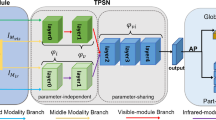
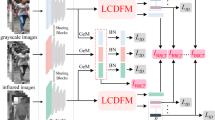
Abstract
Person re-identification (ReID) encompasses two independent study branches, i.e., single-modality and cross-modality identifications. Since single-modality and cross-modality pedestrian data have completely different properties, it is hard to accomplish both tasks at once. However, studying either of the two tasks alone limits the application of person ReID. Therefore, we first explore the relationship between single-modality and cross-modality person ReID and attempt to solve the multi-task optimization problem. To this end, we propose a unified framework, termed UnifiedSC, to mine identity-invariant discriminative features for multi-task person ReID. To effectively optimize the deep model, we construct a collaborative optimization strategy to simultaneously train visible and infrared images from two aspects. On the one hand, two independent classifiers are designed to separately perform single-modality and cross-modality pedestrian identification. On the other hand, we handle the identity-aware feature discrepancy problem at both the feature and classifier levels. At the feature level, we introduce a verification model to distinguish positive/negative sample pairs and employ the weighted regularization triplet to constrain the relative feature distribution. Meanwhile, at the classifier level, we create a shared-weight classifier to map pedestrian features from different domains into a similar feature space. With the promotion of collaborative optimization, the proposed UnifiedSC framework could perceive different pedestrian information and mine identity-invariant features. Our method achieves a mean rank-1 of = 84.7% on the Market1501 and SYSU-MM01 databases, while it also achieves a mean rank-1 of = 78.9% on the DukeMTMC-reID and SYSU-MM01 databases. Abundant experiments adequately demonstrate that UnifiedSC achieves state-of-the-art performance in both tasks and is valuable for person ReID.




Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bai X, Yang M, Huang T, Dou Z, Yu R, Xu Y (2020) Deep-person: Learning discriminative deep features for person re-identification. Pattern Recogn 98:107036
Chen D, Wu P, Jia T, Xu F (2022) Hob-net: high-order block network via deep metric learning for person re-identification. Appl Intell 52:4844–4857
Chen S, Jiang K, Liu X, Yang K, Lei Z (2023) Tgas-reid: Efficient architecture search for person re-identification via greedy decisions with topological order. Appl Intell 53(7):7343–7354
Chen W, Chen X, Zhang J, Huang K (2017) Beyond triplet loss: A deep quadruplet network for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 403–412
Chen X, Zheng X, Lu X (2021) Bidirectional interaction network for person re-identification. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:1935–1948
Chen X, Zheng X, Lu X (2023) Identity feature disentanglement for visible-infrared person re-identification. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications and Applications
Chen Y, Wan L, Li Z, Jing Q, Sun Z (2021b). Neural feature search for rgb-infrared person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 587–597
Fu C, Hu Y, Wu X, Shi H, Mei T, He R (2021) Cm-nas: Cross-modality neural architecture search for visible-infrared person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 11823–11832
Gao X, He F, Zhang S, Luo J, Fan B (2023) A fast nondominated sorting-based moea with convergence and diversity adjusted adaptively. J Supercomputing, pp 1–38
Gao Y, Liang T, Jin Y, Gu X, Liu W, Li Y, Lang C (2021) Mso: Multi-feature space joint optimization network for rgb-infrared person re-identification. In Proceedings of the ACM international conference on multimedia, pp 5257–5265
Gong S, Cheng J, Hou Z (2020) Faster person re-identification. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision, pp 275–292
Guo C, Zhao X, Zou Q (2022) Relation network based on multi-granular hypergraphs for person re-identification. Appl Intell 52(10):11394–11406
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 770–778
He L, Liu W (2020) Guided saliency feature learning for person re-identification in crowded scenes. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision, pp 357–373
He S, Luo H, Wang P, Wang F, Li H, Jiang W (2021) Transreid: Transformer-based object re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 15013–15022
Jia M, Cheng X, Lu S, Zhang J (2022) Learning disentangled representation implicitly via transformer for occluded person re-identification. IEEE Trans Multimed
Li D, Wei X, Hong X, Gong Y (2020a) Infrared-visible cross-modal person re-identification with an x modality. In: Proceedings of the association for the advance of artificial intelligence, pp 4610–4617
Li H, Wu G, Zheng W (2021) Combined depth space based architecture search for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 6729–6738
Li P, Wang Y, Si T, Ullah K, Han W, Wang L (2023) Dsfa: cross-scene domain style and feature adaptation for landslide detection from high spatial resolution images. International Journal of Digital Earth 16(1):2426–2447
Li P, Wang Y, Xu G, Wang L (2023) Landslidecl: towards robust landslide analysis guided by contrastive learning. Landslides 20:461–474
Li S, Yu H, Hu R (2020) Attributes-aided part detection and refinement for person re-identification. Pattern Recogn 97:107016
Liang T, Jin Y, Liu W, Li Y (2023) Cross-modality transformer with modality mining for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans Multimed
Liu C, Chang X, Shen Y (2020) Unity style transfer for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 6887–6896
Liu J, Song W, Chen C, Liu F (2022) Cross-modality person re-identification via channel-based partition network. Appl Intell 52:2423–2435
Lu Z, Lin R, Hu H (2023) Tri-level modality-information disentanglement for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans Multimed
Luo H, Jiang W, Gu Y, Liu F, Liao X, Lai S, Gu J (2020) A strong baseline and batch normalization neck for deep person re-identification. IEEE Trans Multimedia 22(10):2597–2609
Nguyen BX, Nguyen BD, Do T, Tjiputra E, Tran QD, Nguyen A (2021) Graph-based person signature for person re-identifications. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3492–3501
Park H, Lee S, Lee J, Ham B (2021) Learning by aligning: Visible-infrared person re-identification using cross-modal correspondences. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 12046–12055
Qi J, Liang T, Liu W, Li Y, Jin Y (2023) A generative-based image fusion strategy for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Vid Technol
Rao Y, Chen G, Lu J, Zhou J (2021) Counterfactual attention learning for fine-grained visual categorization and re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 1025–1034
Ristani E, Solera F, Zou R, Cucchiara R, Tomasi C (2016) Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision, pp 17–35
Serbetci A, Akgul YS (2020) End-to-end training of cnn ensembles for person re-identification. Pattern Recogn 104:107319
Si T, He F, Li P, Gao X (2023) Tri-modality consistency optimization with heterogeneous augmented images for visible-infrared person re-identification. Neurocomputing 523:170–181
Si T, He F, Li P, Song Y, Fan L (2023) Diversity feature constraint based on heterogeneous data for unsupervised person re-identification. Information Processing & Management 60(3):103304
Si T, He F, Li P, Ye M (2023c) Homogeneous and heterogeneous optimization for unsupervised cross-modality person re-identification in visual internet of things. IEEE Internet of Things Journal
Si T, He F, Wu H, Duan Y (2022) Spatial-driven features based on image dependencies for person re-identification. Pattern Recogn 124:108462
Si T, He F, Zhang Z, Duan Y (2022) Hybrid contrastive learning for unsupervised person re-identification. IEEE Trans Multimedia 25:4323–4334
Si T, Zhang Z, Liu S (2019) Compact triplet loss for person re-identification in camera sensor networks. Ad Hoc Netw 95:101984
Tian X, Zhang Z, Lin S, Qu Y, Xie Y, Ma L (2021) Farewell to mutual information: Variational distillation for cross-modal person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1522–1531
Wan L, Sun Z, Jing Q, Chen Y, Lu L, Li Z (2023) G2da: Geometry-guided dual-alignment learning for rgb-infrared person re-identification. Pattern Recogn 135:109150
Wang G, Yuan Y, Chen X, Li J, Zhou X (2018) Learning discriminative features with multiple granularities for person re-identification. In: ACM International conference on multimedia, pp 274–282
Wang G, Zhang T, Yang Y, Cheng J, Chang J, Liang X, Hou Z (2020) Cross-modality paired-images generation for rgb-infrared person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the association for the advance of artificial intelligence, pp 12144–12151
Wang Z, Jiang J, Wu Y, Ye M, Bai X, Satoh S (2019) Learning sparse and identity-preserved hidden attributes for person re-identification. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:2013–2025
Wei Z, Yang X, Wang N, Gao X (2021) Syncretic modality collaborative learning for visible infrared person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 225–234
Wu A, Zheng W, Yu H, Gong S, Lai J (2017) Rgb-infrared cross-modality person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 5380–5389
Wu G, Zhu X, Gong S (2021) Learning hybrid ranking representation for person re-identification. Pattern Recogn 121:108239
Wu G, Zhu X, Gong S (2022) Learning hybrid ranking representation for person re-identification. Pattern Recogn 121:108239
Wu H, He F, Duan Y, Yan S (2023) Perceptual metric-guided human image generation. Integr Comput-Aided Engineer. 2022, 29(2): 141–151
Ye M, Chen C, Shen J, Shao L (2022) Dynamic tri-level relation mining with attentive graph for visible infrared re-identification. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 17:386–398
Ye M, Ruan W, Du B, Shou MZ (2021) Channel augmented joint learning for visible-infrared recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International conference on computer vision, pp 13567–13576
Ye M, Shen J, J Crandall D, Shao L, Luo J (2020a) Dynamic dual-attentive aggregation learning for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision, pp 229–247
Ye M, Shen J, Lin G, Xiang T, Shao L, Hoi SC (2022) Deep learning for person re-identification: A survey and outlook. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 44(6):2872–2893
Ye M, Shen J, Shao L (2020) Visible-infrared person re-identification via homogeneous augmented tri-modal learning. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 16:728–739
Zhang D, Zhang Z, Ju Y, Wang C, Xie Y, Qu Y (2022) Dual mutual learning for cross-modality person re-identification. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 32(8):5361–5373
Zhang L, Guo H, Zhu K, Qiao H, Huang G, Zhang S, Zhang H, Sun J, Wang J (2022) Hybrid modality metric learning for visible-infrared person re-identification. ACM Trans Multimed Comput Commun Appl 18(1):1–15
Zhang Q, Lai C, Liu J, Huang N, Han J (2022c) Fmcnet: Feature-level modality compensation for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 7349–7358
Zhang Q, Lai J, Xie X (2021) Learning modal-invariant angular metric by cyclic projection network for vis-nir person re-identification. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:8019–8033
Zhang T, Sun X, Li X, Yi Z (2021) Image generation and constrained two-stage feature fusion for person re-identification. Appl Intell 51:7679–7689
Zheng L, Huang Y, Lu H, Yang Y (2019) Pose-invariant embedding for deep person re-identification. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(9):4500–4509
Zheng L, Shen L, Tian L, Wang S, Wang J, Tian Q (2015) Scalable person re-identification: A benchmark. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 1116–1124
Zheng Z, Yang X, Yu Z, Zheng L, Yang Y, Kautz J (2019b) Joint discriminative and generative learning for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp2138–2147
Zheng Z, Zheng L, Yang Y (2017) A discriminatively learned cnn embedding for person reidentification. ACM Trans Multimed Comput Commun Appl 14(1):1–20
Zhong X, Lu T, Huang W, Ye M, Jia X, Lin C (2022) Grayscale enhancement colorization network for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 32:1418–1430
Zhong Z, Zheng L, Zheng Z, Li S, Yang Y (2018) Camera style adaptation for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 5157–5166
Zhou K, Yang Y, Cavallaro A, Xiang T (2021) Learning generalisable omni-scale representations for person re-identification. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 44(9):5056–5069
Zhou Q, Zhong B, Lan X, Sun G, Zhang Y, Zhang B, Ji R (2020) Fine-grained spatial alignment model for person re-identification with focal triplet loss. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:7578–7589
Zhu Y, Yang Z, Wang L, Zhao S, Hu X, Tao D (2020) Hetero-center loss for cross-modality person re-identification. Neurocomputing 386:97–109
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 62072348, the New Introduced Talents Program of University of Jinan under Grant No. 1009569. The numerical calculations in this paper have been done on the supercomputing system in the Supercomputing Center of Wuhan University. The authors would also like to thank the Editor and anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions, which significantly improved the quality of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Tongzhen Si: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Investigation, Validation, Writing - original draft, Writing - revision. Fazhi He: Writing - review, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition. Penglei Li: Methodology, Writing - review, Validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Si, T., He, F. & Li, P. UnifiedSC: a unified framework via collaborative optimization for multi-task person re-identification. Appl Intell 54, 2962–2975 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-05333-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-05333-0