Abstract
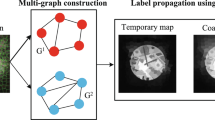
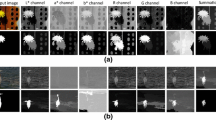
Salient object detection is a challenging task in computer vision and has been used to extract valuable information from many real scenarios. The graph-based detection approach has attracted extensive attention because of its high efficiency and stability. Nevertheless, most existing approaches utilize multiview features to construct graph models, resulting in poor performance in extreme scenes. In graph-based models, the graph structure and neighbourhoods play essential roles in salient object detection performance. In this paper, we propose a novel saliency detection approach via multiview diffusion-based affinity learning with good neighbourhoods. The proposed model includes three components: 1) multiview diffusion-based affinity learning to produce a local/global affinity matrix, 2) subspace clustering to choose good neighbourhoods, and 3) an unsupervised graph-based diffusion model to guide saliency detection. The uniqueness of our affinity graph model lies in exploring multiview handcrafted features to identify different underlying salient objects in extreme scenes. Extensive experiments on several standard databases validate the superior performance of the proposed model over other state-of-the-art methods. The experimental results demonstrate that our graph model with multiview handcrafted features is competitive with the outstanding graph models with multiview deep features.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data Availibility and Acces
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Kong Y, Wang Y, Li A (2021) Spatiotemporal saliency representation learning for video action recognitionl. IEEE Trans Multimed 1. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2021.3066775
Chen Y, Zhang Z, Dong L, Xiong S, Lu X (2024) A joint saliency temporal-spatial-spectral information network for hyperspectral image change detection. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 62:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2023.3344583
Xiao M, Yang B, Wang S, Zhang Z, He Y (2023) Fine coordinate attention for surface defect detection. Eng Appl Artif Intell 123:106368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2023.106368
Lateef F, Kas M, Ruichek Y (2022) Saliency heat-map as visual attention for autonomous driving using generative adversarial network (gan). IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 23(6):5360–5373. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2021.3053178
Sun C, Wu X, Sun J, Sun C, Xu M, Ge Q (2023) Saliency-induced moving object detection for robust rgb-d vision navigation under complex dynamic environments. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2023.3275279
Liu J, Dian R, Li S, Liu H (2023) Sgfusion: A saliency guided deep-learning framework for pixel-level image fusion. Information Fusion 91:205–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2022.09.030
Zhu W, Liang S, Wei Y, Sun J (2014) Saliency optimization from robust background detection. Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2814–2821. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2014.360
Cheng M-M, Mitra NJ, Huang X, Torr PHS, Hu S-M (2015) Global contrast based salient region detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 37(3):569–582. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2345401
Jian M, Wang J, Yu H, Wang G, Meng X, Yang L, Dong J, Yin Y (2021) Visual saliency detection by integrating spatial position prior of object with background cues. Expert Syst Appl 168:114219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.114219
Song S, Jia Z, Yang J, Kasabov N (2022) Salient detection via the fusion of background-based and multiscale frequency-domain features. Inf Sci 618:53–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2022.10.103
Sun X, Zhang X, Xu C, Xiao M, Tang Y (2023) Tensorial multiview representation for saliency detection via nonconvex approach. IEEE Transactions on cybernetics 53(3):1816–1829. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2021.3139037
Li X, Song D, Dong Y (2020) Hierarchical feature fusion network for salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:9165–9175. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2020.3023774
Zong G, Wei L, Guo S, Wang Y (2022) A cascaded refined rgb-d salient object detection network based on the attention mechanism. Appl Intell 53(11):1–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-04186-9
Chen C, Song M, Song W, Guo L, Jian M (2023) A comprehensive survey on video saliency detection with auditory information: The audio-visual consistency perceptual is the key! IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 33(2):457–477. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2022.3203421
Qian X, Zeng Y, Wang W, Zhang Q (2023) Co-saliency detection guided by group weakly supervised learning. IEEE Trans Multimedia 25:1810–1818. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2022.3167805
Wang K, Lin D, Li C, Tu Z, Luo B (2024) Alignment-free rgbt salient object detection: Semantics-guided asymmetric correlation network and a unified benchmark. IEEE Trans Multimedia 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2024.3410542
Goferman S, Zelnik-Manor L, Tal A, (2012) Context-aware saliency detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 34(10):1915–1926. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2011.272
Yang C, Zhang L, Lu H, Ruan X, Yang MH (2013) Saliency detection via graph-based manifold ranking. Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 3166–3173. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2013.407
Li C, Yuan Y, Cai W, Xia Y, Feng DD (2015) Robust saliency detection via regularized random walks ranking. Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 07-12-June, pp 2710–2717. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298887
Moradi M, Bayat F (2021) A salient object segmentation framework using diffusion-based affinity learning. Expert Syst Appl 168:114428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.114428
Zhang YY, Wang H, Lv X, Zhang P (2021) Capturing the grouping and compactness of high-level semantic feature for saliency detection. Neural Netw 142:351–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2021.04.028
Gong A, Huang L, Shi J, Liu C (2022) Unsupervised rgb-t saliency detection by node classification distance and sparse constrained graph learning. Appl Intell 52(1):1030–1043. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02434-y
Ganguly B, Dey D, Munshi S (2022) An unsupervised learning approach for road anomaly segmentation using rgb-d sensor for advanced driver assistance system. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 23(10):19042–19053. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2022.3164847
Zhou L, Yang Z, Yuan Q, Zhou Z, Hu D (2015) Salient Region Detection via Integrating Diffusion-Based Compactness and Local Contrast. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(11):3308–3320. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2015.2438546
Qin Y, Feng M, Lu H, Cottrell G (2018) Hierarchical cellular automata for visual saliency. Int J Comput Vision 126:751–770. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-017-1062-2
Zhang L, Ai J, Jiang B, Lu H, Li X (2018) Saliency Detection via Absorbing Markov Chain with Learnt Transition Probability. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(2):987–998. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2017.2766787
Itti L, Koch C, Niebur E (1998) A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 20(11):1254–1259. https://doi.org/10.1109/34.730558
Yuan B, Han L, Yan H (2021) Explore double-opponency and skin color for saliency detection. Neurocomputing 425:219–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2020.04.089
Huang Z, Chen H-X, Zhou T, Yang Y-Z, Wang C-Y, Liu B-Y (2021) Contrast-weighted dictionary learning based saliency detection for vhr optical remote sensing images. Pattern Recogn 113:107757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107757
Deng C, Yang X, Nie F, Tao D (2020) Saliency Detection via a Multiple Self-Weighted Graph-Based Manifold Ranking. IEEE Trans Multimedia 22(4):885–896. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2019.2934833
Xu M, Liu B, Fu P, Li J, Hu YH, Feng S (2020) Video salient object detection via robust seeds extraction and multi-graphs manifold propagation. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 30(7):2191–2206. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2019.2920652
Xia C, Gao X, Li KC, Zhao Q, Zhang S (2021) Salient object detection based on distribution-edge guidance and iterative bayesian optimization. Applied Intelligence: The International Journal of Artificial Intelligence, Neural Networks, and Complex Problem-Solving Technologies 10:50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-01691-7
Pang Y, Wu C, Wu H, Yu X (2023) Unsupervised multi-subclass saliency classification for salient object detection. IEEE Trans Multimedia 25:2189–2202. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2022.3144070
Pan W, Sun X, Qian Y() Rgb-d saliency detection via complementary and selective learning. Applied Intelligence: The International Journal of Artificial Intelligence, Neural Networks, and Complex Problem-Solving Technologies 53(7):7957–7969. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03612-2
Wang L, Wang L, Lu H, Zhang P, Ruan X (2019) Salient object detection with recurrent fully convolutional networks. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 41(07):1734–1746. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2846598
Xia C, Zhang H, Gao X, Li K (2020) Exploiting background divergence and foreground compactness for salient object detection. Neurocomputing 383(28):194–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2019.09.096
Huang L, Song K, Gong A, Liu C, Yan Y (2020) Rgb-t saliency detection via low-rank tensor learning and unified collaborative ranking. IEEE Signal Process Lett 27:1585–1589. https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2020.3020735
Huang L, Song K, Wang J, Niu M, Yan Y (2022) Multi-graph fusion and learning for rgbt image saliency detection. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 32(3):1366–1377. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3069812
Tu Z, Xia T, Li C, Wang X, Ma Y, Tang J (2020) RGB-T Image Saliency Detection via Collaborative Graph Learning. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia 22(1):160–173. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2019.2924578. arXiv:1905.06741
Xu M, Fu P, Liu B, Li J (2021) Multi-stream attention-aware graph convolution network for video salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:4183–4197. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2021.3070200
Xu M, Fu P, Liu B, Yin H, Li J (2021) A novel dynamic graph evolution network for salient object detection. Appl Intell 52(3):2854–2871. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02479-z
Wu Y, Jia T, Chang X, Wang H, Chen D (2024) Rgb-t saliency detection based on multiscale modal reasoning interaction. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 73:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2024.3419115
Li C, Liu F, Tian Z, Du S, Wu Y (2024) Dagcn: Dynamic and adaptive graph convolutional network for salient object detection. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems 35(6):7612–7626. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3219245
Jiang B, Zhang L, Lu H, Yang C, Yang M-H (2013) Saliency Detection via Absorbing Markov Chain. In: The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp 1665–1672
Yuan Y, Li C, Kim J, Cai W, Feng DD (2018) Reversion correction and regularized random walk ranking for saliency detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(3):1311–1322. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2017.2762422
Achanta R, Shaji A, Smith K, Lucchi A, Fua P, Süsstrunk S (2012) SLIC superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 34(11):2274–2281. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2012.120
Heikkilä M, Pietikäinen M, Schmid C (2009) Description of interest regions with local binary patterns. Pattern Recogn 42(3):425–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2008.08.014
Simoncelli EP, Freeman WT (1995) The steerable pyramid: a flexible architecture for multi-scale derivative computation. In: Proceedings., International Conference on Image Processing, vol 3, pp 444–447. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.1995.537667
Arbeláez P, Maire M, Fowlkes C, Malik J (2011) Contour detection and hierarchical image segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 33(5):898–916. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2010.161
Bai S, Bai X, Tian Q, Latecki LJ (2019) Regularized diffusion process on bidirectional context for object retrieval. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 41(5):1213–1226. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2828815
Tang C, Liu X, Zhu X, Zhu E, Gao W (2020) Cgd: Multi-view clustering via cross-view graph diffusion. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 34(4):5924–5931
You C, Robinson D.P, Vidal R (2016) Scalable sparse subspace clustering by orthogonal matching pursuit. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 3918–3927. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.425
Yan Q, Xu L, Shi J, Jia J (2013) Hierarchical saliency detection. Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 1155–1162. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2013.153
Movahedi V, Elder J.H (2010) Design and perceptual validation of performance measures for salient object segmentation. 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition - Workshops, CVPRW 2010, pp 49–56. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2010.5543739
Li Y, Hou X, Koch C, Rehg JM, Yuille AL (2014) The secrets of salient object segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp,280–287. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2014.43
Li G, Yu Y (2016) Visual saliency detection based on multiscale deep CNN features. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 25(11):5012–5024. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2016.2602079. arXiv:1609.02077
Achantay R, Hemamiz S, Estraday F, Süsstrunky S (2009) Frequency-tuned salient region detection. 2009 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, CVPR Workshops 2009 2009 IEEE, pp 1597–1604. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2009.5206596
Fan D.-P, Gong C, Cao Y, Ren B, Cheng M.-M, Borji A (2018) Enhanced-alignment measure for binary foreground map evaluation. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. IJCAI’18. pp 698–704
Fan D.P, Cheng M.M, Liu Y, Li T, Borji A (2017) Structure-Measure: A New Way to Evaluate Foreground Maps. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, vol 2017-Octob, pp 4558–4567. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.487
Margolin R, Zelnik-Manor L, Tal A (2014) How to evaluate foreground maps. Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 248–255. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2014.39
Peng H, Li B, Ling H, Hu W, Xiong W, Maybank SJ (2017) Salient Object Detection via Structured Matrix Decomposition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(4):818–832. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2562626
Perazzi F, Krahenbuhl P, Pritch Y, Hornung A (2012) Saliency filters: Contrast based filtering for salient region detection. Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 733–740. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2012.6247743
Li X, Lu H, Zhang L, Ruan X, Yang M-H (2013) Saliency detection via dense and sparse reconstruction. In: 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 2976–2983. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2013.370
Qin Y, Lu H, Xu Y, Wang H (2015) Saliency detection via Cellular Automata. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, vol 07-12-June, pp 110–119. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298606
Sun J, Lu H, Liu X (2015) Saliency Region Detection Based on Markov Absorption Probabilities. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(5):1639–1649. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2015.2403241
Fu K, Gu I.Y.H, Gong C, Yang J (2015) Robust manifold-preserving diffusion-based saliency detection by adaptive weight construction. Neurocomputing 175(PartA):336–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.10.066
Zhou L, Yang Z, Zhou Z, Hu D (2017) Salient Region Detection Using Diffusion Process on a Two-Layer Sparse Graph. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(12):5882–5894. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2017.2738839
Wang J, Jiang H, Yuan Z, Cheng MM, Hu X, Zheng N (2013) Salient Object Detection: A Discriminative Regional Feature Integration Approach. Int J Comput Vision 123:251–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-016-0977-3
Cong R, Lei J, Fu H, Hou J, Huang Q, Kwong S (2020) Going From RGB to RGBD Saliency: A Depth-Guided Transformation Model. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics 50(8):3627–3639. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2019.2932005
Wang F, Peng G (2021) Graph-based saliency detection using a learning joint affinity matrix. Neurocomputing 458:33–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2021.03.131
Wang F, Peng G (2022) Graph construction by incorporating local and global affinity graphs for saliency detection. Signal Processing: Image Communication 105:116712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.image.2022.116712
Zhang L, Sun J, Wang T, Min Y, Lu H (23020) Visual saliency detection via kernelized subspace ranking with active learning. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 29:2258–2270. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2019.2945679
Zeng Y, Zhuge Y, Lu H, Zhang L, Qian M, Yu Y (2019) Multi-source weak supervision for saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52104031 and No. 12401673) and the Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi (2024JC-YBQN-0670).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Fan Wang and Mingxian Wang wrote the main manuscript text and Fan Wang prepared all figures. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Ethical Approval
This article complies with ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Wang, M. & Peng, G. Multiview diffusion-based affinity graph learning with good neighbourhoods for salient object detection. Appl Intell 55, 37 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-05847-7
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-05847-7