Abstract
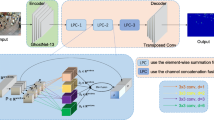
Accurate crowd counting is still challenging due to the variations of crowd heads. Most of crowd counting methods adopt multi-branch networks to extract multi-scale information. However, these networks are too complex to be optimized. To solve these problems, we propose an efficient scale-aware crowd counting network named SC2Net, which adopts the encoder-decoder framework. The encoder uses the first ten layers of VGG16 to extract the primary feature information. The decoder is mainly consisted of our proposed residual pyramid dilated convolution (ResPyDConv) modules to regress predicted density maps. Specifically, the ResPyDConv module is composed of pyramid dilated convolution (PyDConv). Each PyDConv adopts dilated convolutions with different dilated rates. PyDConv divides feature maps into different groups and extracts multi-scale feature information. Extensive experiments are conducted on ShanghaiTech, UCF_CC_50, UCF_QNRF, and NWPU_Crowd datasets. Qualitative and quantitive results show the superiority of our proposed network to the other state-of-the-art methods.





Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Liu J, Gao C, Meng D, Hauptmann AG (2018) Decidenet: Counting varying density crowds through attention guided detection and density estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 5197–5206
Shi Z, Zhang L, Liu Y, Cao X, Ye Y, Cheng M-M, Zheng G (2018) Crowd counting with deep negative correlation learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 5382–5390
Sheng B, Shen C, Lin G, Li J, Yang W, Sun C (2016) Crowd counting via weighted vlad on a dense attribute feature map. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 28(8):1788–1797
Li Y, Zhang X, Chen D (2018) Csrnet: Dilated convolutional neural networks for understanding the highly congested scenes. In: Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1091–1100
Chen X, Bin Y, Sang N, Gao C (2019) Scale pyramid network for crowd counting. In: Winter conference on applications of computer vision, IEEE, pp 1941–1950
Saqib M, Khan SD, Sharma N, Blumenstein M (2019) Crowd counting in low-resolution crowded scenes using region-based deep convolutional neural networks. IEEE Access 7:35317–35329
Cao X, Wang Z, Zhao Y, Su F (2018) Scale aggregation network for accurate and efficient crowd counting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 734–750
Sindagi VA, Patel VM (2017) Generating high-quality crowd density maps using contextual pyramid cnns. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision, pp 1861–1870
Deb D, Ventura J (2018) An aggregated multicolumn dilated convolution network for perspective-free counting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops, pp 195–204
Sam DB, Surya S, Babu RV (2017) Switching convolutional neural network for crowd counting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, IEEE, pp 4031–4039
Gao J, Wang Q, Li X (2019) Pcc net: Perspective crowd counting via spatial convolutional network. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 30(10):3486–3498
Zhang Y, Zhou D, Chen S, Gao S, Ma Y (2016) Single-image crowd counting via multi-column convolutional neural network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 589–597
Sindagi VA, Patel VM (2017) Generating high-quality crowd density maps using contextual pyramid cnns. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision, pp 1861–1870
Babu Sam D, Surya S, Venkatesh Babu R (2017) Switching convolutional neural network for crowd counting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition , pp 5744–5752
Duta IC, Liu L, Zhu F, Shao L (2020) Pyramidal convolution: Rethinking convolutional neural networks for visual recognition. arXiv:2006.11538
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2014) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv:1409.1556
Liu J, Gao C, Meng D, Hauptmann A G (2018) Decidenet: Counting varying density crowds through attention guided detection and density estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 5197–5206
Liu N, Long Y, Zou C, Niu Q, Pan L, Wu H (2019) Adcrowdnet: An attention-injective deformable convolutional network for crowd understanding. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition , pp 3225–3234
Liu W, Salzmann M, Fua P (2019) Context-aware crowd counting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern, pp 5099–5108
Liu L, Qiu Z, Li G, Liu S, Ouyang W, Lin L (2019) Crowd counting with deep structured scale integration network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision, pp 1774–1783
Qiu Z, Liu L, Li G, Wang Q, Xiao N, Lin L (2019) Crowd counting via multi-view scale aggregation networks. In: 2019 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), IEEE, pp 1498–1503
Yan R, Gong S, Zhong S (2019) Crowd counting via scale-adaptive convolutional neural network in extremely dense crowd images. Int J Comput Appl Technol 61(4):318–324
Zhou T, Li L, Li X, Feng C-M, Li J, Shao L (2022) Group-wise learning for weakly supervised semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans Image Process 31:799–811
Wang B, Zhao Y, Li X (2022) Multiple instance graph learning for weakly supervised remote sensing object detection. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 60:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2021.3123231
Lai Q, Zhou T, Khan S, Sun H, Shen J, Shao L (2022) Weakly supervised visual saliency prediction. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2022.3158064
Yang L, Han J, Zhao T, Lin T, Zhang D, Chen J (2021) Background-click supervision for temporal action localization. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3132058
Wang W, Zhou T, Qi S, Shen J, Zhu S-C (2021) Hierarchical human semantic parsing with comprehensive part-relation modeling. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3055780
Zhou T, Li J, Wang S, Tao R, Shen J (2020) Matnet: Motion-attentive transition network for zero-shot video object segmentation. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:8326–8338
Zhou T, Wang S, Zhou Y, Yao Y, Li J, Shao L (2020) Motion-attentive transition for zero-shot video object segmentation. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, vol 34, pp 13066–13073
Zhang A, Shen J, Xiao Z, Zhu F, Zhen X, Cao X, Shao L (2019) Relational attention network for crowd counting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision, pp 6788–6797
Sindagi VA, Patel VM (2019) Ha-ccn: Hierarchical attention-based crowd counting network. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:323–335
Gao J, Wang Q, Yuan Y (2019) Scar: Spatial-/channel-wise attention regression networks for crowd counting. Neurocomputing 363:1–8
Zhang A, Yue L, Shen J, Zhu F, Zhen X, Cao X, Shao L (2019) Attentional neural fields for crowd counting. In: iccv, pp 5714–5723
Guo D, Li K, Zha Z-J, Wang M (2019) Dadnet: Dilated-attention-deformable convnet for crowd counting. In: IEEE International confer ence on multimedia & expo workshops, pp 1823–1832
Kong W, Li H, Xing G, Zhao F (2019) An automatic scale-adaptive approach with attention mechanism-based crowd spatial information for crowd counting. IEEE Access 7:66215–66225
Wang S, Lu Y, Zhou T, Di H, Lu L, Zhang L (2020) Sclnet: Spatial context learning network for congested crowd counting. Neurocomputing 404:227–239
Duan Z, Xie Y, Deng J (2020) Hagn: Hierarchical attention guided network for crowd counting. IEEE Access 8:36376–36385
Liu Y-B, Jia R-S, Liu Q-M, Zhang X-L, Sun H-M (2021) Crowd counting method based on the self-attention residual network. Appl Intell 51(1):427–440
Gu L, Pang C, Zheng Y, Lyu C, Lyu L (2021) Context-aware pyramid attention network for crowd counting. Applied Intelligence, 1–17
Shi Y, Sang J, Wu Z, Wang F, Liu X, Xia X, Sang N (2022) Mgsnet: A multi-scale and gated spatial attention network for crowd counting. Applied Intelligence, 1–11
Li Y-C, Jia R-S, Hu Y-X, Han D-N, Sun H-M (2022) Crowd density estimation based on multi scale features fusion network with reverse attention mechanism. Applied Intelligence, 1–17
Zhang S, Zhang X, Li H, He H, Song D, Wang L (2022) Hierarchical pyramid attentive network with spatial separable convolution for crowd counting. Eng Appl Artif Intell 108:104563
Sindagi VA, Patel VM (2019) Ha-ccn: Hierarchical attention-based crowd counting network. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:323–335
Song Q, Wang C, Wang Y, Tai Y, Wang C, Li J, Wu J, Ma J (2021) To choose or to fuse? scale selection for crowd counting. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol 35, pp 2576–2583
Wang Y, Hu S, Wang G, Chen C, Pan Z (2020) Multi-scale dilated convolution of convolutional neural network for crowd counting. Multimed Tools Appl 79(1):1057–1073
Ilyas N, Ahmad A, Kim K (2019) Casa-crowd: A context-aware scale aggregation cnn-based crowd counting technique. IEEE Access 7:182050–182059
Wang W, Liu Q, Wang W (2022) Pyramid-dilated deep convolutional neural network for crowd counting. Appl Intell 52(2):1825–1837
Yang Y, Li G, Du D, Huang Q, Sebe N (2020) Embedding perspective analysis into multi-column convolutional neural network for crowd counting. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:1395–1407
Jiang X, Xiao Z, Zhang B, Zhen X, Cao X, Doermann D, Shao L (2019) Crowd counting and density estimation by trellis encoder-decoder networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 6133–6142
Yan Z, Yuan Y, Zuo W, Tan X, Wang Y, Wen S, Ding E (2019) Perspective-guided convolution networks for crowd counting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision, pp 952–961
Liu Q, Guo Y, Sang J, Tan J, Wang F, Tian S (2022) Sgcnet: Scale-aware and global contextual network for crowd counting. Applied Intelligence, 1–12
He J, Deng Z, Zhou L, Wang Y, Qiao Y (2019) Adaptive pyramid context network for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 7519–7528
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 770–778
Shi Z, Mettes P, Snoek Cees GM (2019) Counting with focus for free. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision, pp 4200–4209
Xu C, Qiu K, Fu J, Bai S, Xu Y, Bai X (2019) Learn to scale: Generating multipolar normalized density maps for crowd counting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision, pp 8382–8390
Idrees H, Saleemi I, Seibert C, Shah M (2013) Multi-source multi-scale counting in extremely dense crowd images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2547–2554
Idrees H, Tayyab M, Athrey K, Zhang D, Al-Maadeed S, Rajpoot N, Shah M (2018) Composition loss for counting, density map estimation and localization in dense crowds. In: Proceedings of the european conference on computer vision, pp 532–546
Wang Q, Gao J, Lin W, Li X (2020) Nwpu-crowd: A large-scale benchmark for crowd counting and localization. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 43(6):2141–2149
Liu C, Weng X, Mu Y (2019) Recurrent attentive zooming for joint crowd counting and precise localization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1217–1226
Sajid U, Wang G (2020) Plug-and-play rescaling based crowd counting in static images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF winter conference on applications of computer vision, pp 2287–2296
Sajid U, Ma W, Wang G (2021) Multi-resolution fusion and multi-scale input priors based crowd counting. In: 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), IEEE, pp 5790–5797
Sajid U, Sajid H, Wang H, Wang G (2020) Zoomcount: A zooming mechanism for crowd counting in static images. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 30(10):3499–3512
Wang B, Liu H, Samaras D, Nguyen MH (2020) Distribution matching for crowd counting. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 33:1595–1607
Ren S, He K, Girshick R, Sun J (2015) Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Adv Neural Information Processing Syst, vol 28
Ozkaya U, Melgani F, Bejiga MB, Seyfi L, Donelli M (2020) Gpr b scan image analysis with deep learning methods. Measurement 165:107770
Attia A, Dayan S (2018) Detecting and counting tiny faces. arXiv:1801.06504
Iandola F, Moskewicz M, Karayev S, Girshick R, Darrell T, Keutzer K (2014) Densenet: Implementing efficient convnet descriptor pyramids. arXiv:1404.1869
Chen L-C, Zhu Y, Papandreou G, Schroff F, Adam H (2018) Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 801–818
Ma J, Dai Y, Tan Y-P (2019) Atrous convolutions spatial pyramid network for crowd counting and density estimation. Neurocomputing 350:91–101
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai under Grant No. 19ZR1455300, National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 61806126, and Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province under Grant No. F2019201451.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, L., Zhao, H., Zhou, F. et al. SC2Net: Scale-aware Crowd Counting Network with Pyramid Dilated Convolution. Appl Intell 53, 5146–5159 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03648-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03648-4