Abstract
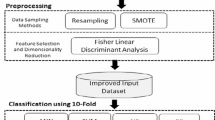
Software Fault Prediction (SFP) is an important process to detect the faulty components of the software to detect faulty classes or faulty modules early in the software development life cycle. In this paper, a machine learning framework is proposed for SFP. Initially, pre-processing and re-sampling techniques are applied to make the SFP datasets ready to be used by ML techniques. Thereafter seven classifiers are compared, namely K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), Naive Bayes (NB), Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA), Linear Regression (LR), Decision Tree (DT), Support Vector Machine (SVM), and Random Forest (RF). The RF classifier outperforms all other classifiers in terms of eliminating irrelevant/redundant features. The performance of RF is improved further using a dimensionality reduction method called binary whale optimization algorithm (BWOA) to eliminate the irrelevant/redundant features. Finally, the performance of BWOA is enhanced by hybridizing the exploration strategies of the grey wolf optimizer (GWO) and harris hawks optimization (HHO) algorithms. The proposed method is called SBEWOA. The SFP datasets utilized are selected from the PROMISE repository using sixteen datasets for software projects with different sizes and complexity. The comparative evaluation against nine well-established feature selection methods proves that the proposed SBEWOA is able to significantly produce competitively superior results for several instances of the evaluated dataset. The algorithms’ performance is compared in terms of accuracy, the number of features, and fitness function. This is also proved by the 2-tailed P-values of the Wilcoxon signed ranks statistical test used. In conclusion, the proposed method is an efficient alternative ML method for SFP that can be used for similar problems in the software engineering domain.















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Abbreviations
- AAE:
-
Average absolute error
- ABC:
-
Artificial bee colony
- ACO:
-
Ant colony optimization
- ADASYN:
-
Adaptive synthetic sampling method
- ALO:
-
Ant lion optimizer
- ANN:
-
Artificial neural networks
- ARE:
-
Average Relative Error
- ASD:
-
Agile software development model
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- BBAT:
-
Binary bat algorithm
- BCS:
-
Binary cuckoo search
- BFFA:
-
Binary firefly algorithm
- BGWO:
-
Binary grey wolf optimization
- BHHO:
-
Binary harris hawk optimization
- BJAYA:
-
Binary jaya algorithm
- BMFO:
-
Binary moth flame optimization
- BN:
-
Bayesian networks
- BQSA:
-
Binary queuing search algorithm
- BWOA:
-
Binary whale optimization algorithm
- CBL:
-
Case-based learning
- COA:
-
Coyote optimization algorithm
- CS:
-
Chi-square
- CSA:
-
Crow search algorithm
- DA:
-
Dragonfly algorithm
- DE:
-
Differential evolution
- DT:
-
Decision tree
- EA:
-
Evolutionary algorithm
- FFA:
-
Firefly algorithm
- FIS:
-
Fuzzy inference system
- FN:
-
False negative
- FP:
-
False positive
- FS:
-
Feature selection
- GA:
-
genetic algorithm
- GBRCR:
-
Gradient boosting regression-based combination rule
- GOA:
-
Grasshopper optimization algorithm
- GP:
-
Genetic programming
- GWO:
-
Grey wolf optimizer
- HHO:
-
Harris hawks optimization
- IG:
-
information gain
- KNN:
-
K-nearest neighbors
- LDA:
-
Linear discriminant analysis
- LR:
-
Linear regression
- LRCR:
-
linear regression-based combination rule
- ML:
-
Machine learning
- MLP:
-
Multi-layer perceptron
- MLR:
-
Multi-nomial logistic regression
- MVO:
-
multiverse optimizer
- NB:
-
Naive Bayes
- OO:
-
Object-Oriented
- PCA:
-
Principle component analysis
- PCC:
-
Pearson correlation coefficient
- PSO:
-
Particle swarm optimization
- QMOOD:
-
Quality metrics for object-oriented design
- RF:
-
Random forest
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- SBWOA:
-
Binary whale optimization algorithm with S-shaped transfer function
- SBEWOA:
-
Enhanced SBWOA
- SC:
-
Soft computing
- SDLC:
-
Software sevelopment life cycle
- SDP:
-
Software defect prediction
- SFP:
-
Software fault prediction
- SMOTE:
-
Synthetic minority oversampling technique
- SSA:
-
Salp swarm algorithm
- SVM:
-
Support vector machine
- TF:
-
Transfer function
- TN:
-
True negative
- TNR:
-
True negative rate
- TP:
-
True positive
- TPR:
-
True positive rate
- VBWOA:
-
Binary whale optimization algorithm with V-shaped transfer function
- WOA:
-
Whale optimization algorithm
References
Honest N (2019) Role of testing in software development life cycle. Int J Comput Sci Eng 7 (05):886–889
Turabieh H, Mafarja M, Li X (2018) Iterated feature selection algorithms with layered recurrent neural network for software fault prediction. Expert Syst Appl 122:12
Tumar I, Hassouneh Y, Turabieh H, Thaher T (2020) Enhanced binary moth flame optimization as a feature selection algorithm to predict software fault prediction. IEEE Access pp(01):1–1
Rathore S, Kumar S (2017) A study on software fault prediction techniques. Artif Intell Rev 05:1–73
Fowler M, Highsmith J et al (2001) The agile manifesto. Softw Dev 9(8):28–35
Royce WW (1987) Managing the development of large software systems: concepts and techniques, pp 1–9, August 1970. In: Reprinted in proceedings of the ninth international conference on software engineering, pp 328–338
Hoda R, Salleh N, Grundy J, Tee HM (2017) Systematic literature reviews in agile software development: a tertiary study. Inf Softw Technol 85:60–70
Rathore SS, Kumar S (2017) A decision tree logic based recommendation system to select software fault prediction techniques. Computing 99:255–285
Gupta D, Saxena K (2017) Software bug prediction using object-oriented metrics. Sadhana - Acad Proc Eng Sci 42(05):655–669
Catal C, Diri B (2009) A systematic review of software fault prediction studies. Expert Syst Appl 36(05):7346–7354
Halstead MH (1977) Elements of software science (operating and programming systems series) USA: Elsevier science inc
McCabe TJ (1976) A complexity measure, IEEE. Trans Softw Eng SE-2(4):308–320
Chidamber SR, Kemerer CF (1994) A metrics suite for object oriented design. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 20(6):476–493
Lorenz M, Kidd J (1994) Object-oriented software metrics: a practical guide. Prentice-Hall, Inc
Bansiya J, Davis CG (2002) A hierarchical model for object-oriented design quality assessment. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 28(1):4–17
Deep Singh P, Chug A (2017) Software defect prediction analysis using machine learning algorithms. In: 2017 7th International conference on cloud computing, data science engineering - confluence, pp 775–781
Qasem O, Akour M (2019) Software fault prediction using deep learning algorithms. Int J Open Source Softw Process 10(10): 1–19
Oliveira J, Pontes K, Sartori I, Embiruçu M (2017) Fault detection and diagnosis in dynamic systems using weightless neural networks. Expert Syst Appl 84:05
Dong X, Yu Z, Cao W, Shi Y, Ma Q (2019) A survey on ensemble learning. Frontiers Comput Sci 14(08):241–258
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45(1):5–32
Parmar A, Katariya R, Patel V (2019) A review on random forest: an ensemble classifier. In: Hemanth J, Fernando X, Lafata P, Baig Z (eds) International conference on intelligent data communication technologies and internet of things (ICICI) 2018. Springer international publishing, Cham, pp 758–763
Shaik AB, Srinivasan S (2019) A brief survey on random forest ensembles in classification model. In: Bhattacharyya S, Hassanien AE, Gupta D, Khanna A, Pan I (eds) International conference on innovative computing and communications. Singapore, Springer Singapore pp 253–260
Khoshgoftaar T, Van Hulse J, Napolitano A (2011) Comparing boosting and bagging techniques with noisy and imbalanced data. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part A 41(05):552–568
Dash M, Liu H (1997) Feature selection for classification. Intell Data Anal 1(3):131–156
Mafarja MM, Mirjalili S (2017) Hybrid whale optimization algorithm with simulated annealing for feature selection. Neurocomputing 260:302–312
Liu H, Motoda H (2012) Feature selection for knowledge discovery and data mining. Springer science & business media, vol 454
Talbi E-G (2009) Metaheuristics: from design to implementation. Wiley, vol 74
Boussaïd I, Lepagnot J, Siarry P (2013) A survey on optimization metaheuristics. Inf Sci 237:82–117
Zhang H, Sun G (2002) Feature selection using tabu search method. Pattern Recognit 35 (3):701–711
Al-Betar MA, Hammouri AI, Awadallah MA, Doush IA (2021) Binary β-hill climbing optimizer with s-shape transfer function for feature selection. J Ambient Intell Humanized Comput 12(1):7637–7665
Boughaci D, Alkhawaldeh AA-S (2018) Three local search-based methods for feature selection in credit scoring. Vietnam J Comput Sci 5(2):107–121
Oreski S, Oreski G (2014) Genetic algorithm-based heuristic for feature selection in credit risk assessment. Expert Syst Appl 41(4):2052–2064
Ma J, Gao X (2020) A filter-based feature construction and feature selection approach for classification using genetic programming. Knowl-Based Syst 196:105806
Zhang Y, Gong D-W, Gao X-Z, Tian T, Sun X-Y (2020) Binary differential evolution with self-learning for multi-objective feature selection. Inf Sci 507:67–85
Wei B, Zhang W, Xia X, Zhang Y, Yu F, Zhu Z (2019) Efficient feature selection algorithm based on particle swarm optimization with learning memory. IEEE Access 7:166066–166078
Faris H, Mafarja MM, Heidari AA, Aljarah I, Ala’M A-Z, Mirjalili S, Fujita H (2018) An efficient binary salp swarm algorithm with crossover scheme for feature selection problems. Knowl-Based Syst 154:43–67
Kassaymeh S, Abdullah S, Al-Betar MA, Alweshah M (2022) Salp swarm optimizer for modeling the software fault prediction problem. J King Saud Univ-Comput Inf Sci 34(6):3365–3378
Hammouri AI, Mafarja M, Al-Betar MA, Awadallah MA, Abu-Doush I (2020) An improved dragonfly algorithm for feature selection. Knowl-Based Syst 203:106131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2020.106131
Awadallah MA, Al-Betar MA, Braik MS, Hammouri AI, Doush IA, Zitar RA (2022) An enhanced binary rat swarm optimizer based on local-best concepts of pso and collaborative crossover operators for feature selection. Comput Bio Med 147:105675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105675
Mafarja MM, Mirjalili S (2019) Hybrid binary ant lion optimizer with rough set and approximate entropy reducts for feature selection. Soft Comput 23(15):6249–6265
Sawalha R, Doush IA (2012) Face recognition using harmony search-based selected features. Int J Hybrid Inf Technol 5(2): 1–16
Alweshah M, Alkhalaileh S, Al-Betar MA, Bakar AA (2022) Coronavirus herd immunity optimizer with greedy crossover for feature selection in medical diagnosis. Knowl-Based Syst 235:107629
Paniri M, Dowlatshahi MB, Nezamabadi-pour H (2020) Mlaco: a multi-label feature selection algorithm based on ant colony optimization. Knowl-Based Syst 192:105285
Al-Betar MA, Hammouri AI, Awadallah MA, Abu Doush I (2021) Binary β-hill climbing optimizer with s-shape transfer function for feature selection. J Ambient Intell Humanized Comput 12(7):7637–7665
Sayed GI, Hassanien AE, Azar AT (2019) Feature selection via a novel chaotic crow search algorithm. Neural Comput Appl 31(1):171–188
Awadallah MA, Al-Betar MA, Hammouri AI, Alomari OA (2020) Binary jaya algorithm with adaptive mutation for feature selection. Arab J Sci Eng 45(12):10875–10890
Selvakumar B, Muneeswaran K (2019) Firefly algorithm based feature selection for network intrusion detection. Comput Security 81:148–155
Zhang Y, Cheng S, Shi Y, Gong D-W, Zhao X (2019) Cost-sensitive feature selection using two-archive multi-objective artificial bee colony algorithm. Expert Syst Appl 137:46–58
de Souza RCT, de Macedo CA, Dos Santos Coelho L, Pierezan J, Mariani VC (2020) Binary coyote optimization algorithm for feature selection. Pattern Recognit 107:107470
Aljarah I, Ala’M A-Z, Faris H, Hassonah MA, Mirjalili S, Saadeh H (2018) Simultaneous feature selection and support vector machine optimization using the grasshopper optimization algorithm. Cognit Computat 10(3):478–495
Karimi A, Irajimoghaddam M, Bastami E (2022) Feature selection using combination of genetic-whale-ant colony algorithms for software fault prediction by machine learning. Electr Cyber Defense, vol 10(1)
Rhmann W (2022) Software vulnerability prediction using grey wolf-optimized random forest on the unbalanced data sets. Int J Appl Metaheuristic Comput (IJAMC) 13(1):1–15
Kassaymeh S, Al-Laham M, Al-Betar MA, Alweshah M, Abdullah S, Makhadmeh SN (2022) Backpropagation neural network optimization and software defect estimation modelling using a hybrid salp swarm optimizer-based simulated annealing algorithm. Knowl-Based Syst 244:108511
Tameswar K, Suddul G, Dookhitram K (2022) A hybrid deep learning approach with genetic and coral reefs metaheuristics for enhanced defect detection in software. Int J Inf Manag Data Insights 2(2):100105
Zamani H, Nadimi-Shahraki MH, Gandomi AH (2022) Starling murmuration optimizer: a novel bio-inspired algorithm for global and engineering optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 392:114616
Zamani H, Nadimi-Shahraki MH, Gandomi AH (2021) Qana: quantum-based avian navigation optimizer algorithm. Eng Appl Artif Intell 104:104314
Shayanfar H, Gharehchopogh FS (2018) Farmland fertility: a new metaheuristic algorithm for solving continuous optimization problems. Appl Soft Comput 71:728–746
Abdollahzadeh B, Gharehchopogh FS, Mirjalili S (2021) African vultures optimization algorithm: a new nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithm for global optimization problems. Comput Industr Eng 158:107408
Abdollahzadeh B, Soleimanian Gharehchopogh F, Mirjalili S (2021) Artificial gorilla troops optimizer: a new nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithm for global optimization problems. Int J Intell Syst 36 (10):5887–5958
Mirjalili S, Lewis A (2016) The whale optimization algorithm. Adv Eng Softw 95:51–67
Mafarja M, Jaber I, Ahmed S, Thaher T (2021) Whale optimisation algorithm for high-dimensional small-instance feature selection. Int J Parallel Emergent Distributed Syst 36(2):80–96
Mafarja M, Mirjalili S (2018) Whale optimization approaches for wrapper feature selection. Appl Soft Comput 62:441–453
Mafarja M, Heidari AA, Habib M, Faris H, Thaher T, Aljarah I (2020) Augmented whale feature selection for iot attacks: structure, analysis and applications. Futur Gener Comput Syst 112:18–40
Nadimi-Shahraki MH, Zamani H, Mirjalili S (2022) Enhanced whale optimization algorithm for medical feature selection: a covid-19 case study. Comput Bio Med 148:105858
Zamani H, Nadimi-Shahraki M-H (2016) Feature selection based on whale optimization algorithm for diseases diagnosis. Int J Comput Sci Inf Security 14(9):1243
Wolpert D, Macready W (1997) No free lunch theorems for optimization. Evolutionary Computat IEEE 01:67–82
Singh A, Bhatia R, Singhrova A (2018) Taxonomy of machine learning algorithms in software fault prediction using object oriented metrics. Procedia Comput Sci 132:993–1001
Yogesh S, Arvinder K, Malhotra R (2009) Software fault proneness prediction using support vector machines. Lecture Notes Eng Comput Sci 2176:07
Khoshgoftaar TM, Seliya N (2003) Software quality classification modeling using the sprint decision tree algorithm. Int J Artif Intell Tools 12(03):207–225
Yuan X, Khoshgoftaar TM, Allen EB, Ganesan K (2000) An application of fuzzy clustering to software quality prediction. In: Application-specific systems and software engineering technology, 2000 proceedings. 3rd IEEE symposium on. IEEE, pp 85–90
Menzies T, Greenwald J, Frank A (2007) Data mining static code attributes to learn defect predictors. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 33(1):2–13
kumar Dwivedi V, Singh MK (2016) Software defect prediction using data mining classification approach. Int J Tech Res Appl 4:31–35
Carrozza G, Cotroneo D, Natella R, Pietrantuono R, Russo S (2013) Analysis and prediction of mandelbugs in an industrial software system. In: Software testing, verification and validation (ICST), 2013 IEEE sixth international conference on. IEEE, pp 262–271
Bisi M, Goyal N (2015) Early prediction of software fault-prone module using artificial neural network. Int J Performability Eng 01:43–52
Caglayan B, Tosun A, Bener A, Miranskyy A (2014) Predicting defective modules in different test phases. Softw Qual J 23:06
Bowes D, Hall T, Petrić J (2018) Software defect prediction: do different classifiers find the same defects? Softw Qual J 26(2):525–552
Thaher T, Khamayseh F (2021) A classification model for software bug prediction based on ensemble deep learning approach boosted with smote technique. In: Sharma H, Saraswat M, Yadav A, Kim JH, Bansal JC (eds) Congress on intelligent systems. (Singapore), Springer Singapore, pp 99–113
Cahill J, Hogan JM, Thomas R (2013) Predicting fault-prone software modules with rank sum classification. In: 2013 22nd Australian software engineering conference. IEEE, pp 211–219
Erturk E, Sezer E (2016) Iterative software fault prediction with a hybrid approach. Appl Soft Comput 49:08
Khoshgoftaar T, Xiao Y, Gao K (2014) Software quality assessment using a multi-strategy classifier. Inf Sci - ISCI 259:02
Carrozza G, Cotroneo D, Natella R, Pietrantuono R, Russo S (2013) Analysis and prediction of mandelbugs in an industrial software system, 03
Rathore S, Kumar S (2017) Towards an ensemble based system for predicting the number of software faults. Expert Syst Appl 82:04
Choudhary GR, Kumar S, Kumar K, Mishra A, Catal C (2018) Empirical analysis of change metrics for software fault prediction. Comput Electr Eng 67:15–24
Shatnawi R (2017) The application of roc analysis in threshold identification, data imbalance and metrics selection for software fault prediction. Innov Syst Softw Eng 13:201–217
Chantar H, Mafarja M, Alsawalqah H, Heidari AA, Aljarah I, Faris H (2020) Feature selection using binary grey wolf optimizer with elite-based crossover for arabic text classification. Neural Comput Appl 32(16):12201–12220
Catal C, Diri B (2009) Investigating the effect of dataset size, metrics sets, and feature selection techniques on software fault prediction problem. Inf Sci 179(03):1040–1058
Balogun AO, Basri S, Abdulkadir SJ, Hashim AS (2019) Performance analysis of feature selection methods in software defect prediction: a search method approach. Appl Sci 9(13):2764
Jia L (2018) A hybrid feature selection method for software defect prediction. In: IOP conference series: materials science and engineering. IOP publishing, vol 394, p 032035
Wahono RS, Herman NS (2014) Genetic feature selection for software defect prediction. Adv Sci Lett 20(1):239–244
Wahono RS, Suryana N, Ahmad S (2014) Metaheuristic optimization based feature selection for software defect prediction. J Softw 9(5):1324–1333
Thaher T, Arman N (2020) Efficient multi-swarm binary harris hawks optimization as a feature selection approach for software fault prediction. In: 2020 11th International conference on information and communication systems (ICICS), pp 249–254
Larranaga P, Calvo B, Santana R, Bielza C, Galdiano J, Inza I, Lozano J, Ar-mañanzas R, Santafé G, Pérez A, Robles V (2006) Machine learning in bioinformatics. Briefings bioinformatics 7(04):86–112
Wang F, Ma S, Wang H, Li Y, Qin Z, Zhang J (2018) A hybrid model integrating improved flower pollination algorithm-based feature selection and improved random forest for nox emission estimation of coal-fired power plants. Measurement 125:303–312
Malekipirbazari M, Aksakalli V (2015) Risk assessment in social lending via random forests. Expert Syst Appl 42(10):4621–4631
He H, Garcia E (2009) Learning from imbalanced data. Knowl Data Eng IEEE Trans 21 (10):1263–1284
Chawla N, Bowyer K, Hall LO, Kegelmeyer WP (2002) Smote: synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J Artif Intell Res (JAIR) 16(01):321–357
Mafarja M, Aljarah I, Heidari AA, Hammouri AI, Faris H, Ala’M A-Z, Mirjalili S (2018) Evolutionary population dynamics and grasshopper optimization approaches for feature selection problems. Knowl-Based Syst 145:25–45
Kumar V, Minz S (2014) Feature selection: a literature review. Smart Comput Rev 4 (01):211–229
Mafarja MM, Mirjalili S (2017) Hybrid whale optimization algorithm with simulated annealing for feature selection. Neurocomputing 260:302–312
Amrieh E, Hamtini T, Aljarah I (2016) Mining educational data to predict student’s academic performance using ensemble methods. Int J Database Theory Appl 9(09):119–136
Mafarja M, Aljarah I, Heidari AA, Faris H, Fournier-Viger P, Li X, Mirjalili S (2018) Binary dragonfly optimization for feature selection using time-varying transfer functions. Knowl-Based Syst 161:185–204
Faris H, Ala’M A-Z, Heidari AA, Aljarah I, Mafarja M, Hassonah MA, Fujita H (2019) An intelligent system for spam detection and identification of the most relevant features based on evolutionary random weight networks. Inf Fusion 48:67–83
Mirjalili S, Lewis A (2013) S-shaped versus v-shaped transfer functions for binary particle swarm optimization. Swarm Evolutionary Computat 9:1–14
Kennedy J, Eberhart RC (1997) A discrete binary version of the particle swarm algorithm. In: Systems, man, and cybernetics, 1997. Computational cybernetics and simulation, 1997 IEEE international conference on. IEEE, vol 5, pp 4104–4108
Rashedi E, Nezamabadi-Pour H, Saryazdi S (2010) Bgsa: binary gravitational search algorithm. Nat Comput 9(3):727–745
Mirjalili S, Dong J (2020) Multi-objective optimization using artificial intelligence techniques. 01
Emary E, Zawbaa HM (2016) Impact of chaos functions on modern swarm optimizers. PloS One 11(7):e0158738
Mirjalili S, Mirjalili SM, Lewis A (2014) Grey wolf optimizer. Adv Eng Softw 69:46–61
Heidari AA, Mirjalili S, Faris H, Aljarah I, Mafarja M, Chen H (2019) Harris hawks optimization: algorithm and applications. Future Generation Comput Syst 97:849–872
(2017). Tera-Promise. http://openscience.us/repo. Last Accessed 24 Nov 2017
Jureczko M, Madeyski L (2010) Towards identifying software project clusters with regard to defect prediction. In: Proceedings of the 6th international conference on predictive models in software engineering, PROMISE ’10, (New York). ACM, pp 9:1–9:10
Chidamber SR, Kemerer CF (1994) A metrics suite for object oriented design. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 20:476–493
Thaher T, Heidari AA, Mafarja M, Dong JS, Mirjalili S (2020) Binary harris hawks optimizer for high-dimensional, low sample size feature selection. Singapore: Springer Singapore, pp 251–272
Thaher T, Chantar H, Too J, Mafarja M, Turabieh H, Houssein EH (2022) Boolean particle swarm optimization with various evolutionary population dynamics approaches for feature selection problems, vol 195
Thaher T, Awad M, Aldasht M, Sheta A, Turabieh H, Chantar H (2022) An enhanced evolutionary based feature selection approach using grey wolf optimizer for the classification of high-dimensional biological data. JUCS - J Univ Comput Sci 28(5):499–539
Chantar H, Thaher T, Turabieh H, Mafarja M, Sheta A (2021) Bhho-tvs: a binary harris hawks optimizer with time-varying scheme for solving data classification problems. Applied Sci 11:14
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mafarja, M., Thaher, T., Al-Betar, M.A. et al. Classification framework for faulty-software using enhanced exploratory whale optimizer-based feature selection scheme and random forest ensemble learning. Appl Intell 53, 18715–18757 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-04427-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-04427-x