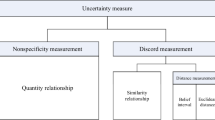
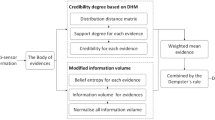
Abstract
As an extension of Bayesian probability theory, the Dempster-Shafer (D-S) evidence theory uses mass function instead of traditional probability distribution. This theory is famous for multi-sensor data fusion and can well represent uncertainty. However, if there are conflicting mass functions, the D-S evidence theory will fail. The existing methods for handling conflicting mass functions do not fully consider the interaction between focal elements. Therefore, to solve the conflict problem, this paper defines the similarity factor and quantity factor of the focal element and then considers the impact of their interaction. After that, we propose a novel reinforced final belief divergence (RFBD) measure to solve the conflicting problem in mass functions from the perspective of divergence measurement. We use several numerical examples to verify the superiority of RFBD in handling conflicting evidence under uncertain conditions. Finally, we combine belief entropy and ambiguity measure to propose the RFBD-based multi-sensor data fusion approach, then achieve target recognition in UCI datasets. The experimental results show that our RFBD is better than the advanced divergence methods currently available.











Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Availability of Data and Materials
All data and models generated or used during the study appear in the submitted article.
Code Availability
The code generated or used during the study is available in a repository or online in accordance with funder data retention policies (https://github.com/fuxiao1014/A-reinforced-final-belief-divergence-for-mass-functions-and-its-application-in-target-recognition)
References
Dong D, Ma C, Wang M, Vu HT, Vanderborght B, Sun Y (2023) A low-cost framework for the recognition of human motion gait phases and patterns based on multi-source perception fusion. Eng Appl Art Intell 120:105886
Li X, Xie Q, Zhu Q, Ren K, Sun J (2023) Knowledge graph-based recommendation method for cold chain logistics. Exp Syst Appl 227:120230
Liao H, Ren Z, Fang R (2020) A Deng-Entropy-Based Evidential Reasoning Approach for Multi-expert Multi-criterion Decision-Making with Uncertainty. Int J Comput Intell Syst 13:1281–1294
Gao J, Xu Z, Liang Z, Mao Y (2022) Two Integral Models and Applications of Hesitant Fuzzy Information Fusion. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 31(1):25–39
Pan Y, Zhang L, Li Z, Ding L (2019) Improved fuzzy Bayesian network-based risk analysis with interval-valued fuzzy sets and D-S evidence theory. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 28(9):2063–2077
Dempster AP (1967) Upper and Lower Probabilities Induced by a Multivalued Mapping. Annal Math Stat 38(2):325–339
Shafer GA (1978) A Mathematical Theory of Evidence. Technomet 20(1):106–106
Liu Z-G, Huang L-Q, Zhou K, Denoeux T (2020) Combination of transferable classification with multisource domain adaptation based on evidential reasoning. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 32(5):2015–2029
Zhou M, Qiao Y-K, Yang J-B, Zhou Y-J, Liu X-B, Wu J (2022) A three-level consensus model for large-scale multi-attribute group decision analysis based on distributed preference relations under social network analysis. Exp Syst Appl 204:117603
Chen Z, Cai R (2022) Updating incomplete framework of target recognition database based on fuzzy gap statistic. Eng Appl Art Intell 107:104521
Cui H, Chang Y, Zhang H, Mi X, Kang B (2023) Determine the number of unknown targets in the open world from the perspective of bidirectional analysis using Gap statistic and Isolation forest. Inf Sci 623:832–856
Zhao J, Cheong KH (2023) Early identification of diffusion source in complex networks with evidence theory. Inf Sci 642:119061
Chen L, Deng Y, Cheong KH (2023) The Distance of Random Permutation Set. Inf Sci 628:226–239
Chen Z, Cai R (2024) “Symmetric Renyi-Permutation divergence and conflict management for random permutation set,” Exp Syst Appl, vol 238, no A,
Xiao F, Cao Z, Jolfaei A (2021) A Novel Conflict Measurement in Decision-Making and Its Application in Fault Diagnosis. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 29(1):186–197
Wang Y-C, Wang J, Huang M-J, Wang M-H (2022) An evidence combination rule based on a new weight assignment scheme. Soft Comput 26(15):7123–7137
Zhao K, Chen Z, Sun S, Sun R, Yuan G (2022) A novel evidence combination rule based on compromise conflict indicator and conflict focal element. Knowl-Based Syst 257:109898
Deng X, Xue S, Jiang W (2023) A novel quantum model of mass function for uncertain information fusion. Inf Fusion 89:619–631
Deng Y, Shi W, Zhu Z, Liu Q (2004) Combining belief functions based on distance of evidence. Dec Supp Syst 38(3):489–493
Chen X, Deng Y (2022) An evidential software risk evaluation model. Math 10(13):2325
Liu X, Liu S, Xiang J, Sun R (2023) A conflict evidence fusion method based on the composite discount factor and the game theory. Inf Fusion 94:1–16
Xiao F (2021) CED: A Distance for Complex Mass Functions. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 32(4):1525–1535
Li R, Chen Z, Li H, Tang Y (2022) A new distance-based total uncertainty measure in Dempster-Shafer evidence theory. Applied Intell 52(2):1209–1237
Liu P, Xiao F (2022) “Earth Mover’s divergence of belief function,” Comput Applied Math, vol 41, no 6,
Song Y, Deng Y (2019) Divergence measure of belief function and its application in data fusion. IEEE Access 7:107465–107472
Chen Z, Cai R (2022) A novel divergence measure of mass function for conflict management. Int J Intell Syst 37(6):3709–3735
Xiao F (2020) A new divergence measure for belief functions in D-S evidence theory for multisensor data fusion. Inf Sci 514:462–483
Liu B, Deng Y, Cheong KH (2022) An improved multisource data fusion method based on a novel divergence measure of belief function. Eng Appl Art Intell 111:104834
Ding J, Zhang C, Li D, Sangaiah A K (2023) “Hyperautomation for Air Quality Evaluations: A Perspective of Evidential Three-way Decision-making,” Cogn Comput,
Singh S, Anand V, Bera PK (2023) A Delay-Tolerant low-duty cycle scheme in wireless sensor networks for IoT applications. Int J Cogn Comput Eng 4:194–204
Chen L, Deng Y, Cheong KH (2023) Permutation Jensen-Shannon divergence for Random Permutation Set. Eng Appl Art Intell 119:105701
Xiao F (2019) Multi-sensor data fusion based on the belief divergence measure of evidences and the belief entropy. Inf Fusion 46:23–32
Pan L, Gao X, Deng Y, Cheong KH (2022) Enhanced mass Jensen-Shannon divergence for information fusion. Exp Syst Appl 209:118065
Gao X, Xiao F (2022) “An improved belief \(\chi \) 2 divergence for Dempster-Shafer theory and its applications in pattern recognition,” Comput Applied Math, vol 41, no 6,
Zeng J, Xiao F (2023) “A fractal belief KL divergence for decision fusion,” Eng Appl Art Intell, vol 121,
Zhu C, Xiao F (2023) A belief Renyi divergence for multi-source information fusion and its application in pattern recognition. Applied Intell 53:8941–8958
Hua Z, Jing X (2023) An improved belief Hellinger divergence for Dempster-Shafer theory and its application in multi-source information fusion. Applied Intell 53(14):17965–17984
Yang C, Xiao F (2023) An exponential negation of complex basic belief assignment in complex evidence theory. Inf Sci 622:1228–1251
Cui H, Liu Q, Zhang J, Kang B (2019) An improved deng entropy and its application in pattern recognition. IEEE Access 7:18284–18292
Huang Y, Xiao F (2023) “Fractal belief Jensen-Shannon divergence-based multi-source information fusion for pattern classification,” Eng Appl Art Intell, vol 126, 2023
Liu B, Deng Y, Cheong K H (2022) “An improved multisource data fusion method based on a novel divergence measure of belief function,” Eng Appl Art Intell, vol 111,
Sun C, Li S, Deng Y (2020) “Determining Weights in Multi-Criteria Decision Making Based on Negation of Probability Distribution under Uncertain Environment,” Math, vol 8, no 2,
Kang B-Y, Li Y, Deng Y, Zhang Y-J, Deng X-Y (2012) Determination of basic probability assignment based on interval numbers and its application. Acta Electron Sinica 40(6):1092
Xia J, Feng Y, Liu L, Liu D, Fei L (2018) An evidential reliability indicator-based fusion rule for Dempster-Shafer theory and its applications in classification. IEEE Access 6:24912–24924
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors took part in this study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix A
Appendix A
Readers can refer to Table 14 below to better understand the RFBD proposed in this paper and the multi-sensor data fusion method based on RFBD.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, F., Chen, Z. & Cai, R. A reinforced final belief divergence for mass functions and its application in target recognition. Appl Intell 55, 135 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-05955-4
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-05955-4