Abstract
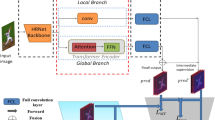
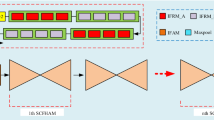
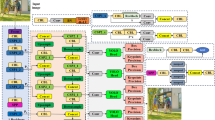
Human pose estimation is a fundamental and challenging task in the field of computer vision. Hard scenarios, such as occlusion and background confusion, set a great challenge for high-level feature representation because both detailed and multi-scale context must be correctly reasoned. In this paper, we propose a structure-context complementary network (SCC-Net) characterized by the complementarity between a pixel-wise enhanced attention mechanism and atrous convolution-based module. The proposed cross-coordinate attention bottleneck (CCAB) aims to utilize a cross-guide mechanism to promote the robustness of the existing coordinate attention module (CAM) for the background impact. As a complementary module for CCAB, waterfall residual atrous pooling (WRAP) is proposed to refine structure consistency by generating multi-scale features without the feature sparse defect of atrous-based methods. We evaluate our proposed modules and holistic SCC-Net on the COCO and MPII benchmark datasets. Ablation experiments demonstrate that our proposed modules can efficiently boost the performance of body joint detection. Competitive performance is also achieved by our holistic SCC-Net compared to other state-of-the-art methods.









Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Andriluka M, Pishchulin L, Gehler P, Schiele B (2014) 2d human pose estimation: New benchmark and state of the art analysis. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3686–3693
Artacho B, Savakis A (2020) Unipose: Unified human pose estimation in single images and videos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 7035–7044
Artacho B, Savakis A (2021) Unipose+: A unified framework for 2d and 3d human pose estimation in images and videos IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence
Bello I, Zoph B, Vaswani A, Shlens J, Le QV (2019) Attention augmented convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, pp 3286–3295
Bi HB, Lu D, Zhu HH, Yang LN, Guan HP (2021) STA-net: spatial-temporal attention network for video salient object detection. Appl Intell 51(6):3450–3459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-01961-4https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-01961-4
Cao Z, Hidalgo G, Simon T, Wei SE, Sheikh Y (2021) Openpose: Realtime multi-person 2d pose estimation using part affinity fields. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 43(01):172–186
Carion N, Massa F, Synnaeve G, Usunier N, Kirillov A, Zagoruyko S (2020) End-to-end object detection with transformers. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 213–229
Chen K, Wang J, Pang J, Cao Y, Xiong Y, Li X, Sun S, Feng W, Liu Z, Xu J et al (2019) Mmdetection: Open mmlab detection toolbox and benchmark. arXiv:1906.07155
Chen LC, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, Murphy K, Yuille AL (2018) Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 40(4):834–848. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184
Chen X, Yuille A (2014) Articulated pose estimation by a graphical model with image dependent pairwise relations. In: Proceedings of the 27th International conference on neural information processing systems-volume 1, pp 1736–1744
Chen Y, Kalantidis Y, Li J, Yan S, Feng J (2018) A 2-nets: double attention networks. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, pp 350–359
Chen Y, Wang Z, Peng Y, Zhang Z, Yu G, Sun J (2018) Cascaded pyramid network for multi-person pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 7103–7112
Chu X, Ouyang W, Wang X, et al. (2016) Crf-cnn: Modeling structured information in human pose estimation. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 29:316–324
Chu X, Yang W, Ouyang W, Ma C, Yuille AL, Wang X (2017) Multi-context attention for human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1831–1840
Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, Li LJ, Li K, Fei-Fei L (2009) Imagenet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: 2009 IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, pp 248–255
Ding H, Jiang X, Shuai B, Liu AQ, Wang G (2018) Context contrasted feature and gated multi-scale aggregation for scene segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2393–2402
Dong L, Chen X, Wang R, Zhang Q, Izquierdo E (2017) Adore: An adaptive holons representation framework for human pose estimation. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology
Dong X, Yu J, Zhang J (2022) Joint usage of global and local attentions in hourglass network for human pose estimation. Neurocomputing 472:95–102
Fan H, Zhuo T, Yu X, Yang Y, Kankanhalli M (2021) Understanding atomic hand-object interaction with human intention IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 770–778
He T, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Zhang Z, Xie J, Li M (2019) Bag of tricks for image classification with convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 558–567
Hou Q, Zhou D, Feng J (2021) Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 13713–13722
Hu J, Shen L, Albanie S, Sun G, Vedaldi A (2018) Gather-excite: Exploiting feature context in convolutional neural networks. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 31:9401–9411
Hu J, Shen L, Sun G (2018) Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 7132–7141
Hua G, Li L, Liu S (2020) Multipath affinage stacked—hourglass networks for human pose estimation. Front Comput Sci 14(4):1–12
Huang J, Zhou W, Li H, Li W (2018) Attention-based 3d-cnns for large-vocabulary sign language recognition. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 29(9):2822–2832
Huang Z, Ke W, Huang D (2020) Improving object detection with inverted attention. In: 2020 IEEE Winter conference on applications of computer vision (WACV). IEEE, pp 1294–1302
Huang Z, Wang X, Huang L, Huang C, Wei Y, Liu W (2019) Ccnet: Criss-cross attention for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International conference on computer vision, pp 603–612
Ke L, Chang MC, Qi H, Lyu S (2018) Multi-scale structure-aware network for human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the european conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 713–728
Khirodkar R, Chari V, Agrawal A, Tyagi A (2021) Multi-instance pose networks: Rethinking top-down pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International conference on computer vision, pp 3122–3131
Kong K, Shin S, Lee J, Song WJ (2018) How to estimate global motion non-iteratively from a coarsely sampled motion vector field. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 29(12):3729–3742
Kreiss S, Bertoni L, Alahi A (2019) Pifpaf: Composite fields for human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 11977–11986
Li Y, Zhang S, Wang Z, Yang S, Yang W, Xia ST, Zhou E (2021) Tokenpose: Learning keypoint tokens for human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International conference on computer vision, pp 11313–11322
Lin TY, Maire M, Belongie S, Hays J, Perona P, Ramanan D, Dollár P, Zitnick CL (2014) Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 740–755
Linsley D, Shiebler D, Eberhardt S, Serre T (2019) Learning what and where to attend. In: International conference on learning representations
Liu JJ, Hou Q, Cheng MM, Wang C, Feng J (2020) Improving convolutional networks with self-calibrated convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 10096–10105
Liu S, Bai X, Fang M, Li L, Hung CC (2021) Mixed graph convolution and residual transformation network for skeleton-based action recognition. Applied Intelligence p 1–12
Luo Y, Xu Z, Liu P, Du Y, Guo JM (2018) Multi-person pose estimation via multi-layer fractal network and joints kinship pattern. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(1):142–155
Misra D, Nalamada T, Arasanipalai AU, Hou Q (2021) Rotate to attend: Convolutional triplet attention module. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter conference on applications of computer vision, pp 3139–3148
Mo S, Cai M, Lin L, Tong R, Chen Q, Wang F, Hu H, Iwamoto Y, Han XH, Chen YW (2021) Mutual information-based graph co-attention networks for multimodal prior-guided magnetic resonance imaging segmentation IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology
Newell A, Yang K, Deng J (2016) Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 483–499
Nie X, Feng J, Xing J, Xiao S, Yan S (2018) Hierarchical contextual refinement networks for human pose estimation. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(2):924–936
Nie X, Feng J, Zhang J, Yan S (2019) Single-stage multi-person pose machines. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International conference on computer vision, pp 6951–6960
Park J, Woo S, Lee JY, Kweon IS (2018) Bam: Bottleneck attention module. arXiv:1807.06514
Peng G, Zheng Y, Li J, Yang J (2021) A single upper limb pose estimation method based on the improved stacked hourglass network. Int J Appl Math Comput Sci 31(1):123–133
Ruggero Ronchi M, Perona P (2017) Benchmarking and error diagnosis in multi-instance pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 369–378
Selvaraju RR, Cogswell M, Das A, Vedantam R, Parikh D, Batra D (2017) Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 618–626
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2014) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv:1409.1556
Song K, Yang H, Yin Z (2018) Multi-scale attention deep neural network for fast accurate object detection. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 29(10):2972–2985
Su K, Yu D, Xu Z, Geng X, Wang C (2019) Multi-person pose estimation with enhanced channel-wise and spatial information. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 5674–5682
Sun K, Xiao B, Liu D, Wang J (2019) Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 5693–5703
Tompson JJ, Jain A, LeCun Y, Bregler C (2014) Joint training of a convolutional network and a graphical model for human pose estimation. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 27:1799–1807
Tong H, Fang Z, Wei Z, Cai Q, Gao Y (2021) Sat-net: a side attention network for retinal image segmentation. Appl Intell 51(7):5146–5156
Tsotsos JK (1990) Analyzing vision at the complexity level. Behav Brain Sci 13(3):423–445
Tsotsos JK (2011) A computational perspective on visual attention
Wan T, Luo Y, Zhang Z, Ou Z (2022) Tsnet: Tree structure network for human pose estimation. 2 16:551–558
Wei SE, Ramakrishna V, Kanade T, Sheikh Y (2016) Convolutional pose machines. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 4724–4732
Woo S, Park J, Lee JY, Kweon IS (2018) Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 3–19
Wu H, Ma X, Li Y (2021) Spatiotemporal multimodal learning with 3d cnns for video action recognition. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology
Xiang S, Chen X, Zhou J (2021) An efficient method for boosting human pose estimation. In: 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Broadband Multimedia Systems and Broadcasting (BMSB). https://doi.org/10.1109/BMSB53066.2021.9547183, pp 1–6
Xiao B, Wu H, Wei Y (2018) Simple baselines for human pose estimation and tracking. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 466–481
Xie S, Girshick R, Dollár P, Tu Z, He K (2017) Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1492–1500
Xu X, Zou Q, Lin X Cfenet: Content-aware feature enhancement network for multi-person pose estimation. Applied Intelligence p 1–22
Yang S, Quan Z, Nie M, Yang W (2020) Transpose: Towards explainable human pose estimation by transformer. arXiv:2012.14214
Yang Y, Ramanan D (2011) Articulated pose estimation with flexible mixtures-of-parts. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1385–1392
Zhang H, Ouyang H, Liu S, Qi X, Shen X, Yang R, Jia J (2019) Human pose estimation with spatial contextual information. arXiv:1901.01760
Zhao L, Wang N, Gong C, Yang J, Gao X (2021) Estimating human pose efficiently by parallel pyramid networks. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:6785–6800
Zhu Z, Xu M, Bai S, Huang T, Bai X (2019) Asymmetric non-local neural networks for semantic segmentation. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF International conference on computer vision (ICCV)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 61902404, 62001475, 62071472, in part by the Program for “Industrial IoT and Emergency Collaboration” Innovative Research Team in China University of Mining and Technology (CUMT) under Grant 2020ZY002, in part by the Special Fund for cultivating major projects in China University of Mining and Technology (CUMT) under Grand 2020-10991, in part by the Graduate Research and Innovation Projects of Jiangsu Province (KYCX21_2241), in part by China Scholarship Council under Grand 202106420091, and in part by the Yulin smart energy big data application joint Key Laboratory under Grant 202100208-01.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, K., Sun, Y., Cheng, X. et al. Combining detailed appearance and multi-scale representation: a structure-context complementary network for human pose estimation. Appl Intell 53, 8097–8113 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03909-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03909-2