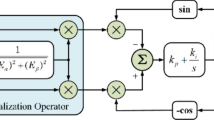
Abstract
Surface-mounted permanent magnet synchronous motor (SPMSM) is widely used in the industrial field with excellent performance, and the rise of artificial intelligence has also promoted its development. In order to improve the estimation accuracy and response of speed and position angle in the SPMSM sensorless control system, a novel sliding mode control model reference adaptive system (NSMC-MRAS) observer based on variable step hill climbing method for online optimization is proposed. Firstly, an MRAS adaptive observer was constructed, and a conventional SMC controller is used instead of the PI regulator to improve the robustness of the SPMSM parameters. Aiming at the problem of chattering caused by the sign function sgn(s), an improved NSMC-MRAS sensorless control strategy using the continuous function sigmoid(s) is proposed, which effectively suppresses the chattering phenomenon. To address the position estimation errors caused by non ideal factors such as control delay, filtering phase shift, and parameter deviation, the artificial intelligence variable step hill climbing method is used for online optimization and adaptive compensation. The experimental results show that the proposed NSMC-MRAS sensorless control strategy based on variable step hill climbing method for online optimization can quickly and accurately estimate the speed and position angle of SPMSM, improved the control performance and intelligence level of the system.











Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
The data are not publicly available due to copyright issues with co-developers. They are restricted to the experimental results.
References
Fang S, Wang Y, Wang W et al (2022) Design of permanent magnet synchronous motor servo system based on improved particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans Power Electron 37(5):5833–5846
Nair SV, Harikrishnan P, Hatua K (2022) Six-step operation of a symmetric dual three-phase PMSM with minimal circulating currents for extended speed range in electric vehicles. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 69(8):7651–7662
Chen S, Zhao Y, Qiu H et al (2020) High-precision rotor position correction strategy for high-speed permanent magnet synchronous motor based on resolver. IEEE Trans Power Electron 35(9):9716–9726
Ge Y, Song W, Yang Y et al (2023) A Polar-Coordinate-Multisignal-Flux-Observer-Based PMSM Non-PLL Sensorless Control. IEEE Trans Power Electron 38(9):10579–10583
Yan H, Wang W, Xu Y et al (2023) Position sensorless control for PMSM drives with single current sensor. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 70(1):178–188
Tian L, Wang Z, Yu Q et al (2023) Current reconstruction by one-step compensation for permanent magnet synchronous motor with fixed sampling interval in position sensorless control. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 70(1):200–210
Chen L, Jin Z, Shao K et al (2024) Sensorless fixed-time sliding mode control of pmsm based on barrier function adaptive super-twisting observer. IEEE Trans Power Electron 39(3):3037–3051
Qiu X, Ji J, Zhou D et al (2022) A modified flux observer for sensorless direct torque control of dual three-phase PMSM considering open-circuit fault. IEEE Trans Power Electron 37(12):15356–15369
Mai Z, Xiao F, Fu K et al (2021) HF pulsating carrier voltage injection method based on improved position error signal extraction strategy for PMSM position sensorless control. IEEE Trans Power Electron 36(8):9348–9360
Lu W, Zhao Y, Yan B et al (2022) Self-balancing control of yarn number based on a novel sensorless PMSM speed drive system. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 27(6):4293–4303
Ding L, Li YW, Zargari NR (2021) Discrete-time SMO sensorless control of current source converter-fed pmsm drives with low switching frequency. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 68(3):2120–2129
Chen Y, Yang T, Fan L et al (2023) Sensorless control design of high-speed electric drives in discrete-time domain for mild-hybrid turboprop aircraft applications. IEEE Trans Transport Electrific 9(3):3601–3619
Sun X, Zhang Y, Tian X et al (2022) Speed sensorless control for IPMSMs using a modified MRAS with gray wolf optimization algorithm. IEEE Trans Transport Electrific 8(1):1326–1337
Zhang R, Feng Y, Shi P et al (2023) Tire-road friction coefficient estimation for distributed drive electric vehicles using PMSM sensorless control. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 72(7):8672–8685
Wu J, Zhang J, Nie B et al (2022) Adaptive control of PMSM servo system for steering-by-wire system with disturbances observation. IEEE Trans Transport Electrific 8(2):2015–2028
Yoo J, Lee J, Sul SK (2021) Analysis of instability in torque control of sensorless PMSM drives in flux weakening region. IEEE Trans Power Electron 36(9):10815–10826
Wang Y, Xu Y, Zou J (2020) ILC-based voltage compensation method for PMSM sensorless control considering inverter nonlinearity and sampling current DC bias. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 67(7):5980–5989
Xu J, Du Y, Fang H et al (2020) A robust observer and nonorthogonal PLL-based sensorless control for fault-tolerant permanent magnet motor with guaranteed postfault performance. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 67(7):5959–5970
Wu C, Zheng L, Shi S et al (2023) A Quasi Edge Aligned Pulse-Width Modulation to Enhance Low-Speed Sensorless Control of PMSMs With a Single DC-Bus Current Sensor. IEEE Trans Energy Conver 38(4):2919–2928
Tan LN, Cong TP, Cong DP (2021) Neural network observers and sensorless robust optimal control for partially unknown PMSM with disturbances and saturating voltages. IEEE Trans Power Electron 36(10):12045–12056
Nguyen TT, Tran HN, Nguyen TH et al (2023) recurrent neural network-based robust adaptive model predictive speed control for PMSM with parameter mismatch. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 70(6):6219–6228
You S, Gil J, Kim W (2023) Adaptive neural network control using nonlinear information gain for permanent magnet synchronous motors. IEEE Trans Cybernetics 53(3):1392–1404
Yao C, Sun Z, Xu S et al (2022) ANN optimization of weighting factors using genetic algorithm for model predictive control of PMSM drives. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 58(6):7346–7362
Song J, Wang YK, Zheng WX et al (2023) Adaptive terminal sliding mode speed regulation for PMSM under neural-network-based disturbance estimation: a dynamic-event-triggered approach. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 70(8):8446–8456
Karabacak M, Fernandez-Ramirez LM, Kamal T et al (2019) A new hill climbing maximum power tracking control for wind turbines with inertial effect compensation. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 66(11):8545–8556
Yang L, Gao H, Ling Y et al (2022) Localization method of wide-area distribution multistatic sky-wave over-the-horizon radar. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 19:1–5
Choi E, Namgoong G, Park W et al (2022) A 1.4mW to 119mW, Wide Output Power Range Energy Harvesting System With 2-D Fast MPPT Based on HC for 1k to 50k Illuminated Solar Cell. IEEE Trans Circ Syst II: Express Briefs 69(11):4389–4393
Kumar N, Singh B, Wang J et al (2020) A framework of L-HC and AM-MKF for accurate harmonic supportive control schemes. IEEE Trans Circ Syst I: Regular Pap 67(12):5246–5256
Raiker GA, Loganathan U, Reddy S (2021) Current control of boost converter for PV interface with momentum-based perturb and observe MPPT. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 57(4):4071–4079
Lu W, Tang B, Ji K et al (2021) A new load adaptive identification method based on an improved sliding mode observer for PMSM position servo system. IEEE Trans Power Electron 36(3):3211–3223
Yim J, You S, Lee Y et al (2023) Chattering attenuation disturbance observer for sliding mode control: application to permanent magnet synchronous motors. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 70(5):5161–5170
Kashif M, Singh B (2023) Modified active-power MRAS based adaptive control with reduced sensors for PMSM operated solar water pump. IEEE Trans Energy Conver 38(1):38–52
Liu ZH, Nie J, Wei HL et al (2022) Second-order ESO-based current sensor fault-tolerant strategy for sensorless control of PMSM with B-phase current. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 27(6):5427–5438
Novak Z (2024) Confidence weighted learning entropy for fault-tolerant control of a PMSM with a high-resolution hall encoder. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 71(7):5176–5186
Badini SS, Verma V (2020) A new stator resistance estimation technique for vector-controlled PMSM drive. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 56(6):6536–6545
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2020YFE0205400), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52337002 and 52305541).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The first author Zhe Song is the designer of method and the writer of paper. He is the major contributor of this paper. The second author Weihong Zhou edits this paper and provides experimental assistance. The corresponding author Xi Xiao provides comprehensive guidance. The fourth author Jiayue Zhou provides valuable advice and help.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and informed consent
Used experiment data was conducted by the authors and have no associated privacy and copyright issues.
Competing interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Song, Z., Zhou, W., Xiao, X. et al. Application of hill climbing method in position angle compensation for SPMSM. Appl Intell 54, 8889–8901 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-05594-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-05594-9