Abstract
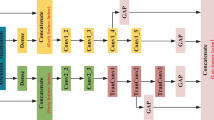
Fault diagnosis is an important subfield of prognostic and health management (PHM). Intelligent fault diagnosis based on deep learning is the most popular data-driven method of the present. However, current researches are prone to ignoring the strong noisy backgroundin real working conditions and cannot achieve excellent performance in actual application. As we all know, noise reduction and feature extraction are two vital aspects in mechanicalfault diagnosis. In this article, an intelligent diagnostic model based onimproved stacked convolutional auto-encoder (ISCAE) and parallel attention-based convolutional blocks (PACB) is proposed. ISCAE-based module is constructed to reduce the noise of raw signals and then PACB-based module can synchronouslyextract local spatial feature and global feature automatically.To equalize the role of above-mentioned two modules which are serial in the proposed model, two modules are trained and optimized synchronously to simultaneously adjust the neural network weights. The capability and effectiveness of the model are evaluated using a dataset collected from real operating environment of main reducer. The comparative analysisresults show that the ISCAE-PACB-based model can reach the accuracy of 98.95% and is superior to existing models.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Jiang GJ, Yang JS, Cheng TC, Sun HH (2023) Remaining useful life prediction of rolling bearings based on bayesian neural network and uncertainty quantification. Qual Reliab Eng Int 39(5):1756–1774
Ye Q, Liu CH et al (2021) An unsupervised deep feature learning model based on parallel convolutional autoencoder for intelligent fault diagnosis of main reducer[J]. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience
Han T, Ma RY, Zheng JG (2021) Combination bidirectional long short-term memory and capsule network for rotating machinery fault diagnosis. Measurement 176:109208
Ye Q, Liu SH, Liu CH (2020) A deep learning model for fault diagnosis with a deep neural network and feature fusion on multi-channel. Sens Signals[J] Sens 20(15)
Guo J, Yang Y, Li H, Dai L, Huang B (2024) A parallel deep neural network for intelligent fault diagnosis of drilling pumps. Eng Appl Artif Intell 133:108071
Wu MY, Ye Q, Mu JX et al (2023) Remaining useful life Prediction via adata-driven deep learning fusion model–CALAP[J]. IEEE Access 11:112085–112096
Zhou FA, Liu S, Fujita H et al (2024) Fault diagnosis based on federated learning driven by dynamic expansion for model layers of imbalanced client. Expert Syst Appl 238:121982
Lei YG, Yang B, Jiang XW et al (2020) Applications of machine learning to machine fault diagnosis: a review and roadmap. Mech Syst Signal Process 138:106587
Ribeiro RF, Areias IAND, Gomes GF (2021) Fault detection and diagnosis using vibration signalanalysis in frequency domain for electric motors considering different real fault types. Sens Rev 41(3):311–319
He F, Ye Q (2022) A bearing fault diagnosis method based on wavelet packettransform and convolutional neural network optimized bySimulated annealing Algorithm. Sensors 22(4):1410
Zhang HR, Sun JX, Hou KN et al (2022) Improved information entropy weighted vague support vector machine method for transformer fault diagnosis. High Voltage 7(3):510–522
Xie X, Xiong GJ, Chen J et al (2022) Universal transparent artificial neural network-based fault section diagnosis models for power systems. Adv Theory Simul 5(4):2100402
Huang GB, Zhu Q (2006) Extreme learning machine theory and applications. Neurocomputing 70(1–3):489–501
Sikder N, Arif AM, Manjurul I et al (2021) Induction motor bearing fault classification using extreme learning machine based on power features. Arab J Sci Eng 46(9):8475–8491
Jiang Z, Zhou J, Ma YZ (2022) Fault diagnosis for rolling bearing based on parameter transfer bayesian network[J]. Qual Reliab Eng Int 38(8):4291–4308
Zhang ZQ, ,Zhou FN, Zhang CS et al (2023) A personalized federated learning-based fault diagnosis method for data suffering from network attacks. Appl Intell 53(19):22834–22849
Gong B, An AM, Shi YK (2024) Photovoltaic arrays fault diagnosis based on an improved dilated convolutional neural network with feature-enhancement. Meas Sci Technol 35(1):015011
Zhang FF, Chen LB, Dai YY et al (2024) Bearing Fault diagnosis based on convolution neural network with logistic chaotic map. Adv Theory Simul 7(5):2301090
Yu WK, Zhao CH (2020) Broad convolutional neural network based industrialprocess fault diagnosis with incremental learning capability. IEEE TransInd Electron 67(6):5081–5091
Qin CJ, Jin YR, Zhang ZN et al (2023) Anti-noise diesel engine misfire diagnosis using a multi-scale CNN-LSTM neural network with denoising module. CAAI Trans Intell Technol 8(3):963–986
Plakias S, Boutalis YS (2020) Fault detection and identification of rollingelement bearings with attentive dense CNN. Neurocomputing 405:208–217
Wang YX, Yan J, Ye X et al (2022) Few-shot transfer learning with attention mechanism for high-voltage circuit breaker fault diagnosis. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 58(3):3353–3360
Chen YM, Wang YZ, Yu Y et al (2023) A fault diagnosis method for the autonomous underwater vehicle via meta-self-attention multi-scale CNN. J Mar Sci Eng 11(6):1121
Xing ZK, Liu YB, Wang Q et al (2022) Multi-sensor signals with parallel attention convolutional neural network for bearing fault diagnosis. AIP Adv 12(7):075020
Li X, Zhang W, Ding Q (2019) Understanding and improving deep learning-based rolling bearing fault diagnosis with attention mechanism. Signal Process 161:136–154
Liu CD, Zhang LX, Yao R et al (2021) Dual attention-based temporalconvolutional network for fault prognosis under time-time-varying operatingconditions. IEEE Trans InstrumMeas 70:3512210
Chegini SN, Bagheri A, Najafi F (2019) Application of a new EWT-based denoising technique in bearing fault diagnosis. Measurement 144:275–297
Dinesh PS, Manikandan M (2022) Fully convolutional deep stacked denoising sparse auto encoder network for partial face reconstruction. Pattern Recogn 130:108783
Yu JB (2019) Evolutionary manifold regularized stacked denoisingautoencoders for gearbox fault diagnosis. Knowl Based Syst 178:111–122
Gu K, Zhang Y, Liu X et al (2021) DWT-LSTM-based fault diagnosis of rolling bearings with multi-sensors. Electronics 10(17):2076
Wang YM, Cao GQ (2023) A multiscale convolution neural network for bearing fault diagnosis based on frequency division denoising under complex noise conditions. Complex Intell Syst 9(4):4263–4285
Guo FY, Zhang YC, Wang Y et al (2020) Fault detectionof reciprocating compressor valve based on one-dimensional convolutional neural network. Math Prob Engi 2020:8058723
Song Q, Zhao SF, Wang MS (2020) On the accuracy of fault diagnosis for rolling element bearings using improved DFA and multi-sensor data fusion method. Sensors 20(22):6465
Zhao ZQ, Jiao YH, Zhang X (2023) A Fault diagnosis method of rotor system based on parallel convolutional neural network architecture with attention mechanism. J Signal Process Syst 95(8):965–977
Zhong XY, Li YF, Xia TY (2023) Parallel learning attention-guided CNN for signal denoising and mechanical fault diagnosis. J Brazi Soc Mech Sci Eng 45(5):239
Wei AA, Han SY, Li W et al (2023) A new framework for intelligent fault diagnosis of spiral bevel gears with unbalanced data. Appl Intell 53(18):21312–21324
Karnavas YL, Plakias S, Chasiotis ID (2021) Extracting spatially global and local attentive features for rolling bearing fault diagnosis in electrical machines using attention stream networks. IET Electr Power Appl 15(7):903–915
Rai K, Hojatpanah F, Ajaei FB et al (2022) Deep learning for high-impedance fault detection and classification: transformer-CNN. Neural Comput Appl 34(16):14067–14084
Wu PL, Nie XY, Xie G (2021) Multi-sensor signal fusion for a compound fault diagnosis method with strong generalization and noise-tolerant performance. Meas Sci Technol 32(3):035108
Ma YL, Cheng JS, Wang P et al (2022) A novel Lanczos quaternion singular spectrum analysis method and its application to bevel gear fault diagnosis with multi-channel signals. Mech Syst Signal Process 168:108679
Che C, Wang H, Ni X et al (2020) Intelligent fault diagnosis method of rolling bearing based on stacked denoisingautoencoder and convolutional neural network. Ind Lubr Tribol 72(7):947–953
Sun C, Ma M, Zhao ZB et al (2019) Deep transfer learning based on sparse auto-encoder for remaining useful life prediction of tool in manufacturing. IEEE Trans Ind Informatics 2019:1–10
Guo QW, Li YB, Song Y et al (2020) Intelligent fault diagnosis method based on full 1-D convolutional generative adversarial network. IEEE Trans Industrial Inf 16(3):2044–2053
Zhang S, Zhang SB, Wang BN et al (2020) Deep learning algorithms for bearing fault diagnostics—a comprehensive review. IEEE Access 8:29857–29881
Hu J, Shen L, Sun G (2018) Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit 2018:7132–7141
Huang G, Liu Z, Maaten LVD et al (2017) Densely connected convolutional networks. Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit 2017:2261–2269
Acknowledgements
The researches were funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62006028), the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (Grant No.2023AFB909).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qing Ye carries out research and designedthe technical routes, completed the simulation experiments and implemented the main framework, wrote the thesis; Changhua Liu modified and proofread the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, Q., Liu, C. Intelligent fault diagnosis of automobile main reducer based onstacked convolutional auto-encoder and parallel attention-based convolutional blocks. Appl Intell 55, 24 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-05868-2
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-05868-2