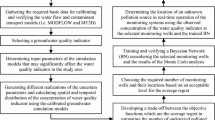
Abstract
In the near future, it is estimated that our world would attend a war over waters. Whereas, the effluents of the laundry of phosphate damages more and more the watershed in mining areas. The analysis of these impacts is in fact a crucial task for the preservation of the area’s water resources. In this paper, we introduced a hybrid approach-based Bayesian network model construction for assessing the phosphate laundry effluents effects. We proposed a novel discrete Bayesian Network model which is built using a hybrid approach based on Expert and data-oriented methods for structure learning. Our aim is to propose a novel data-oriented method for resolving the Bayesian network (BN) structure learning that will be improved basing on the experts’ knowledge for efficient modelling of the cause-effect relationships. And then the parameters learning procedure is performed basing on the Expectation Maximization algorithm (EM). The evaluation of the proposed data-oriented method based on two well-known benchmarking BNs demonstrates the superiority of the proposed method in terms of BN structure evaluation metrics (i.e. structure difference, correct edges, added edges, reversed edges and deleted edges). The proposed BN model allows the assessment of the groundwater quality taking into consideration several chemical factors and influencers on the absorption of discharged metals. Depending on a real collected water samples from the Gafsa phosphatic areas (southwestern Tunisia), we built the BN model which permits the analysis of different basic physico-chemical variables and its dependencies. Moreover, the generated results illustrate that our technique has higher performance compared with the other Bayesian techniques.














Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Pradhan S (2017) Water war thesis: a myth or a reality. Int J Arts Humanit Soc Sci 2:12–15
Freedman B, Hutchinson TC (1981) Sources of metal and elemental contaminants of terrestrial environments. In: Lepp NW (ed) Effect of heavy metal pollution on plants. Metals in the environment, vol. II. London and New Jersey, p 35–94
Webber (1981) Trace metals in agriculture. In: Lepp NW (ed) Effect of heavy metal pollution on plants. Metals in the environment, vol. II. London and New Jersey, p 159–184
Marzougui S, Sdiri A, Rekhiss F (2016) Heavy metals’ mobility from phosphate washing effluents discharged in the Gafsa area (southwestern Tunisia). Arab J Geosci 9(12):599
Yang Z, Yang Z, Yin J (2018) Realising advanced risk-based port state control inspection using data-driven Bayesian networks. Transp Res A Policy Pract 110:38–56
Cano A, Masegosa AR, Moral S (2011) A method for integrating expert knowledge when learning Bayesian networks from data. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B (Cybernetics) 41(5):1382–1394
Yet B, Perkins Z, Fenton N, Tai N, Marsh W (2014) Not just data: A method for improving prediction with knowledge. J Biomed Inform 48:28–37
Lee S, Kim SB (2019) Parallel Simulated Annealing with a Greedy Algorithm for Bayesian Network Structure Learning. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 32(6):1157–1166
Dempster AP, Laird NM, Rubin DB (1977) Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. J R Stat Soc Ser B Stat Methodol 39(1):1–22
Huang L, Cai G, Yuan H, Chen J (2019) A hybrid approach for identifying the structure of a Bayesian network model. Expert Syst Appl 131:308–320
Tsamardinos I, Aliferis CF, Statnikov A (2003) Time and sample efficient discovery of Markov blankets and direct causal relations. In: Proceedings of the Ninth ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp 673–678
Behjati S, Beigy H (2020) Improved K2 algorithm for Bayesian network structure learning. Eng Appl Artif Intell 91:103617
Jiang Y, Liang Z, Gao H, Guo Y, Zhong Z, Yang C, Liu J (2018) An improved constraint-based Bayesian network learning method using Gaussian kernel probability density estimator. Expert Syst Appl 113:544–554
Pearl J (2014) Probabilistic reasoning in intelligent systems: networks of plausible inference. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Spirtes P, Glymour C (1991) An algorithm for fast recovery of sparse causal graphs. Soc Sci Comput Rev 9(1):62–72
Tsamardinos I, Aliferis CF, Statnikov AR, Statnikov E (2003) Algorithms for large scale Markov blanket discovery. In: Proceedings of the Sixteenth International Florida Artificial Intelligence Research Society Conference, vol 2, pp 376–380
De Morais SR, Aussem A (2010) An efficient and scalable algorithm for local Bayesian network structure discovery. In: Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases, pp 164–179
Suzuki J, Kawahara J (2017) Branch and bound for regular Bayesian network structure learning. In: Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence, Sydney, Australia Google Scholar, pp 581–592
Jaakkola T, Sontag D, Globerson A, Meila M (2010) Learning Bayesian network structure using LP relaxations. In: Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, pp 358–365
Bartlett M, Cussens J (2017) Integer linear programming for the Bayesian network structure learning problem. Artif Intell 244:258–271
Campos CPd, Ji Q (2011) Efficient structure learning of Bayesian networks using constraints. J Mach Learn Res 12(Mar):663–689
Koivisto M, Sood K (2004) Exact Bayesian structure discovery in Bayesian networks. J Mach Learn Res 5(May):549–573
Silander T, Myllymaki P (2012) A simple approach for finding the globally optimal Bayesian network structure. arXiv preprint arXiv:1206.6875
Yuan C, Malone BM (2012) An improved admissible heuristic for learning optimal Bayesian networks. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence, Catalina Island, CA, USA, August 14-18, 2012, pp 924–933
Cooper GF, Herskovits E (1992) A Bayesian method for the induction of probabilistic networks from data. Mach Learn 9(4):309–347
Tabar VR, Eskandari F, Salimi S, Zareifard H (2018) Finding a set of candidate parents using dependency criterion for the K2 algorithm. Pattern Recognit Lett 111:23–29
Ai X (2017) Node importance ranking of complex networks with entropy variation. Entropy 19(7):303
Dash D, Druzdzel MJ (1999) A hybrid anytime algorithm for the construction of causal models from sparse data. In: Proceedings of the Fifteenth International Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence. Morgan Kaufmann, pp 142–149
Gámez JA, Mateo JL, Puerta JM (2011) Learning Bayesian networks by hill climbing: efficient methods based on progressive restriction of the neighborhood. Data Min Knowl Discov 22(1):106–148
Tsamardinos I, Brown LE, Aliferis CF (2006) The max-min hill-climbing Bayesian network structure learning algorithm. Mach Learn 65(1):31–78
De Campos LM, Castellano JG (2007) Bayesian network learning algorithms using structural restrictions. Int J Approx Reason 45(2):233–254
Amirkhani H, Rahmati M, Lucas PJ, Hommersom A (2016) Exploiting experts’ knowledge for structure learning of bayesian networks. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(11):2154–2170
Tang C, Yi Y, Yang Z, Sun J (2016) Risk analysis of emergent water pollution accidents based on a Bayesian Network. J Environ Manage 165:199–205
Wang J, Liu S (2018) Novel binary encoding water cycle algorithm for solving Bayesian network structures learning problem. Knowl Based Syst 150:95–110
Wang J, Liu S (2019) A novel discrete particle swarm optimization algorithm for solving bayesian network structures learning problem. Int J Comput Math 96(12):2423–2440
Gheisari S, Meybodi MR (2016) Bnc-pso: structure learning of bayesian networks by particle swarm optimization. Inf Sci 348:272–289
Chickering DM, Heckerman D, Meek C (2004) Large-sample learning of Bayesian networks is NP-hard. J Mach Learn Res 5(Oct):1287–1330
Constantinou AC, Fenton N, Neil M (2016) Integrating expert knowledge with data in Bayesian networks: Preserving data-driven expectations when the expert variables remain unobserved. Expert Syst Appl 56:197–208
Benmohamed E, Ltifi H, Ben Ayed M (2020) Hybrid data analysis approach based on improved K2PC algorithm and expert knowledge: application for assessing impact of the phosphate laundry effluents. In: Proceeding of International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition ICDAR
Masmoudi K, Abid L, Masmoudi A (2019) Credit risk modeling using Bayesian network with a latent variable. Expert Syst Appl 127:157–166
Benmohamed E, Ltifi H, Ayed MB (2020) Hybrid structure learning approach for assessing the phosphate laundries impact. Int J Comput Inf Eng 14(11):430–436
Benmohamed E, Ltifi H, Ayed MB (2020) A Novel Bayesian Network Structure Learning Algorithm: Best ParentsChildren. In: 2019 IEEE 14th International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Knowledge Engineering (ISKE). IEEE, pp 743-749
Benmohamed E, Ltifi H, Ayed MB (2020) ITNO-K2PC: An improved K2 algorithm with information-theorycentered node ordering for structure learning. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences 2020
Ltifi H, Benmohamed E, Kolski C, Ayed MB (2020) Adapted visual analytics process for intelligent decision-making: application in a medical context. Int J Inf Technol Decis Mak (IJITDM) 19(01):241–282
Ltifi H, Benmohamed E, Kolski C, Ayed MB (2016) Enhanced visual data mining process for dynamic decision-making. Knowl Based Syst 112:166–181
Pineo D, Ware C (2012) Data visualization optimization via computational modeling of perception. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 18(2):309–320
Zheng J, Jiang Z, Chellappa R (2016) Cross-view action recognition via transferable dictionary learning. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(6):2542–2556
Chen YC, Wheeler TA, Kochenderfer MJ (2017) Learning discrete Bayesian networks from continuous data. J Artif Intell Res 59:103–132
Saraiya P, North C, Duca K (2005) An insight-based methodology for evaluating bioinformatics visualizations, IEEE transactions on visualization and computer graphics, vol 11, pp 443–4564
Khan U, Haleem A (2015) Improving to amart organization: An integrated ISM and fuzzy-MICMAC modelling of barriers. J Manuf Technol Manag 26(6):807–829
Acknowledgements
The research leading to these results has received funding from the Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research of Tunisia under the grant agreement number LR11ES48.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benmohamed, E., Ltifi, H. & Ayed, M.B. Bayesian model construction based on data-experts oriented approaches for assessing the phosphate effluents effects. Appl Intell 52, 16475–16496 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-03105-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-03105-8