Abstract
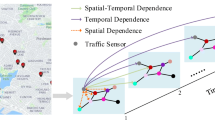
The application of intelligent transportation systems (ITSs) relies heavily on accurate traffic prediction, which hinges on effectively capturing spatial-temporal features. Current methodologies often address spatial and temporal dependencies separately, which limits their ability to synchronize modeling efforts. Moreover, existing graph convolutional network (GCN) approaches primarily support transductive learning and fall short in inductive tasks. To address these challenges, this paper introduces a novel spatial-temporal synchronous GraphSAGE (STS-GraphSAGE) model for traffic prediction. By integrating spatial and temporal correlations into a unified graph structure, STS-GraphSAGE achieves synchronous learning of these dependencies. Specifically, we introduce the Spearman correlation coefficient to compensate for the spatial adjacency matrix, facilitating the construction of an inclusive spatial graph. Coupled with a causal temporal graph, this forms a spatial-temporal synchronous graph that is capable of capturing intricate dependencies across both dimensions. Furthermore, our model employs multiple STS-GraphSAGE layers equipped with attention mechanisms to inductively aggregate spatial-temporal features from neighboring nodes. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets validate the effectiveness of STS-GraphSAGE, which significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in traffic prediction tasks.











Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data Availability
Data generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Jiang W, Luo J (2022) Graph neural network for traffic forecasting: A survey. Expert Syst Appl 207:117921
Wang A, Ye Y, Song X et al (2023) Traffic prediction with missing data: A multi-task learning approach. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 24(4):4189–4202
Xu M, Qiu TZ, Fang J, et al (2023a) Signal-control refined dynamic traffic graph model for movement-based arterial network traffic volume prediction. Expert Syst Appl 228:120393
Xu Y, Lu Y, Ji C, et al (2023b) Adaptive graph fusion convolutional recurrent network for traffic forecasting. IEEE Internet Things J 10(13):11465–11475
Huang X, Jiang Y, Tang J (2023) Mapredrnn: Multi-attention predictive rnn for traffic flow prediction by dynamic spatio-temporal data fusion. Appl Intell 53(16):19372–19383
Li Y, Yu R, Shahabi C et al (2018) Diffusion convolutional recurrent neural network: Data-driven traffic forecasting. International Conference on Learning Representations. Vancouver, Canada, pp 1–16
Zhao L, Song Y, Zhang C et al (2020) T-gcn: A temporal graph convolutional network for traffic prediction. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 21(9):3848–3858
Yao Z, Xia S, Li Y et al (2023) Transfer learning with spatial–temporal graph convolutional network for traffic prediction. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 24(8):8592–8605
Chen L, Shao W, Lv M et al (2022) Aargnn: An attentive attributed recurrent graph neural network for traffic flow prediction considering multiple dynamic factors. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 23(10):17201–17211
Yu B, Yin H, Zhu Z (2018) Spatio-temporal graph convolutional networks: A deep learning framework for traffic forecasting. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, pp 3634–3640
Guo S, Lin Y, Feng N, et al (2019) Attention based spatial-temporal graph convolutional networks for traffic flow forecasting. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Hawaii, USA, pp 922–929
Qi J, Zhao Z, Tanin E et al (2023) A graph and attentive multi-path convolutional network for traffic prediction. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 35(7):6548–6560
Fu J, Zhou W, Chen Z (2024) Bayesian graph convolutional network for traffic prediction. Neurocomput 582:127507
Song C, Lin Y, Guo S, et al (2020) Spatial-temporal synchronous graph convolutional networks: A new framework for spatial-temporal network data forecasting. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, pp 914–921
Li M, Zhu Z (2021) Spatial-temporal fusion graph neural networks for traffic flow forecasting. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Online, pp 4189–4196
Jin G, Li F, Zhang J et al (2023) Automated dilated spatio-temporal synchronous graph modeling for traffic prediction. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 24(8):8820–8830
Wei Z, Zhao H, Li Z et al (2023) Stgsa: A novel spatial-temporal graph synchronous aggregation model for traffic prediction. IEEE/CAA J of Automat Sinica 10(1):226–238
Zhang T, Shan HR, Little MA (2022) Causal graphsage: A robust graph method for classification based on causal sampling. Pattern Recognit 128:108696
Kumar SV, Vanajakshi L (2015) Short-term traffic flow prediction using seasonal arima model with limited input data. Eur Transp Res Rev 7(3):21
Chandra SR, Al-Deek H (2009) Predictions of freeway traffic speeds and volumes using vector autoregressive models. J Intell Transp Syst 13(2):53–72
Jeong YS, Byon YJ, Castro-Neto MM et al (2013) Supervised weighting-online learning algorithm for short-term traffic flow prediction. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 14(4):1700–1707
Zheng Z, Su D (2014) Short-term traffic volume forecasting: A k-nearest neighbor approach enhanced by constrained linearly sewing principle component algorithm. Transp Res C, Emerg Technol 43:143–157
Liu M, Zhu T, Ye J et al (2023) Spatio-temporal autoencoder for traffic flow prediction. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 24(5):5516–5526
Zheng H, Lin F, Feng X et al (2021) A hybrid deep learning model with attention-based conv-lstm networks for short-term traffic flow prediction. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 22(11):6910–6920
Bruna J, Zaremba W, Szlam A et al (2014) Spectral networks and locally connected networks on graphs. International Conference on Learning Representations. Banff National Park, Canada, pp 1–14
Defferrard M, Bresson X, Vandergheynst P (2016) Convolutional neural networks on graphs with fast localized spectral filtering. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, pp 1–9
Kipf TN, Welling M (2017) Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. International Conference on Learning Representations. Toulon, France, pp 1–14
Wu Z, Pan S, Long G, et al (2019) Graph wavenet for deep spatial-temporal graph modeling. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Macau, China, pp 1907–1913
Bai L, Yao L, Li C, et al (2020) Adaptive graph convolutional recurrent network for traffic forecasting. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Online, pp 17804–17815
Zheng C, Fan X, Wang C, et al (2020) Gman: A graph multi-attention network for traffic prediction. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, pp 1234–1241
Zou G, Lai Z, Wang T et al (2024) Mt-stnet: A novel multi-task spatiotemporal network for highway traffic flow prediction. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 25(7):8221–8236
Yang C, Pei Z (2023) Long-short term spatio-temporal aggregation for trajectory prediction. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 24(4):4114–4126
Xu X, Zhang T, Xu C et al (2023) Spatial–temporal tensor graph convolutional network for traffic speed prediction. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 24(1):92–103
Luo G, Zhang H, Yuan Q et al (2022) Estnet: Embedded spatial-temporal network for modeling traffic flow dynamics. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 23(10):19201–19212
Long W, Xiao Z, Wang D et al (2023) Unified spatial-temporal neighbor attention network for dynamic traffic prediction. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 72(2):1515–1529
Wang T, Chen J, Lü J et al (2023) Synchronous spatiotemporal graph transformer: A new framework for traffic data prediction. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 34(12):10589–10599
Hamilton W, Ying Z, Leskovec J (2017) Inductive representation learning on large graphs. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA, pp 1024–1034
Liu J, Ong GP, Chen X (2020) Graphsage-based traffic speed forecasting for segment network with sparse data. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 23(3):1755–1766
Liu T, Jiang A, Zhou J et al (2023) Graphsage-based dynamic spatial-temporal graph convolutional network for traffic prediction. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 24(10):11210–11224
Lablack M, Shen Y (2023) Spatio-temporal graph mixformer for traffic forecasting. Exp Syst Appl 228:120281
Sutskever I, Vinyals O, Le QV (2014) Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Montréal, Canada, pp 3104–3112
Fu R, Zhang Z, Li L (2016) Using lstm and gru neural network methods for traffic flow prediction. 31st Youth Acad. Annu. Conf. Chinese Assoc. Autom, Wuhan, China, pp 324–328
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 62476145; in part by the Humanity and Social Science Foundation of Ministry of Education of China under Grant 24YJAZH126; in part by the 6th “333 Talents” Technology Research and Development Talent Foundation of Jiangsu Province; in part by the Transportation Technology and Achievement Transformation Foundation of Jiangsu Province under Grant 2024G01; in part by the Postgraduate Research and Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province under Grant KYCX23_3396.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript entitled.
Ethical and Informed Consent for Data Used
Written informed consent for publication of this paper was obtained from all authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, X., Bao, Y. & Shi, Q. Spatial-temporal synchronous graphsage for traffic prediction. Appl Intell 55, 82 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-05970-5
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-05970-5