Abstract
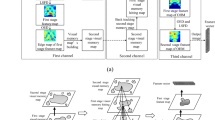
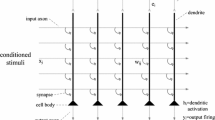
The object image is occluded by obstacles or some of its pixels are removed, which results in incomplete features of the object image and increases the difficulty of object recognition. Aiming at the problem, this paper studies an occluded object image recognition method based on visual memory selection model (VMSM). Automatic selection of visual memory points from original image is implemented firstly. The visual memory points are extended into visual memory regions of 61 × 61 pixels, in which the visual memory regions cover the salient feature of the original training image. Then, Hebbian association learning among identity cells, label cells and sensory neurons is executed. Moreover, saccade sequence is adopted for simulating the biomimetic visual characteristics. And the grid cell model is utilized to provide vector navigation and path integration for the saccade sequence. What’s more, the grid cell model is adopted to encode translation vectors between visual memory regions. According to the vector navigation function of grid cell model and the firing response of neurons during saccade process. A unique vector is produced by the start visual memory region and the destination visual memory of each saccade. The visual memory regions correspond to the label cell in the brain. The labeled cell will activate the identity cell to generate a firing rate response and the firing value is accumulated after each saccade. Once the accumulated value of an identity cell reaches the recognition threshold of 0.9, the occluded object image is considered to be of this identity cell corresponding image category. Through some experimental analysis, the proposed VMSM shows a better recognition result. The average recognition accuracy of real-world occluded FD, FRD, SD and AR database is 90%, 93.3%, 86.7% and 90.5%.












Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Gao QH, Wan TR, Tang W, et al. (2019) Object registration in semi-cluttered and partial-occluded scenes for augmented reality [J]. Multimed Tools Appl 78(11):15079–15099Gao Q H, Wan T R, Tang Wet al Object registration in semi-cluttered and partial-occluded scenes for augmented reality [J]. Multimed Tools Appl, 2019, 78(11): 15079–15099
Hsiao E, Hebert M (2014) Occlusion reasoning for object detection under arbitrary viewpoint [J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 36(9):1803–1815
Li D, Li L, Li Y, Yang F, Zuo X (2018) A multi-type features method for leg detection in 2-D laser range data [J]. IEEE Sensors J 18(4):1675–1684
Jiang J, Yilmaz A (2014) Persistent tracking of static scene features using geometry [J]. Comput Vis Image Underst 120(1):141–156
Lowe DG (2004) Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints [J]. Int J Comput Vis 60(2):91–110
Figat J, Kornuta T, Kasprzak W (2014) Performance evaluation of binary descriptors of local features [C]//. International Conference on Computer Vision and Graphics (ICCVG):187–194
Manoranjitham R, Deepa P (2018) Efficient invariant interest point detector using bilateral-Harris corner detector for object recognition application [J]. Multimed Tools Appl 77(8):9365–9378
Soleimanizadeh S, Mohamad D, Saba T, et al. Recognition of oartially occluded objects based on the three different color spaces (RGB, YCbCr, HSV) [J]. 3D Res, 2015, 6(3): 1–10
Priya L, Anand S (2018) Object recognition and 3D reconstruction of occluded objects using binocular stereo [J]. Cluster Computing-the Journal of Networks Software Tools and Applications 21(1):29–38
Sadeghzadeh A, Ebrahimnezhad H (2020) Pose-invariant face recognition based on matching the occlusion free regions aligned by 3D generic model [J]. IET Comput Vis 14(5):268–277
Riesenhuber M, Poggio T (1999) Hierarchical models of object recognition in cortex [J]. Nat Neurosci 2(11):1019–1025
Lecun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G (2015) Deep learning [J]. Nature 521(7553):436–444
Wu WY, Lin SY (2005) Two-stage neural network for recognizing partially occluded objects [J]. Imaging Science Journal 53(3):132–139
Hossain D, Nilwong S, Tran Duc D, et al. A faster R-CNN approach for partially occluded robot object recognition [C]// 2019 Third IEEE International Conference on Robotic Computing(IRC). 2019: 568–573
Song L, Gong D, Li Z et al (2019) Occlusion robust face recognition based on mask learning with pairwise differential siamese network [C]//. IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) 2019:773–782
Kortylewski A, Liu Q, Wang H et al (2020) Combining compositional models and deep networks for robust object classification under occlusion [C]//. IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV) 2020:1322–1330
Li Y, Fang Y, Wang X, Song L, Huang R, Han Z, Gong G, Bi Y (2018) Connectivity of the ventral visual cortex is necessary for object recognition in patients [J]. Hum Brain Mapp 39(7):2786–2799
Ptak R, Lazeyras F (2019) Functional connectivity and the failure to retrieve meaning from shape in visual object agnosia [J]. Brain Cogn 131(1):94–101
Alameer A, Ghazaei G, Degenaar P, Chambers JA, Nazarpour K (2016) Object recognition with an elastic net-regularized hierarchical MAX model of the visual cortex [J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters 23(8):1062–1066
Nau M, Schroder TN, Bellmund JLS et al (2018) Hexadirectional coding of visual space in human entorhinal cortex [J]. Nat Neurosci 21(2):188–199
An J, Hsiao JH (2021) Modulation of mood on eye movement and face recognition performance [J]. Emotion 21(3):617–630
Hafting T, Fyhn M, Molden S, Moser MB, Moser EI (2005) Microstructure of a spatial map in the entorhinal cortex [J]. Nature 436(7052):801–806
Muja M, Lowe DG (2014) Scalable nearest neighbor algorithms for high dimensional data [J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 36(11):2227–2240
Liu K, Skibbe H, Schmidt T, Blein T, Palme K, Brox T, Ronneberger O (2014) Rotation-invariant HOG descriptors using fourier analysis in polar and spherical coordinates [J]. Int J Comput Vis 106(3):342–364
Yang J, Lu Z, Tang YY, Yuan Z, Chen Y (2020) Quasi Fourier-Mellin transform for affine invariant features [J]. IEEE Trans Image Process 29(1):4114–4129
Mennesson J, Saint-Jean C, Mascarilla L (2014) Color Fourier-Mellin descriptors for image recognition [J]. Pattern Recogn Lett 40(1):27–35
Yu L, Zhou K, Yang Y, Chen H (2017) Bionic RSTN invariant feature extraction method for image recognition and its application [J]. IET Image Process 11(4):227–236
Deng L, Wang Y, Liu B, Liu W, Qi Y (2018) Biological modeling of human visual system for object recognition using GLoP filters and sparse coding on multi-manifolds [J]. Mach Vis Appl 29(6):965–977
Henderson JM, Weeks PA, Hollingworth A (1999) The effects of semantic consistency on eye movements during complex scene viewing [J]. Journal of Experimental Psychology-Human Perception and Performance 25(1):210–228
Erdem UM, Hasselmo M (2012) A goal-directed spatial navigation model using forward trajectory planning based on grid cells [J]. Eur J Neurosci 35(6):916–931
Bush D, Barry C, Manson D, Burgess N (2015) Using grid cells for navigation [J]. Neuron 87(3):507–520
Peng L, Chen L, Wu M, Chen G (2019) Complex activity recognition using acceleration, vital sign, and location data [J]. IEEE Trans Mob Comput 18(7):1488–1498
Sherrill KR, Chrastil ER, Ross RS, Erdem UM, Hasselmo ME, Stern CE (2015) Functional connections between optic flow areas and navigationally responsive brain regions during goal-directed navigation [J]. Neuroimage 118(1):386–396
Saleem AB, Diamanti EM, Fournier J, Harris KD, Carandini M (2018) Coherent encoding of subjective spatial position in visual cortex and hippocampus [J]. Nature 562(7725):124–142
Bicanski A, Burgess N (2019) A computational model of visual recognition memory via grid cells [J]. Curr Biol 29(6):979–995
Cheon SH, Eom IK, Moon YH (2016) Fast descriptor extraction method for a SURF-based interest point [J]. Electron Lett 52(4):274–275
Jayech K, Mahjoub M A. Object recognition based on dynamic random forests and SURF descriptor [C]// International Conference on Intelligent Data Engineering and Automated Learning. 2017: 355–364
Nasibov EN, Ulutagay G (2009) Robustness of density-based clustering methods with various neighborhood relations [J]. Fuzzy Sets Syst 160(24):3601–3615
Kryszkiewicz M, Lasek P. TI-DBSCAN: clustering with DBSCAN by means of the triangle inequality [C]// International Conference on Rough Sets & Current Trends in Computing. 2010: 60–69
Luchi D, Rodrigues AL, Varejao FM (2019) Sampling approaches for applying DBSCAN to large datasets [J]. Pattern Recogn Lett 117(1):90–96
Schubert E, Sander J, Ester M, Kriegel HP, Xu X (2017) DBSCAN revisited, revisited: why and how you should (still) use DBSCAN [J]. ACM Trans Database Syst 42(3):1–21
Mcnaughton BL, Battaglia FP, Jensen O et al (2006) Path integration and the neural basis of the 'cognitive map' [J]. Nat Rev Neurosci 7(8):663–678
Fiete IR, Burak Y, Brookings T (2008) What grid cells convey about rat location [J]. J Neurosci 28(27):6858–6871
Xie Y, Liu L-F, Li C-H et al (2009) Unifying visual saliency with HOG feature learning for traffic sign detection [C]//. IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium 2009:24–29
Senthilkumar R, Gnanamurthy RK (2016) A comparative study of 2DPCA face recognition method with other statistically based face recognition methods [J]. Journal of The Institution of Engineers 97(3):425–430
Agrawal G, Maurya S K. Synthetically occluded face recognition using local complex binary pattern [C]// 2014 International Conference on Data Mining and Intelligent Computing (ICDMIC). 2014: 1–5
Wu CY, Ding JJ (2018) Occluded face recognition using low-rank regression with generalized gradient direction [J]. Pattern Recogn 80(1):256–268
Trigueros DS, Meng L, Hartnett M (2018) Enhancing convolutional neural networks for face recognition with occlusion maps and batch triplet loss [J]. Image Vis Comput 79(1):99–108
Zheng W, Gou C, Wang F-Y (2020) A novel approach inspired by optic nerve characteristics for few-shot occluded face recognition [J]. Neurocomputing 376(1):25–41
Zeng D, Veldhuis R, Spreeuwers L et al (2021) Occlusion‐invariant face recognition using simultaneous segmentation. In: Occlusion-invariant face recognition using simultaneous segmentation [J]. IET Biometrics
Maghari AYA (2021) Recognition of partially occluded faces using regularized ICA [J]. Inverse Problems in Science and Engineering 29(8):1158–1177
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61976224 and 61976088.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approvals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, M., Yu, L., Zhou, K. et al. Occlusion tolerant object recognition using visual memory selection model. Appl Intell 52, 15575–15599 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03253-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03253-5