Abstract
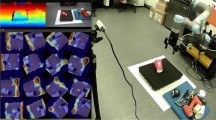
As the first step in grasping operations, vision-guided grasping actions play a crucial role in enabling intelligent robots to perform complex interactive tasks. In order to solve the difficulties in data set preparation and consumption of computing resources before and during training network, we introduce a method of training human grasping strategies based on small sample representative data sets, and learn a human grasping strategy through only one depth image. Our key idea is to use the entire human grasping area instead of multiple grasping gestures so that we can greatly reduce the preparation of dataset. Then the grasping strategy is trained through the q-learning framework, the agent is allowed to continuously explore the environment so that it can overcome lack of data annotation and prediction in early stage of the visual network, then successfully map the human strategy into visual prediction. Considering the widespread clutter environment in real tasks, we introduce push actions and adopt a staged reward function to make it conducive to the grasping. Finally we learned the human grasping strategy and applied it successfully, and stably executed it on objects that not seen before, improved the convergence speed and grasping effect while reducing the consumption of computing resources. We conducted experiments on a Doosan robotic arm equipped with an Intel Realsense camera and a two-finger gripper, and achieved human strategy grasping with a high success rate in cluttered scenes.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
Available upon reasonable request
Code availability
Not applicable
Materials availability
Not applicable
References
Di Napoli C, Ercolano G, Rossi S (2023) Personalized home-care support for the elderly: a field experience with a social robot at home. User Model User-Adap Inter 33(2):405–440
Li L, Foo MJ, Chen J, Tan KY, Cai J, Swaminathan R, Chua KSG, Wee SK, Kuah CWK, Zhuo H et al (2023) Mobile robotic balance assistant (mrba): a gait assistive and fall intervention robot for daily living. J. NeuroEngineering Rehabil 20(1):29
Blindheim K, Solberg M, Hameed IA, Alnes RE (2023) Promoting activity in long-term care facilities with the social robot pepper: a pilot study. Inf Health Soc Care 48(2):181–195
Shimoga KB (1996) Robot grasp synthesis algorithms: A survey. Int J Robot Res 15(3):230–266
Cui J, Trinkle J (2021) Toward next-generation learned robot manipulation. Sci Robot 6(54):9461
Suomalainen M, Karayiannidis Y, Kyrki V (2022) A survey of robot manipulation in contact. Robot Auton Syst 156:104224
Wang P, Manhardt F, Minciullo L, Garattoni L, Meier S, Navab N, Busam B (2021) Demograsp: Few-shot learning for robotic grasping with human demonstration. In: 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp 5733–5740. IEEE
Ye J, Wang J, Huang B, Qin Y, Wang X (2023) Learning continuous grasping function with a dexterous hand from human demonstrations. IEEE Robot Autom Lett 8(5):2882–2889
Mandikal P, Grauman K (2021) Learning dexterous grasping with object-centric visual affordances. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp 6169–6176. IEEE
Kokic M, Kragic D, Bohg J (2020) Learning task-oriented grasping from human activity datasets. IEEE Robot Autom Lett 5(2):3352–3359
Brahmbhatt S, Handa A, Hays J, Fox D (2019) Contactgrasp: Functional multi-finger grasp synthesis from contact. In: 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp 2386–2393. IEEE
Rohmer E, Singh S.P, Freese M (2013) V-rep: A versatile and scalable robot simulation framework. In: 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp 1321–1326. IEEE
Galarza BR, Ayala P, Manzano S, Garcia MV (2023) Virtual reality teleoperation system for mobile robot manipulation. Robot 12(6):163
Ye J, Wang J, Huang B, Qin Y, Wang X (2023) Learning continuous grasping function with a dexterous hand from human demonstrations. IEEE Robot Autom Lett 8(5):2882–2889
Xu B, Zhang K, Yang X, Liu D, Hu C, Li H, Song A (2022) Natural grasping movement recognition and force estimation using electromyography. Front Neurosci 16:1020086
Yu X, Liu P, He W, Liu Y, Chen Q, Ding L (2022) Human-robot variable impedance skills transfer learning based on dynamic movement primitives. IEEE Robot Autom Lett 7(3):6463–6470
Maranci E, D’Avella S, Tripicchio P, Avizzano CA (2024) Enabling grasp synthesis approaches to task-oriented grasping considering the end-state comfort and confidence effects. IEEE Robot Autom Lett 9(6):5695–5702. https://doi.org/10.1109/LRA.2024.3396102
Zhang H, Yang D, Wang H, Zhao B, Lan X, Ding J, Zheng N (2022) Regrad: A large-scale relational grasp dataset for safe and object-specific robotic grasping in clutter. IEEE Robot Autom Lett 7(2):2929–2936. https://doi.org/10.1109/LRA.2022.3142401
Holomjova V, Starkey AJ, Yun B, Meißner P (2023) One-shot learning for task-oriented grasping. IEEE Robot Autom Lett 8(12):8232–8238. https://doi.org/10.1109/LRA.2023.3326001
Yu S, Zhai DH, Xia Y (2023) Robotic grasp detection based on category-level object pose estimation with self-supervised learning. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron
Liu X, Yuan X, Zhu Q, Wang Y, Feng M, Zhou J, Zhou Z (2023) A depth adaptive feature extraction and dense prediction network for 6-d pose estimation in robotic grasping. IEEE Trans Ind Inf
Chai Z, Liu C, Xiong Z (2023) Multi-pyramid-based hierarchical template matching for 6d pose estimation in industrial grasping task. Ind Robot Int J Robot Res Appl
Sundermeyer M, Mousavian A, Triebel R, Fox D (2021) Contact-graspnet: Efficient 6-dof grasp generation in cluttered scenes. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp 13438–13444. IEEE
Breyer M, Chung JJ, Ott L, Siegwart R, Nieto J (2021) Volumetric grasping network: Real-time 6 dof grasp detection in clutter. In: Conference on Robot Learning, pp 1602–1611. PMLR
Mousavian A, Eppner C, Fox D (2019) 6-dof graspnet: Variational grasp generation for object manipulation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 2901–2910
Hang K, Morgan AS, Dollar AM (2019) Pre-grasp sliding manipulation of thin objects using soft, compliant, or underactuated hands. IEEE Robot Autom Lett 4(2):662–669
Song C, Boularias A (2020) A probabilistic model for planar sliding of objects with unknown material properties: Identification and robust planning. In: 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp 5311–5318. IEEE
Song C, Boularias A (2020) Identifying mechanical models of unknown objects with differentiable physics simulations. In: Learning for Dynamics and Control, pp 749–760. PMLR
Cao H, Zeng W, Wu I (2022) Reinforcement learning for picking cluttered general objects with dense object descriptors. In: 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp 6358–6364. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA46639.2022.9811911
Ceola F, Rosasco L, Natale L (2024) Resprect: Speeding-up multi-fingered grasping with residual reinforcement learning. IEEE Robot Autom Lett 9(4):3045–3052. https://doi.org/10.1109/LRA.2024.3363532
Liu F, Sun F, Fang B, Li X, Sun S, Liu H (2023) Hybrid robotic grasping with a soft multimodal gripper and a deep multistage learning scheme. IEEE Trans Robot 39(3):2379–2399. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2023.3238910
Zeng A, Song S, Welker S, Lee J, Rodriguez A, Funkhouser T (2018) Learning synergies between pushing and grasping with self-supervised deep reinforcement learning. In: 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp 4238–4245. IEEE
Zeng A, Song S, Yu KT, Donlon E, Hogan FR, Bauza M, Ma D, Taylor O, Liu M, Romo E et al (2022) Robotic pick-and-place of novel objects in clutter with multi-affordance grasping and cross-domain image matching. Int J Robot Res 41(7):690–705
Huang B, Han SD, Boularias A, Yu J (2021) Dipn: Deep interaction prediction network with application to clutter removal. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp 4694–4701. IEEE
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 770–778
Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, Li LJ, Li K, Fei-Fei L (2009) Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In: 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 248–255. Ieee
Wang Z, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR, Simoncelli EP (2004) Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans Image Process 13(4):600–612
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Foundation of National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 62373086, 62373087, Liaoning Revitalization Talents Program under Grant XLYC2203013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Manyi Shi. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Manyi Shi and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest/Competing interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Shi, M., Chen, C. et al. One image for one strategy: human grasping with deep reinforcement based on small-sample representative data. Appl Intell 55, 31 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-05919-8
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-05919-8