Abstract
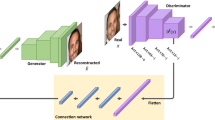
Exploring the relationship between different features in multi-label learning and generating controllable features of multi-label images have always been hot topics. Unlike most other methods, in order to make the processing of the network more intuitive and convincing, we designed a generative adversarial network with a nested structural causal mechanism. The network has two functions: generating feature labels and generating multi-label images. We restore the adjacency matrix between individual features in the labels by applying an additional network layer with acyclic constraints, so as to obtain the corresponding causal directed acyclic graph. In this way, the network can autonomously learn the causal relationships between features and generate feature labels from them, enabling feature separation at the causal level. A particular innovation is that we can also add intervention mechanism to the label generation process to answer the “what if” question in the causality theory at the feature level. Finally, the second part of the network maps the labels to images, completing the entire process of multi-label image generation. We performed a series of experiments to demonstrate the effectiveness of the embedded causal mechanism in qualitative and quantitative terms.





Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Mirza M, Osindero S (2014) Conditional generative adversarial nets. arXiv:1411.1784
Odena A, Olah C, Shlens J (2017) Conditional image synthesis with auxiliary classifier gans. In: International conference on machine learning, PMLR
Li C et al (2017) Triple generative adversarial nets. arXiv:1703.02291
Reed S et al (2016) Generative adversarial text to image synthesis. In: International conference on machine learning, PMLR
Zhu J-Y et al (2017) Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision
Liu Z et al (2015) Deep learning face attributes in the wild. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision
Xu T et al (2018) Attngan: Fine-grained text to image generation with attentional generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition
Lee M, Seok J (2019) Controllable generative adversarial network. Ieee. Access 7:28158–28169
He Z et al (2019) Attgan: Facial attribute editing by only changing what you want. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 28(11):5464–5478
Liu M et al (2019) STGAN: A unified selective transfer network for arbitrary image attribute editing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition
Spirtes P et al (2000) Causation, prediction, and search. MIT press
Huang B et al (2018) Generalized score functions for causal discovery. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery & data mining
Lopez-Paz D et al (2017) Discovering causal signals in images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition
Besserve M et al (2018) Group invariance principles for causal generative models. In: International conference on artificial intelligence and statistics. PMLR
Kocaoglu M et al (2017) Causalgan: Learning causal implicit generative models with adversarial training. arXiv:1709.02023
Pan W, Cui S, Zhang C (202) Unsupervised disentanglement learning by intervention
Yu Y et al (2019) Dag-gnn: Dag structure learning with graph neural networks. In: International conference on machine learning, PMLR
Gulrajani I et al (2017) Improved training of wasserstein gans. arXiv:1704.00028
Arjovsky M, Chintala S, Bottou L (2017) Wasserstein generative adversarial networks. In: International conference on machine learning, PMLR
Zheng X et al (2018) Dags with no tears: Continuous optimization for structure learning. arXiv:1803.01422
Lachapelle S et al (2019) Gradient-based neural dag learning. arXiv:1906.02226
Camino R, Christian H, Radu S (2018) Generating multi-categorical samples with generative adversarial networks. arXiv:1807.01202
Choi E et al (2017) Generating multi-label discrete patient records using generative adversarial networks. Machine learning for healthcare conference, PMLR
Moraffah R et al (2020) Causal adversarial network for learning conditional and interventional distributions. arXiv:2008.11376
Heusel M et al (2017) Gans trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local nash equilibrium. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 30
Shmelkov K, Cordelia S, Karteek A (2018) How good is my GAN?. In: Proceedings of the european conference on computer vision (ECCV)
Colombo D et al (2012) Learning high-dimensional directed acyclic graphs with latent and selection variables. Ann Stati 40(1):294–321
Zhu S, Ng I, Chen Z (2019) Causal discovery with reinforcement learning. arXiv:1906.04477
Tsamardinos I, Brown LE, Aliferis CF (2006) The max-min hill-climbing Bayesian network structure learning algorithm. Machine Learning 65(1):31–78
Ge Y et al (2020) Zero-shot synthesis with group-supervised learning. arXiv:2009.06586
Shen Y et al (2020) Interfacegan: Interpreting the disentangled face representation learned by gans. In: IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence
Judea P (2000) Models, reasoning and inference. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Major Science and Technology Projects of China (grant no. 2018AAA0100703), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 61977012), and the Central Universities Project in China at Chongqing University (nos. 2021CDJYGRH011, 2017CDJSK06PT10, 2020CDJSK06PT14).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Liao, J., Zhang, Y. et al. CMGAN: A generative adversarial network embedded with causal matrix. Appl Intell 52, 16233–16245 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-03094-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-03094-8