Abstract
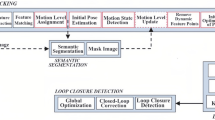
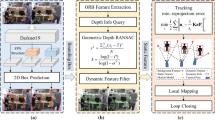
Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) is a key technique for mobile robotics. Moving objects can vastly impair the performance of a visual SLAM system. To deal with the problem, a new semantic visual SLAM system for indoor environments is proposed. Our system adds a semantic segmentation network and geometric model to detect and remove dynamic feature points on moving objects. Moreover, a 3D point cloud map with semantic information is created using semantic labels and depth images. We evaluate our method on the TUM RGB-D dataset and real-world environments. The evaluation metrics used are absolute trajectory error and relative position error. Experimental results show our method improves the accuracy in dynamic scenes compared to ORB-SLAM3 and other advanced methods.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data generated and analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Klein G, Murray D (2007) Parallel tracking and mapping for small ar workspaces. In: 2007 6th IEEE and ACM international symposium on mixed and augmented reality, IEEE, pp 225–234
Mur-Artal R, Montiel JMM, Tardos JD (2015) Orb-slam: a versatile and accurate monocular slam system. IEEE Trans Robot 31(5):1147–1163
Mur-Artal R, Tardós J D (2017) Orb-slam2: an open-source slam system for monocular, stereo, and RGB-D cameras. IEEE Trans Robot 33(5):1255–1262
Campos C, Elvira R, Rodríguez JJG, Montiel JM, Tardós JD (2021) Orb-slam3: an accurate open-source library for visual, visual–inertial, and multimap slam. IEEE Trans Robot 37(6):1874–1890
Engel J, Schöps T, Cremers D (2014) Lsd-slam: large-scale direct monocular slam. In: European conference on computer vision, Springer, pp 834–849
Wang R, Schworer M, Cremers D (2017) Stereo dso: large-scale direct sparse visual odometry with stereo cameras. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 3903–3911
Zhou Y, Wang Y, Poiesi F, Qin Q, Wan Y (2022) Loop closure detection using local 3d deep descriptors. IEEE Robot Autom Lett 7(3):6335–6342
Tian Y, Wang Y, Ouyang M, Shi X (2021) Hierarchical segment-based optimization for slam. In: 2021 IEEE/RSJ International conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS), IEEE, pp 6573–6580
Yang B, Xu X, Ren J, Cheng L, Guo L, Zhang Z (2022) Sam-net: semantic probabilistic and attention mechanisms of dynamic objects for self-supervised depth and camera pose estimation in visual odometry applications. Pattern Recog Lett 153: 126–135
Matsuki H, Scona R, Czarnowski J, Davison AJ (2021) Codemapping: real-time dense mapping for sparse slam using compact scene representations. IEEE Robot Autom Lett 6(4):7105–7112
Cadena C, Carlone L, Carrillo H, Latif Y, Scaramuzza D, Neira J, Reid I, Leonard JJ (2016) Past, present, and future of simultaneous localization and mapping: toward the robust-perception age. IEEE Trans Robot 32(6):1309–1332
Cheng T, Wang X, Chen S, Zhang W, Zhang Q, Huang C, Zhang Z, Liu W (2022) Sparse instance activation for real-time instance segmentation. In: Proc. IEEE conf. computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR)
Davison AJ, Reid ID, Molton ND, Stasse O (2007) Monoslam: real-time single camera slam. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 29(6):1052–1067
Elvira R, Tardós JD, Montiel JM (2019) Orbslam-atlas: a robust and accurate multi-map system. In: 2019 IEEE/RSJ International conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS), IEEE, pp 6253–6259
Forster C, Pizzoli M, Scaramuzza D (2014) Svo: fast semi-direct monocular visual odometry. In: 2014 IEEE International conference on robotics and automation (ICRA), IEEE, pp 15–22
Newcombe RA, Lovegrove SJ, Davison AJ (2011) Dtam: dense tracking and mapping in real-time. In: 2011 International conference on computer vision, IEEE, pp 2320–2327
Li S, Lee D (2017) Rgb-d slam in dynamic environments using static point weighting. IEEE Robot Autom Lett 2(4):2263– 2270
Sun Y, Liu M, Meng MQ-H (2017) Improving rgb-d slam in dynamic environments: a motion removal approach. Robot Auton Syst 89:110–122
Xu G, Yu Z, Xing G, Zhang X, Pan F (2022) Visual odometry algorithm based on geometric prior for dynamic environments. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 122(1):235–242
Tan W, Liu H, Dong Z, Zhang G, Bao H (2013) Robust monocular slam in dynamic environments. In: 2013 IEEE International symposium on mixed and augmented reality (ISMAR), IEEE, pp 209–218
Fischler MA, Bolles RC (1981) Random sample consensus: a paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Commun ACM 24(6):381–395
Bescos B, Fácil JM, Civera J, Neira J (2018) Dynaslam: tracking, mapping, and inpainting in dynamic scenes. IEEE Robot Autom Lett 3(4):4076–4083
He K, Gkioxari G, Dollár P, Girshick R (2017) Mask r-CNN. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 2961–2969
Bescos B, Campos C, Tardós JD, Neira J (2021) Dynaslam ii: tightly-coupled multi-object tracking and slam. IEEE Robot Autom Lett 6(3):5191–5198
Yu C, Liu Z, Liu X-J, Xie F, Yang Y, Wei Q, Fei Q (2018) Ds-slam: a semantic visual slam towards dynamic environments. In: 2018 IEEE/RSJ International conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS), IEEE, pp 1168–1174
Badrinarayanan V, Kendall A, Cipolla R (2017) Segnet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(12):2481–2495
Cheng J, Wang Z, Zhou H, Li L, Yao J (2020) Dm-slam: a feature-based slam system for rigid dynamic scenes. ISPRS Int J Geo-Inform 9(4):202
Zhong F, Wang S, Zhang Z, Wang Y (2018) Detect-slam: making object detection and slam mutually beneficial. In: 2018 IEEE Winter conference on applications of computer vision (WACV), IEEE, pp 1001–1010
Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Szegedy C, Reed S, Fu C-Y, Berg AC (2016) Ssd: single shot multibox detector. In: European conference on computer vision, Springer, pp 21–37
Fan Y, Zhang Q, Tang Y, Liu S, Han H (2022) Blitz-slam: a semantic slam in dynamic environments. Pattern Recog 121:108225
Dvornik N, Shmelkov K, Mairal J, Schmid C (2017) Blitznet: a real-time deep network for scene understanding. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 4154–4162
Liu Y, Miura J (2021) Rds-slam: real-time dynamic slam using semantic segmentation methods. IEEE Access 9:23772–23785
Liu Y, Miura J (2021) Rdmo-slam: real-time visual slam for dynamic environments using semantic label prediction with optical flow. IEEE Access 9:106981–106997
Krishna K, Murty MN (1999) Genetic k-means algorithm. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybernet Part B (Cybernet) 29(3):433–439
Wu W, Guo L, Gao H, You Z, Liu Y, Chen Z (2022) YOLO-SLAM: a semantic SLAM system towards dynamic environment with geometric constraint. Neural Comput Appl 34(8):6011–6026. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06764-3
Sturm J, Engelhard N, Endres F, Burgard W, Cremers D (2012) A benchmark for the evaluation of rgb-d slam systems. In: 2012 IEEE/RSJ International conference on intelligent robots and systems, IEEE, pp 573–580
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the support of the Anhui Natural Science Fund (No.2108085QF286).
Funding
This research was funded by the Anhui Natural Science Fund (No.2108085QF286).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Conflict of Interests
The author declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, J., Jiang, X., Yu, C. et al. Dynamic visual simultaneous localization and mapping based on semantic segmentation module. Appl Intell 53, 19418–19432 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-023-04531-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-023-04531-6