Abstract
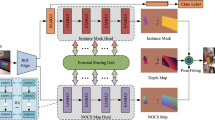
Six-degree-of-freedom (6DoF) object pose estimation is a critical task for robot manipulation, autonomous vehicles, and augmented reality. Category-level 6DoF object pose estimation is trending because it can generalize to same-category unknown objects. However, existing mean shape based methods do not consider that predicting adjustment must model shape differences, which makes these methods still suffer from shape variations among same-category objects, limiting their accuracy. Also, existing methods overlook the importance of object segmentation to 6DoF pose estimation and use an RGB-based object segmentation method with low accuracy. To address these problems, we propose difference-aware shape adjustment and RGB-D feature fusion-based object segmentation for category-level 6DoF object pose estimation. The proposed method encodes shape differences, improving mean shape adjustment and alleviating same-category shape variations. Specifically, a difference-aware shape adjustment network (DASAN) is proposed to model shape differences between the object instance and mean shape by feature subtraction with an attention mechanism. We also propose an RGB-D feature fusion-based object segmentation method that uses a coarse-to-fine framework: a 2D detector and a novel RGB-D feature fusion-based binary classification network for coarse and fine segmentation. Experiments on two well-known datasets demonstrate the proposed method’s state-of-the-art (SOTA) pose estimation accuracy. In addition, we construct comparative experiments on the latest dataset (Wild6D) and a self-collected dataset (OBJECTS) and achieve high accuracies, demonstrating the strong generalizability of the proposed method. Also, we apply the proposed method to unknown object grasping, thus demonstrating the practicability of the proposed method.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data generated and analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Mei J, Jiang X, Ding H (2022) Spatial feature mapping for 6dof object pose estimation. Pattern Recogn 131:108835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2022.108835. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031320322003168
Jiang J, He Z, Zhao X et al (2022) MLFNet: monocular lifting fusion network for 6dof texture-less object pose estimation. Neurocomputing 504:16–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2022.06.096. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092523122200827X
Peng S, Zhou X, Liu Y et al (2022) Pvnet: pixel-wise voting network for 6DoF object pose estimation. IEEE TPAMI 44(6):3212–3223. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2020.3047388
Shukla P, Pramanik N, Mehta D et al (2022) Generative model based robotic grasp pose prediction with limited dataset. Appl Intell 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-03011-z
Yu J, Arab A, Yi J et al (2022) Hierarchical framework integrating rapidly-exploring random tree with deep reinforcement learning for autonomous vehicle. Appl Intell 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-04358-7
Tang F, Wu Y, Hou X et al (2020) 3D mapping and 6D pose computation for real time augmented reality on cylindrical objects. IEEE TCSVT 30(9):2887–2899. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2019.2950449
Yan G, Woźniak M (2022) Accurate key frame extraction algorithm of video action for aerobics online teaching. Mob Netw Appl 27(3):1252–1261. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-022-01939-1
Wieczorek M, Siłka J, Woźniak M et al (2022) Lightweight convolutional neural network model for human face detection in risk situations. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 18(7):4820–4829. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2021.3129629
Woźniak M, Wieczorek M, Siłka J et al (2021) Body pose prediction based on motion sensor data and recurrent neural network. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 17(3):2101–2111. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2020.3015934
Zhang Y, Yi J, Chen Y et al (2022) Pose estimation for workpieces in complex stacking industrial scene based on RGB images. Appl Intell 52(8):8757–8769. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02857-7
Park K, Patten T, Prankl J et al (2019) Multi-task template matching for object detection, segmentation and pose estimation using depth images. In: ICRA. pp 7207–7213. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2019.8794448
Cheng J, Liu P, Zhang Q et al (2021) Real-time and efficient 6-D pose estimation from a single RGB image. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 70:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2021.3115564
Liu J, Sun W, Liu C et al (2022) HFF6D: hierarchical feature fusion network for robust 6D object pose tracking. IEEE TCSVT 1–1. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2022.3181597
Wang C, Xu D, Zhu Y et al (2019) Densefusion: 6D object pose estimation by iterative dense fusion. In: CVPR. pp 3343–3352. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00346
Huang WL, Hung CY, Lin IC (2021) Confidence-based 6D object pose estimation. IEEE Trans Multimedia 1–1. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2021.3092149
Chen W, Jia X, Chang HJ et al (2020) G2l-net: global to local network for real-time 6D pose estimation with embedding vector features. In: CVPR. pp 4232–4241. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00429
Wada K, Sucar E, James S et al (2020) Morefusion: multi-object reasoning for 6D pose estimation from volumetric fusion. In: CVPR. pp 14528–14537. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01455
Wang H, Sridhar S, Huang J et al (2019) Normalized object coordinate space for category-level 6D object pose and size estimation. In: CVPR. pp 2642–2651. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00275
Tian M, Ang MH, Lee GH (2020) Shape prior deformation for categorical 6D object pose and size estimation. In: ECCV. pp 530–546. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58589-1_32
Chen K, Dou Q (2021) SGPA: structure-guided prior adaptation for category-level 6D object pose estimation. In: ICCV. pp 2753–2762. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00277
Chen D, Li J, Wang Z et al (2020) Learning canonical shape space for category-level 6D object pose and size estimation. In: CVPR. pp 11973–11982. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01199
Chen W, Jia X, Chang HJ et al (2021) FS-Net: fast shape-based network for category-level 6D object pose estimation with decoupled rotation mechanism. In: CVPR. pp 1581–1590. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00163
Deng X, Geng J, Bretl T et al (2022) iCaps: iterative category-level object pose and shape estimation. IEEE Robot Autom Lett 7(2):1784–1791. https://doi.org/10.1109/LRA.2022.3142441
You Y, Shi R, Wang W et al (2022) CPPF: towards robust category-level 9D pose estimation in the wild. In: CVPR. pp 6866–6875. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00674
Chen X, Dong Z, Song J et al (2020) Category level object pose estimation via neural analysis-by-synthesis. In: ECCV. pp 139–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58574-7_9
Irshad MZ, Kollar T, Laskey M et al (2022) CenterSnap: single-shot multi-object 3D shape reconstruction and categorical 6D pose and size estimation. In: ICRA. pp 10632–10640. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA46639.2022.9811799
He K, Gkioxari G, Dollár P et al (2017) Mask R-CNN. In: ICCV. pp 2980–2988. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.322
Qi CR, Liu W, Wu C et al (2018) Frustum pointnets for 3D object detection from RGB-D data. In: CVPR. pp 918–927. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00102
Leng J, Liu Y (2022) Context augmentation for object detection. Appl Intell 52(3):2621–2633. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-02037-z
Zhang SX, Zhu X, Hou JB et al (2022) Graph fusion network for multi-oriented object detection. Appl Intell 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03396-5
Zhao H, Shi J, Qi X et al (2017) Pyramid scene parsing network. In: CVPR. pp 6230–6239. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.660
Aoki Y, Goforth H, Srivatsan RA et al (2019) PointNetLK: robust and efficient point cloud registration using pointnet. In: CVPR. pp 7156–7165. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00733
Fu Y, Wang X (2022) Category-level 6D object pose estimation in the wild: a semi-supervised learning approach and a new dataset. In: NIPS. pp 1–15. https://openreview.net/forum?id=FgDzS8_Fz7c
Marion P, Florence PR, Manuelli L et al (2018) Label fusion: a pipeline for generating ground truth labels for real RGBD data of cluttered scenes. In: ICRA. pp 3235–3242. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2018.8460950
Pan X, Xia Z, Song S et al (2021) 3D object detection with pointformer. In: CVPR. pp 7459–7468. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00738
Liu Z, Lin Y, Cao Y et al (2021) Swin transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In: ICCV. pp 9992–10002. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00986
Wu T, Tang S, Zhang R et al (2021) CGNet: a light-weight context guided network for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:1169–1179. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2020.3042065
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (U1813205), Hunan Provincial Science and Technology Foundation (2020GK2025), Shenzhen Science and Technology Foundation (2021Szvup035), State Key Laboratory of Advanced Design and Manufacturing for Vehicle Body Open Foundation, Hunan Key Laboratory of Intelligent Robot Technology in Electronic Manufacturing Open Foundation, Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (2022JJ50205).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Sun, W., Liu, J. et al. Fine segmentation and difference-aware shape adjustment for category-level 6DoF object pose estimation. Appl Intell 53, 23711–23728 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-023-04688-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-023-04688-0