Abstract
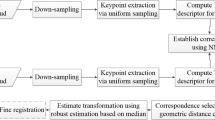
3D point cloud registration has a wide range of applications in object shape detection, robot navigation and 3D reconstruction. Aiming at the problems of the traditional ICP registration algorithm, such as slow convergence speed and high requirements for the initial point cloud position, this paper proposes a coarse-fine point cloud registration method based on a fast and robust local point-pair feature (LPPF) and the ICP algorithm. The LPPF feature descriptor is an improved descriptor for the local application of classic point-pair features and is a histogram descriptor formed by counting the feature information of the local point cloud neighborhood. This paper completes point cloud registration through keypoint extraction, LPPF feature description, feature matching, coarse registration and fine registration. To verify the effectiveness of this method, under the evaluation indices of L1, RMSE and MAE, we analyzed the experimental results from the three aspects of descriptors, coarse registration and coarse-fine registration. Under Gaussian noise conditions, LPPF compared to the second-ranked descriptor, the L1 scores of LPPF on the Stanford, Kinect and Princeton datasets increased by 12%, 12.4% and 9.1%, respectively. The coarse registration experiment is compared with 5 classic descriptors on 3 commonly used datasets. The LPPF feature descriptor has higher registration accuracy and less registration time. Finally, the coarse-fine registration experiment shows that our method can reduce the number of iterations of the ICP algorithm by 77% under optimal conditions.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Orts-Escolano S, Garcia-Rodriguez J, Morell V, Cazorla M, Perez JAS, Garcia-Garcia A (2016) 3D surface reconstruction of Noisy point clouds using growing neural gas: 3D object/scene reconstruction. Neural Process Lett 43(2):401–423
Li B, Zhang Y, Zhao B, Shao H (2020) 3D-ReConstnet: a single-view 3D-object point cloud reconstruction network. IEEE Access 8:83782–83790
Song L, Sun S, Yang Y, Zhu X, Guo Q, Yang H (2019) A multi-view stereo measurement system based on a laser scanner for fine workpieces. Sensors 19(2):381
Feng H, Ren X, Li L, Zhang X, Chen H (2021) A novel feature-guided trajectory generation method based on point cloud for robotic grinding of freeform welds. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 115(5–6):1763–1781
Cai J, Martorella M, Liu Q, Ding Z, Giusti E, Long T (2020) Automatic target recognition based on alignments of three-dimensional interferometric ISAR images and CAD models. IEEE Trans Aerosp Electron Syst 56(6):4872–4888
Kim P, Park J, Cho YK, Kang J (2019) UAV-assisted autonomous mobile robot navigation for as-is 3D data collection and registration in cluttered environments. Autom Constr 106:102918
Ye Y, Chen H, Zhang C, Hao X, Zhang Z (2019) SARPNET: shape attention regional proposal network for liDAR-based 3D object detection. Neurocomputing 379:53–63
Besl PJ, McKay ND (1992) A method for registration of 3-D shapes. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 14(2):239–256
Servos J, Waslander SL (2017) Multi-Channel generalized-ICP: a robust framework for multi-channel scan registration. Robot Auton Syst 87:247–257
Yang J, Li H, Campbell D, Jia Y (2016) Go-ICP: a globally optimal solution to 3D ICP point-set registration. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 38(11):2241–2254
Bouaziz S, Tagliasacchi A, Pauly M (2013) Sparse iterative closest point. Comp Graph Forum 32(05):113–123
Yao ZW, Zhao QX, Li XF, Bi QS (2021) Point cloud registration algorithm based on curvature feature similarity. Measurement 177:109274
Radu Bogdan Rusu, Nico Blodow, Zoltan Csaba Marton, Michael Beetz (2008) Aligning Point Cloud Views using Persistent Feature Histograms. IEEE/RSJ Int Conf Intell Robots Syst
Radu Bogdan Rusu, Nico Blodow, Michael Beetz (2009) Fast point feature histograms (fpfh) for 3d registration. IEEE Int Conf Robot Autom
Radu Bogdan Rusu, Gary Bradski, Romain Thibaux, John Hsu (2010) Fast 3D Recognition and Pose Using the Viewpoint Feature Histogram. IEEE/RSJ Int Conf Intell Robot Syst
Aldoma A, Vincze M, Blodow N (2011) CAD-model recognition and 6DOF pose estimation using 3D cues. IEEE Int Conf Comp Vis Workshops
Li MY, Hashimoto K (2017) Curve set feature-based robust and fast pose estimation algorithm. Sensors 17(8):1782
Ulas C, Temeltas H (2013) 3D multi-layered Normal distribution transform for fast and Long range scan matching. J Intell Robot Syst 71(1):85–108
Mohamad M, Rappaport D, Greenspan M (2014) Generalized 4-Points Congruent Sets for 3D Registration. 2014 2nd International Conference on 3D Vision :83–90
Mellado N, Aiger D, Mitra N (2014) SUPER 4PCS fast global Pointcloud registration via smart indexing. Comp Graph Forum 33(5):205–215
Ge XM (2017) Automatic markerless registration of point clouds with semantic-keypoint-based 4-points congruent sets. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 130:344–357
Salti S, Tombari F, Di Stefano L (2014) SHOT: unique signatures of histograms for surface and texture description. Comput Vis Image Underst 125:251–264
Frome A, Huber D, Kolluri R, Bülow T, Malik J (2004) Recognizing objects in range data using regional point descriptors. In: Computer vision (ECCV). Springer, Berlin, pp 224–237
Kiforenko L, Drost B, Tombari F, Kruger N, Buch AG (2018) A performance evaluation of point pair features. Comput Vis Image Underst 166:66–80
Zhao H, Tang M, Ding H (2020) Hoppf: a novel local surface descriptor for 3D object recognition. Pattern Recogn 103:196–213
Liu WB, Sun W, Wang SX, Liu Y (2021) Coarse registration of point clouds with low overlap rate on feature regions. Signal Proc-Image Commun 98:116428
Huang Y, Da FP (2019) Registration algorithm for point cloud based on normalized cross-correlation. IEEE Access 7:137136–137146
Quan SW, Yang JQ (2020) Compatibility-guided sampling consensus for 3-D point cloud registration. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 58(10):7380–7392
Jin YH, Lee WH (2019) Fast cylinder shape matching using random sample consensus in large scale point cloud. Appl Sci-Basel 9(5):974
Fontana S, Cattaneo D, Ballardini AL, Vaghi M, Sorrenti DG (eds) (2021) A benchmark for point clouds registration algorithms. Robot Auton Syst 140:103734
Francois P, Ming L, Francis C, Roland S (2012) Challenging data sets for point cloud registration algorithms. Int J Robot Res 31(14):1705–1711
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, X., Liu, Z., Zhu, J. et al. Coarse-fine point cloud registration based on local point-pair features and the iterative closest point algorithm. Appl Intell 52, 12569–12583 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03201-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03201-3