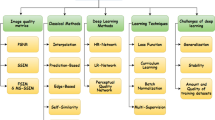
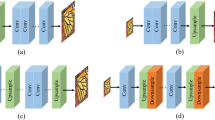
Abstract
Super-resolution (SR) reconstruction is a hot topic in medical image processing. SR implies reconstructing corresponding high-resolution (HR) images from observed low-resolution (LR) images or image sequences. In recent years, significant breakthroughs in SR based on deep learning have been made, and many advanced results have been achieved. However, there is a lack of review literature that summarizes the field’s current state and provides an outlook on future developments. Therefore, we provide a comprehensive summary of the literature on medical image SR (MedSR) based on deep learning since 2018 in five aspects: (1) The SR problem of medical images is described, and the methods of image degradation are summarized. (2) We divide the existing studies into three categories: two-dimensional image SR (2DISR), three-dimensional image SR (3DISR), and video SR (VSR). Each category is subdivided. We analyze the network structure and method characteristics of typical methods. (3) Existing SR reconstruction quality evaluation metrics are presented in detail. (4) The application of MedSR methods based on deep learning is discussed. (5) We discuss the challenges of this phase and point out valuable research directions.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Azadbakht J, Khoramian D, Lajevardi ZS, Elikaii F et al (2021) A review on chest CT scanning parameters implemented in COVID-19 patients: bringing low-dose CT protocols into play. J Radiol Nucl Med 52(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43055-020-00400-1
Xia Y, Ravikumar N, Greenwood JP et al (2021) Super resolution of cardiac MR cine imaging using conditional GANs and unsupervised transfer learning. Med Image Anal 71:102037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2021.102037
Li Y, Sixou B, Peyrin F (2021) A review of the deep learning methods for medical images super resolution problems. Irbm 42(2):120–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irbm.2020.08.004
Rohith G, Kumar LS (2021) Paradigm shifts in super-resolution techniques for remote sensing applications. Vis Comput 37(7):1965–2008. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-020-01957-8
Shang T, Dai Q, Zhu S et al (2020) Perceptual extreme super-resolution network with receptive field block. IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops (CCPRW), pp 440–441
Lyakhov PA, Valuev GV, Valueva MV et al (2021) Single image Super-Resolution method based on bilinear interpolation and U-Net combination. Mediterranean Conference on Embedded Computing (MECO), pp 1–4
Xiang R, Yang H, Yan Z et al (2022) Super-resolution reconstruction of GOSAT CO2 products using bicubic interpolation. Geocarto International, pp 1–25
Lin Z, Shum HY (2004) Fundamental limits of reconstruction-based super resolution algorithms under local translation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 26(1):83–97. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2004.10003
Ebner M, Patel P, Atkinson D et al (2019) Reconstruction-based super-resolution for high-resolution abdominal MRI: a preliminary study. International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (ISMRM), pp 1–3
Shao Z, Wang L, Wang Z et al (2019) Remote sensing image super-resolution using sparse representation and coupled sparse autoencoder. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 12(8):2663–2674
Deka B, Datta S, Mullah HU et al (2020) Diffusion-weighted and spectroscopic MRI super-resolution using sparse representations. Biomed Signal Process Control 60(5):101941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2020.101941
Li Y, Song B, Guo J et al (2019) Super-resolution of brain MRI images using overcomplete dictionaries and nonlocal similarity. IEEE Access 7:25897–25907. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2900125
Chao D, Chen CL, He K et al (2014) Learning a deep convolutional network for image Super-Resolution. European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp 184–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10593-2_13
Yang F, Yang H, Fu J et al (2020) Learning texture transformer network for image super-resolution. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 5791–5800. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00583
Liu H, Ruan Z, Zhao P et al (2022) Video super-resolution based on deep learning: a comprehensive survey. Artif Intell Rev 55:5981–6035. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-022-10147-y
Wang Z, Chen J, Hoi S (2020) Deep Learning for Image super-resolution: A Survey. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 43(10):3365–3387. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2020.2982166
Chen Z, Pawar K, Ekanayake M et al (2022) Deep learning for image enhancement and correction in magnetic resonance imaging—state-of-the-art and challenges. J Digit Imaging, pp 1–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-022-00721-9
Zheng Y, Zhen B, Chen A (2020) A hybrid convolutional neural network for super-resolution reconstruction of MR images. Med Phys 47(7):3013–3022. https://doi.org/10.1002/mp.14152
Park S, Gach HM, Kim S et al (2021) Autoencoder-inspired convolutional network-based super-resolution method in MRI. IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med 9:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1109/JTEHM.2021.3076152
Zhang K, Gool LV, Timofte R (2020) Deep unfolding network for image super-resolution. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 3214–3223. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00328
Song H, Xu W, Liu D et al (2021) Multi-Stage feature fusion network for video super-resolution. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:2923–2934. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2021.3056868
Masutani EM, Naeim B, Albert H (2020) Deep learning single-frame and multi-frame super-resolution for cardiac MRI. Radiology 295(3):552–561. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2020192173
Lyu Q, Shan H, Steber C et al (2020) Multi-contrast super-resolution MRI through a progressive network. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(9):2738–2749. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2020.2974858
Lin JY, Chang YC, Hsu WH (2020) Efficient and phase-aware video super-resolution for Cardiac MRI. In: Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention (MICCAI), pp 66–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59719-1_7
Lyu Q, Shan H, Wang G (2020) MRI super-resolution with ensemble learning and complementary priors. IEEE Trans Comput Imaging 6:615–624. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCI.2020.2964201
Lyu Q, Shan H, Xie Y et al (2021) Cine cardiac MRI motion artifact reduction using a recurrent neural network. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 40(8):2170–2181. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2021.3073381
Sander J, Vos BD, Igum I (2022) Autoencoding Low-Resolution MRI for semantically smooth interpolation of anisotropic MRI. Med Image Anal 78:102393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2022.102393
Li J, Koh JC, Lee WS (2020) HRINEt: Alternative supervision network for high-resolution CT image interpolation. IEEE International Conference on Image Processing(ICIP), pp 1916–1920. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP40778.2020.9191060
Lu Z, Li Z, Wang J et al (2021) Two-Stage self-supervised cycle-consistency network for reconstruction of thin-slice MR images. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87231-1_1
Wang L, Zhu H, He Z et al (2022) Adjacent slices feature transformer network for single anisotropic 3D brain MRI image super-resolution. Biomed Signal Process Control 72:103339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2021.103339
Lepcha DC, Goyal B, Dogra A et al (2023) Image super-resolution: a comprehensive review, recent trends, challenges and applications. Inform Fusion 91:230–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2022.10.007
Nie S, Ma C, Chen D et al (2020) A dual residual network with channel attention for image restoration. European Conference on Computer Vision Workshops(ECCVW), pp 352–363. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-68238-5_27
Liu J, Tang J, Wu G (2020) Residual feature distillation network for lightweight image Super-Resolution. European Conference on Computer Vision Workshops(ECCVW), pp 41–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-67070-2_2
Song D, Xu C, Jia X et al (2020) Efficient residual dense block search for image Super-Resolution. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol 34, pp 2007–12014. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v34i07.6877
Zhang Y, Tian Y, Kong Y et al (2020) Residual dense network for image restoration. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell(PAMI) 43(7):2480–2495. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2020.2968521
Shuang LA, Cxa B, Xs A et al (2021) Progressive face super-resolution with cascaded recurrent convolutional network. Neurocomputing 449:357–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2021.03.124
Hui Z, Li J, Gao X et al (2021) Progressive perception-oriented network for single image super-resolution. Inf Sci 546(2):769–786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2020.08.114
Hu X, Naiel MA, Wong A et al (2019) RUNEt: A robust Unet architecture for image super-resolution. Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), pp 505–507. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2019.00073
Yan Y, Liu C, Chen C et al (2021) Fine-grained attention and feature-sharing generative adversarial networks for single image super-resolution. IEEE Trans Multimedia 24:1473–1487. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2021.3065731
Hui Z, Gao X, Yang Y et al (2019) Lightweight image super-resolution with information multi-distillation network. Acm International Conference(ACM), pp 2024–2032. https://doi.org/10.1145/3343031.3351084
Chudasama V, Nighania K, Upla K et al (2021) E-comsupresnet: enhanced face super-resolution through compact network. IEEE Trans Biom Behav Identity Sci 3(2):166–179. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBIOM.2021.3059196
Chen C, Gong D, Wang H et al (2021) Learning spatial attention for face Super-Resolution. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:1219–1231. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2020.3043093
Guo Y, Chen J, Wang J et al (2020) Closed-loop matters: dual regression networks for single image super-resolution. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 5406–5415. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00545
Wang H, Hu Q, Wu C et al (2021) DCLNEt: Dual closed-loop networks for face super-resolution. Knowl Based Syst 222(33):106987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2021.106987
Li J, Fang F, Mei K et al (2018) Multi-scale residual network for image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp 517–532. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01237-3_32
Kim J, Lee JK, Lee KM (2016) Accurate image Super-Resolution using very deep convolutional networks. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 1646–1654. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.182
Xue X, Wang Y, Li J et al (2020) Progressive sub-band residual-learning network for MR image super resolution. IEEE J Biomed Health Informa 24(2):377–386. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2019.2945373
He K, Zhang X, Ren S et al (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 770–778. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90
Qiu D, Zheng L, Zhu J et al (2021) Multiple improved residual networks for medical image super-resolution. Futur Gener Comput Syst 116:200–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2020.11.001
Ding P, Li Z, Zhou Y et al (2019) Deep residual dense U-Net for resolution enhancement in accelerated MRI acquisition. Image Processing, pp 110–117
Zheng H, Wang X, Gao X (2018) Fast and accurate single image super-resolution via information distillation network. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 723–731. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00082
Chen Y, Zheng Q, Chen J (2022) Double paths network with residual information distillation for improving lung CT image super resolution. Biomed Signal Process Control 73:103412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2021.103412
Ledig C, Theis L, Huszar F et al (2017) Photo-Realistic Single image Super-Resolution using a generative adversarial network. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 105–114. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.19
Wang X, Yu K, Wu S et al (2018) ESRGAN: Enhanced super-resolution generative adversarial networks. European Conference on Computer Vision Workshops(ECCVW), pp 63–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-11021-5_5
Chan KCK, Wang X, Xu X et al (2021) GLEAN: Generative latent bank for Large-Factor image Super-Resolution. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 14240–14249
Zhu J, Yang G, Lio P (2019) How can we make GAN perform better in single medical image super-resolution? a lesion focused multi-scale approach. IEEE 16th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), pp 1669–1673. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISBI.2019.8759517
Ren H, El-Khamy M, Lee J (2017) Image super resolution based on fusing multiple convolution neural networks. IEEE/ CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), pp 1050–1057. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2017.142
Zhu JY, Park T, Isola P et al (2017) Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp 2223–2232. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.244
Lyu Q, You C, Shan H et al (2019) Super-resolution MRI and CT through GAN-circle. Developments in X-Ray Tomography XII 111130X:202–208. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2530592
Mei Y, Fan Y, Zhou Y et al (2020) Image super-resolution with cross-scale non-local attention and exhaustive self-exemplars mining. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 5689–5698. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00573
Cai J, Meng ZB, Ho CM (2020) Residual channel attention generative adversarial network for image super-resolution and noise reduction. IEEE/ CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), pp 1852–1861. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW50498.2020.00235
Mei Y, Fan Y, Zhou Y (2021) Image super-resolution with non-local sparse attention. Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 3516–3525
Li G, Lv J, Tong X et al (2021) High-Resolution Pelvic MRI reconstruction using a generative adversarial network with attention and cyclic loss. IEEE Access 105951-105964:9. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3099695
Gu Y, Zeng Z, Chen H et al (2020) MedSRGAN: medical images super-resolution using generative adversarial networks. Multimed Tools Appl 79(3):21815–21840. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-08980-w
Zhang Y, Li K, Li K et al (2018) Image super-resolution using very deep residual channel attention networks. European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp 294–310. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_18
Ashish V, Noam S, Niki P et al (2017) Attention is all you need. Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), pp 6000–6010
Liang J, Cao J, Sun G et al (2021) SwinIR: Image Restoration Using Swin Transformer. International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), pp 1833–1844. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCVW54120.2021.00210
Chu X, Tian Z, Wang Y et al (2021) Twins: Revisiting the design of spatial attention in vision transformers. Neural Inf Process Syst 34:9355–9366
Feng CM, Yan Y, Fu H et al (2021) Task transformer network for joint MRI reconstruction and super-resolution. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) , pp 307–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87231-1_30
Zhang Z, Yu L, Liang X et al (2021) TransCT: Dual-path transformer for low dose computed tomography. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), pp 55–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87231-1_6
Zhou S, Zhang J, Zuo W et al (2020) Cross-scale internal graph neural network for image super-resolution. Neural Inf Process Syst 33:3499–3509
Yan Y, Ren W, Hu X et al (2021) SRGAT: Single image super-resolution with graph attention network. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:4905–4918. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2021.3077135
Zhang Y, Li K, Li KP et al (2021) MR Image Super-Resolution with squeeze and excitation reasoning attention network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 13420–13429
Xiang L, Chen Y, Chang W et al (2019) Deep-learning-based multi-modal fusion for fast MR reconstruction. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 66(7):2105–2114. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2018.2883958
Lu L, Li W, Tao X et al (2021) MASA-SR : Matching acceleration and spatial adaptation for reference-based image super-resolution. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 6364–6373
Feng CM, Fu H, Yuan S et al (2021) Multi-Contrast MRI super-resolution via a multi-stage integration network. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) , pp 140–149. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87231-1_14
Feng CM, Yan Y, Chen G et al (2021) Multi-Modal Transformer for accelerated MR imaging. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, pp 1–1. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2022.3180228
Georgescu MI, Ionescu RT, Miron AI et al (2023) Multimodal multi-head convolutional attention with various kernel sizes for medical image super-resolution. Workshop on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), pp 1–12
Georgescu MI, Ionescu RT, Verga N (2020) Convolutional neural networks with intermediate loss for 3D super-resolution of CT and MRI scans. IEEE Access 8:49112–49124. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2980266
Lim B, Son S, Kim H et al (2017) Enhanced deep residual networks for single image Super-Resolution. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), pp 136–144. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2017.151
Xie Y, Xiao J, Sun M et al (2020) Feature representation matters: end to end learning for Reference-Based image super resolution. In: European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp 230–245. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58548-8_14
Li G, Lv J, Tian Y et al (2022) Transformer-empowered multi-scale contextual matching and aggregation for Multi contrast MRI super-resolution. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 20636–20645
Madhu M, Ramanarayanan S, Ram K et al (2021) Reference based Texture transfer for Single Image Super-resolution of Magnetic Resonance images. IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), pp 579–583
Liu Z, Lin Y, Cao Y et al (2021) Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 10012–10022. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00986
Zeng K, Zheng H, Cai C et al (2018) Simultaneous single-and multi-contrast super-resolution for brain MRI images based on a convolutional neural network. Comput Biol Med 99:133–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2018.06.010
Ji S, Xu W, Yang M et al (2013) 3D Convolutional Neural Networks for Human Action Recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35 (1):221–231. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2012.59
Koktzoglou I, Huang R, Ankenbrandt WJ et al (2021) Super-resolution head and neck MRA using deep machine learning. Magn Reson Med 86(1):335–345. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.28738
Chen Y, Shi F, Christodoulou AG et al (2018) Efficient and accurate MRI super-resolution using a generative adversarial network and 3D multi-level densely connected network. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), pp 91–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00928-1_11
Pham C-H, Ducournau A, Fablet R et al (2017) Brain MRI super-resolution using deep 3D convolutional networks. IEEE 14th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), pp 197–200
Kudo A, Kitamura Y, Li Y et al (2019) Virtual thin slice: 3D conditional GAN-based super-resolution for CT slice interval. In: Machine Learning for Medical Image Reconstruction (MLMIR), pp 91–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-33843-5_9
Chen Y, Xie Y, Zhou Z et al (2018) Brain MRI super resolution using 3D deep densely connected neural networks. IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), pp 739–742. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISBI.2018.8363679
Wang J, Chen Y, Wu Y et al (2020) Enhanced generative adversarial network for 3D brain MRI super-resolution. Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), pp 3627–3636. https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV45572.2020.9093603
Du J, He Z, Wang L et al (2020) Super-resolution reconstruction of single anisotropic 3D MR images using residual convolutional neural network. Neurocomputing 392:209–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.10.102
Peng C, Lin WA, Liao H et al (2020) SAINT: Spatially aware interpolation network for medical slice synthesis. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 7750–7759. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00777
Peng C, Zhou SK, Chellappa R (2021) DA-VSR : Domain adaptable volumetric Super-Resolution for medical images. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) , pp 75–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87231-1_8
Zhao C, Dewey BE, Pham DL et al (2020) SMORE: A self-supervised anti-aliasing and super-resolution algorithm for MRI using deep learning. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 40(3):805–817. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2020.3037187
Sood RR, Shao W, Kunder C et al (2021) 3D Registration of pre-surgical prostate MRI and histopathology images via super-resolution volume reconstruction. Med Image Anal 69:101957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2021.101957
Siyuan Z, Jingxian D, Caiwen J et al (2020) 2D CNN-Based Slices-to-Volume Superresolution Reconstruction. IEEE Access 8:86357–86366. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2992481
Berthelot D, Raffel C, Roy A et al (2019) Understanding and improving interpolation in autoencoders via an adversarial regularizer. International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) (Poster)
Wu Z, Wei J, Wang J et al (2022) Slice imputation: Multiple intermediate slices interpolation for anisotropic 3D medical image segmentation. Comput Biol Med, vol 105667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105667
Xue T, Chen B, Wu J et al (2019) Video enhancement with Task-Oriented flow. Int J Comput Vis 127(8):1106–1125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-018-01144-2
Chu M, Xie Y, Mayer J et al (2020) Learning temporal coherence via self-supervision for GAN-based video generation. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 75:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1145/3386569.3392457
Li W, Tao X, Guo T et al (2020) Mucan: Multi-correspondence aggregation network for video super-resolution. European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 335–351. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58607-2_20
Ren S, Li J, Guo K et al (2021) Medical video super-resolution based on asymmetric back-projection network with multilevel error feedback. IEEE Access 9:17909–17920. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3054433
Sun D, Yang X, Liu MY et al (2018) Pwc-net: Cnns for optical flow using pyramid, warping, and cost volume. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 8934–8943
Karani N, Zhang L, Tanner C et al (2017) Temporal interpolation of abdominal MRIs acquired during free-breathing. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), pp 359–367. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66185-8-41
Guo Y, Bi L, Ahn E et al (2020) A spatiotemporal volumetric interpolation network for 4d dynamic medical image. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 4726–4735. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00478
Karani N, Zhang L, Tanner C et al (2019) An image interpolation approach for acquisition time reduction in navigator-based 4D MRI. Med Image Anal 54:20–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2019.02.008
Lucas A, Lopez-Tapia S, Molina R et al (2019) Generative adversarial networks and perceptual losses for video super-resolution. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(7):3312–3327. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2019.2895768
Kim SY, Lim J, Na T et al (2019) Video super-resolution based on 3d-cnns with consideration of scene change. IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp 2831–2835. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2019.8803297
Isobe T, Jia X, Gu S et al (2020) Video super-resolution with recurrent structure-detail network. European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 645–660. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58610-2_38
Liu H, Zhao P, Ruan Z et al (2021) Large motion video super-resolution with dual subnet and multi-stage communicated upsampling. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, vol 35, pp 2127–2135
Graves A (1997) Long short-term memory. Neural Comput 9(8):1735–1780. https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735
Tian Y, Zhang Y, Fu Y et al (2020) Tdan: Temporally-deformable alignment network for video super-resolution. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 3360–3369. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00342
Ying X, Wang L, Wang Y et al (2020) Deformable 3d convolution for video super-resolution. IEEE Signal Process Lett 27:1500–1504. https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2020.3013518
Song H, Xu W, Liu D et al (2021) Multi-Stage Feature fusion network for video Super-Resolution. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:2923–2934. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2021.3056868
Chan KCK, Wang X, Yu K et al (2021) Basic VSR : The search for essential components in video super-resolution and beyond. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 4947–4956
ITU-T RECOMMENDATION P (1999) Subjective video quality assessment methods for multimedia applications. pp 34-35
Lai WS, Huang JB, Ahuja N et al (2018) Fast and accurate image super-resolution with deep laplacian pyramid networks. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 41(11):2599–2613. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2865304
Wang Z, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR et al (2004) Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans On Image Process 13(4):600–612. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2003.819861
Zhang Z, Dai G, Liang X et al (2018) Can signal-to-noise ratio perform as a baseline indicator for medical image quality assessment. IEEE Access 6:11534–11543. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2796632
Preedanan W, Kondo T, Bunnun P et al (2018) A comparative study of image quality assessment. International Workshop on Advanced Image Technology (IWAIT), pp 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/IWAIT.2018.8369657
Wang Z, Simoncelli EP, Bovik AC (2003) Multiscale structural similarity for image quality assessment. Asilomar Conf Signals Syst Comput 2:1398–1402. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACSSC.2003.1292216
Sheikh HR, Bovik AC, De Veciana G (2005) An information fidelity criterion for image quality assessment using natural scene statistics. IEEE Trans Image Process 14(12):2117–2128. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2005.859389
You C, Li G, Zhang Y et al (2019) CT Super-resolution GAN constrained by the identical, residual, and cycle learning ensemble (GAN-CIRCLE). IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(1):188–203. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2019.2922960
Yang CY, Ma C, Yang MH (2014) Single-image super-resolution: a benchmark. European conference on computer vision, pp 372–386. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10593-2_25
Zhang R, Isola P, Efros AA et al (2018) The unreasonable effectiveness of deep features as a perceptual metric. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 586–595. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00068
Mittal A, Soundararajan R, Bovik AC (2012) Making a “completely blind” image quality analyzer. IEEE Signal Process Lett 20(3):209–212. https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2012.2227726
Venkatanath N, Praneeth D, Chandrasekhar B et al (2015) Blind image quality evaluation using perception based features. National Conference on Communications (NCC), pp 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/NCC.2015.7084843
Ma C, Yang CY, Yang X et al (2017) Learning a no-reference quality metric for single-image super-resolution. Comput Vis Image Underst 158:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cviu.2016.12.009
Zhang L, Zhang L, Mou X et al (2011) FSIM: A feature similarity index for image quality assessment. IEEE Trans Image Process 20(8):2378–2386. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2011.2109730
Dai D, Wang Y, Chen Y et al (2016) Is image super-resolution helpful for other vision tasks?. IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), pp 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV.2016.7477613
Haris M, Shakhnarovich G, Ukita N (2021) Task-driven super resolution: Object detection in low-resolution images. Neural Information Processing, pp 387–395
Sajjadi MSM, Scholkopf B, Hirsch M (2017) Enhancenet: Single image super-resolution through automated texture synthesis. IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), pp 4491–4500. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.481
Bai Y, Zhang Y, Ding M et al (2018) Sod-mtgan: Small object detection via multi-task generative adversarial network. IEEE European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp 206–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01261-8_13
Blau Y, Michaeli T (2018) The perception-distortion tradeoff. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 6228–6237. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00652
Giannakidis A, Oktay O, Keegan J et al (2017) Super-resolution reconstruction of late gadolinium cardiovascular magnetic resonance images using a residual convolutional neural network. International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (ISMRM), pp 1–3
Steeden JA, Quail M, Gotschy A et al (2020) Rapid whole-heart CMR with single volume super-resolution. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 22(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12968-020-00651-x
Ferdian E, Suinesiaputra A, Dubowitz DJ et al (2020) 4DFlowNet: super-resolution 4D flow MRI using deep learning and computational fluid dynamics. Front Phys 8:138. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphy.2020.00138
Wang S, Qin C, Savioli N et al (2021) Joint motion correction and super resolution for cardiac segmentation via latent optimisation. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), pp 14–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87199-4_2
Ye X, Sun Z, Xu R, Wang Z et al (2022) Low-Dose CT Reconstruction via Dual-Domain learning and controllable modulation. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), pp 549–559
Boudraa S, Melouah A, Merouani HF (2020) Improving mass discrimination in mammogram-CAD system using texture information and super-resolution reconstruction. Evol Syst 11(4):697–706
Sood RR, Shao W, Kunder C et al (2021) 3D Registration of pre-surgical prostate MRI and histopathology images via super-resolution volume reconstruction. Med Image Anal 69:101957
Yamawaki K, Sun Y, Han XH (2021) Blind image super resolution using deep unsupervised learning. Electronics 10(21):2591. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10212591
Liang Y (2021) Unsupervised super resolution reconstruction of traffic surveillance vehicle images. International Conference on Machine Learning and Computing (ICMLC), pp 336–341. https://doi.org/10.1145/3457682.3457734
Skandarani Y, Lalande A, Afilalo J et al (2021) Generative adversarial networks in cardiology. Canadian Journal of Cardiology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjca.2021.11.003
Yoo J, Ahn N, Sohn KA (2020) Rethinking data augmentation for image super-resolution: a comprehensive analysis and a new strategy. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 8375–8384. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00840
Jin X, Xu J, Tasaka K et al (2021) Multi-task learning-based all-in-one collaboration framework for degraded image super-resolution. ACM Trans Multimed Comput, Commun Appl (TOMM) 17(1):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1145/3417333
Hu X, Mu H, Zhang X et al (2019) Meta-SR: A magnification-arbitrary network for super-resolution. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 1575–1584. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00167
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2015) Very deep convolutional networks for Large-Scale image recognition. International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), pp 1–14
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62072089) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (N2116016, N2104001, N2019007, N2224001-10).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This work is mainly carried out by the first author under the guidance of the second author and the corresponding author. Other authors assisted.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, H., Wang, Z., Liu, X. et al. Deep learning in medical image super resolution: a review. Appl Intell 53, 20891–20916 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-023-04566-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-023-04566-9