Abstract
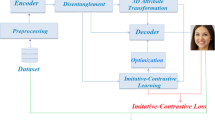
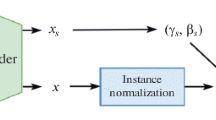
In this paper, we address the task of facial aesthetics enhancement (FAE). Existing methods have made great progress, however, beautified images generated by existing methods are extremely prone to over-beautification, which limits the application of existing aesthetic enhancement methods in real scenes. To solve this problem, we propose a new method called aesthetic enhanced perception generative adversarial network (AEP-GAN). We builds three blocks to complete facial beautification guided by facial aesthetic landmarks: an aesthetic deformation perception block (ADP), an aesthetic synthesis and removal block (ASR), and a dual-agent aesthetic identification block (DAI). The ADP learns the implicit aesthetic transformation between the landmarks of the source image and enhanced image. ASR ensures the consistency of image identity before and after beautification. The DAI distinguishes between the source images and generated images. At the same time, to prevent over-beautification, we constructed a real-world facial wedding photography dataset to enable the model to learn human aesthetics. To evaluate the effectiveness of the AEP-GAN, this paper adopted the wedding photography dataset for training, the SCUT-FBP5500 dataset, and the high-resolution Asian face dataset for testing. Experiments showed that the AEP-GAN addresses the over-beautification problem and achieves excellent results.

































Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Thakerar JN, Saburo I (1979) Cross-cultural comparisons in interpersonal attraction of females toward males. J Soc Psychol 108(1):121–122
Kim WH, Choi JH, Lee JS (2020) Objectivity and subjectivity in aesthetic quality assessment of digital photographs. IEEE Trans Affect Comput 11(3):493–506
Chen Y, Hu Y, Zhang L, Li P, Zhang C (2018) Engineering deep representations for modeling aesthetic perception. IEEE Trans Cybern 48(11):3092–3104
Tommer L, Daniel CO, Gideon D, Dani L (2008) Data-driven enhancement of facial attractiveness. ACM Trans Graph 27(3):38
Seo M, Chen Y-W, Aoki H (2011) Automatic transformation of ”kogao” (small face) based on fast b-spline approximation. J Inf Hiding Multimed Sig Process 2:192–203
Sun M, Zhang D, Yang J (2011) Face attractiveness improvement using beauty prototypes and decision. In: The First Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition, pp 283–287
Roy H, Dhar S, Dey K, Acharjee S, Ghosh D (2018) An automatic face attractiveness improvement using the golden ratio. In: Advanced Computational and Communication Paradigms, pp 755–763
Grammer K, Thornhill R (1994) Human (homo sapiens) facial attractiveness and sexual selection: The role of symmetry and averageness, vol 108, pp 233–42
Langlois JH, Roggman LA (1990) Attractive faces are only average. Psychol Sci 1(2):115–121
Hu S, Shum HPH, Liang X, Li FWB, Aslam N (2021) Facial reshaping operator for controllable face beautification. Expert Syst Appl 167:114067
Arakawa K, Nomoto K (2005) A system for beautifying face images using interactive evolutionary computing. 2005
Hara K, Maeda A, Inagaki H, Kobayashi M, Abe M (2009) Preferred color reproduction based on personal histogram transformation. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 55(2):855–863
Ohchi S, Sumi S, Arakawa K (2010) A nonlinear filter system for beautifying facial images with contrast enhancement. In: 2010 10th International Symposium on Communications and Information Technologies, pp 13–17
Diamant N, Zadok D, Baskin C, Schwartz E, Bronstein AM (2019) Beholder-gan: Generation and beautification of facial images with conditioning on their beauty level. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. IEEE, Taipei, Taiwan, pp 739–743
Liu X, Wang R, Chen C-F, Yin M, Peng H, Ng S, Li X (2019) Face beautification: Beyond makeup transfer. In: Frontiers in Computer Science
Huang Z, Suen CY (2021) Identity-preserved face beauty transformation with conditional generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition. IEEE, Virtual Event / Milan, Italy, pp 7273–7280
Zhou Y, Xiao Q (2020) Gan-based facial attractiveness enhancement. CoRR. arXiv:2006.02766
He J, Wang C, Zhang Y, Guo J, Guo Y (2020) Fa-gans: Facial attractiveness enhancement with generative adversarial networks on frontal faces. CoRR. arXiv:2005.08168
Zhang M, Wu S, Siyuan D, Qian W, Jieyi C, Qiao L, Yang Y, Tan J, Yuan Z, Peng Q, Yu L, Navarro N, Tang K, Ruiz-Linares A, Wang J-C, Claes P, Jin L, Li J, Wang S (2022) Genetic variants underlying differences in facial morphology in east asian and european populations. Nat Genet 54:1–9
Meitu Meitu AI Open Platform. https://ai.meitu.com/index,
MEGVII Face++ Open Platform. https://www.faceplusplus.com,
Zhu J, Park T, Isola P, Efros AA (2017) Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE Computer Society, Venice, Italy, pp 2242–2251
Liang L, Lin L, Jin L, Xie D, Li M (2018) SCUT-FBP5500: A diverse benchmark dataset for multi-paradigm facial beauty prediction. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition. IEEE Computer Society, Beijing, China, pp 1598–1603
Lee C, Schramm MT, Boutin M, Allebach JP (2009) An algorithm for automatic skin smoothing in digital portraits. In: Proceedings of the 16th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. ICIP’09, pp 3113–3116
Guo D, Sim T (2009) Digital face makeup by example. In: 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 73–79
Liu L, Xing J, Liu S, Xu H, Zhou X, Yan S (2014) ”wow! you are so beautiful today!”, vol 11
Melacci S, Sarti L, Maggini M, Gori M (2010) A template-based approach to automatic face enhancement. Pattern Anal Appl 13(3):289–300
Galton, Francis (1879) Composite portraits. J Anthropol Inst 8:132–144
Zhang S, He F (2020) DRCDN: learning deep residual convolutional dehazing networks. Vis Comput 36(9):1797–1808
Si T, He F, Zhang Z, Duan Y (2022) Hybrid contrastive learning for unsupervised person re-identification, vol 1–1
Tang W, He F, Liu Y (2022) Ydtr: Infrared and visible image fusion via y-shape dynamic transformer
Goodfellow IJ, Jean PA, Mirza M, Xu B, David WF, Ozair S, Courville AC, Bengio Y (2014) Generative adversarial networks. CoRR. arXiv:1406.2661
Arjovsky M, Chintala S, Bottou L (2017) Wasserstein GAN. CoRR. arXiv:1701.07875
Gulrajani I, Ahmed F, Arjovsky M, Dumoulin V, Courville AC (2017) Improved training of wasserstein gans. CoRR. arXiv:1704.00028
Karras T, Aila T, Laine S, Lehtinen J (2018) Progressive growing of gans for improved quality, stability, and variation. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations. OpenReview.net, Vancouver, BC, Canada
Karras T, Laine S, Aila T (2021) A style-based generator architecture for generative adversarial networks. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 43(12):4217–4228
Karras T, Laine S, Aittala M, Hellsten J, Lehtinen J, Aila T (2020) Analyzing and improving the image quality of StyleGAN. In: Proc. CVPR
Isola P, Zhu J, Zhou T, Efros AA (2017) Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE Computer Society, Honolulu, HI, USA, pp 5967–5976
Choi Y, Choi MJ, Kim M, Ha JW, Kim S, Choo J (2017) Stargan: Unified generative adversarial networks for multi-domain. image-to-image translation. CoRR. arXiv:1711.09020
Li M, Huang H, Ma L, Liu W, Zhang T, Jiang Y (2018) Unsupervised image-to-image translation with stacked cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of The15th European Conference, 11213. Springer, Munich, Germany, pp 186–201
Li T, Qian R, Dong C, Liu S, Yan Q, Zhu W, Lin L (2018) Beautygan: Instance-level facial makeup transfer with deep generative adversarial network. In: Proceedings of the 26th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, pp 645–653
Chen H-J, Hui K-M, Wang S-Y, Tsao L-W, Shuai H-H, Cheng W-H (2019) Beautyglow: On-demand makeup transfer framework with reversible generative network. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 10034–10042
Mirza M, Osindero S (2014) Conditional generative adversarial nets. CoRR. arXiv:1411.1784
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [Nos. 61972060, 62027827 and 62221005], National Key Research and Development Program of China (Nos. 2019YFE0110800), Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing [cstc2020jcyj-zdxmX0025, cstc2019cxcyljrc-td0270].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript entitled.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
All authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Li, W., Gao, X. et al. AEP-GAN: Aesthetic Enhanced Perception Generative Adversarial Network for Asian facial beauty synthesis. Appl Intell 53, 20441–20468 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-023-04576-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-023-04576-7