergence-based cross entropy and uncertainty measures of Atanassov’s intuitionistic fuzzy sets with their application in decision making. Appl Soft Comput 84 (105):703
Tang M, Liao H, Herrera-Viedma E, Chen CP, Pedrycz W (2020) A dynamic adaptive subgroup-to-subgroup compatibility-based conflict detection and resolution model for multicriteria large-scale group decision making. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2020.2974924
Verano DA, Husnawati H, Ermatita E (2020) Implementation of autoregressive integrated moving average model to forecast raw material stock in the digital printing industry. J Inform Technol Comput Sci 5 (1):13
Wang C, Koh JM, Cheong KH, Xie NG (2019) Progressive information polarization in a complex-network entropic social dynamics model. IEEE Access 7:35,394–35,404
Wen T, Pelusi D, Deng Y (2020) Vital spreaders identification in complex networks with multi-local dimension. Knowl-Based Syst 195(105):717
Xiao B, Xu W, Guo J, Lam HK, Ren H (2020) Depth estimation of hard inclusions in soft tissue by autonomous robotic palpation using deep recurrent neural network. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng PP (99):1–9
Xiao F (2020) CEQD: A complex mass function to predict interference effects. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2020.3040770
Xiao F (2020) Evidence combination based on prospect theory for multi-sensor data fusion. ISA Trans 106:253–261
Xiao F (2021) On the maximum entropy negation of a complex-valued distribution. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems 29(11):3259–3269
Xiao F (2021) CaFtR: A fuzzy complex event processing method. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems DOI10.1007/s40,815–021–01,118–6
Xiao F (2021) CED: A distance for complex mass functions. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 32(4):1525–1535
Xiao F (2021) GIQ: A generalized intelligent quality-based approach for fusing multi-source information. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 29(7):2018–2031
Xiong L, Su X, Qian H (2021) Conflicting evidence combination from the perspective of networks. Inf Sci 580:408–418
Xu X, Xu H, Wen C, Li J, Hou P, Zhang J (2018) A belief rule-based evidence updating method for industrial alarm system design. Control Eng Pract 81:73–84
Xu X, Zheng J, Yang J, Xu D, Chen Y (2017) Data classification using evidence reasoning rule. Knowl-Based Syst 116:144– 151
Xue Y, Deng Y (2021) Interval-valued belief entropies for Dempster Shafer structures. Soft Comput 25:8063–8071
Ye Y, Hang XR, Koh JM, Miszczak JA, Cheong KH (2020) Xie, N.g.: Passive network evolution promotes group welfare in complex networks. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals 130(109):464
Zhao J, Deng Y (2020) Complex network modeling of evidence theory. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.3023760
Zhou M, Liu X, Chen Y, Yang J (2018) Evidential reasoning rule for MADM with both weights and reliabilities in group decision making. Knowl-Based Syst 143:142–161
Acknowledgements
The authors greatly appreciate the reviewers’ suggestions and the editor’s encouragement. This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62003280).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, X., Xiao, F. Combining time-series evidence: A complex network model based on a visibility graph and belief entropy. Appl Intell 52, 10706–10715 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02956-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02956-5