Abstract
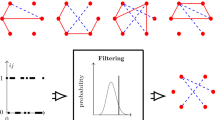
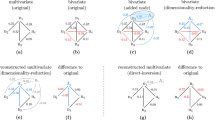
A denoised complex network framework employing a detrended partial cross-correlation analysis-based coefficient for achieving the intrinsic scale-dependent correlations between each pair of variables is developed to explore the interrelatedness of multiple nonstationary variables in the real-world. In doing this, we start with introducing the detrended partial cross-correlation coefficient into random matrix theory, and executing a denoising process through correlation matrix reconfiguration, which is followed by utilizing the denoised correlation matrix to construct a planar maximally filtered graph network. It allows us assess the interactions among complex objects more accurately. The effectiveness of our proposed method is validated through the numerical experiments simulating the eigenvalue distribution, and the results show that our method accurately locates the maximum eigenvalue at a specific scale, but existing methods fail to achieve. As a practical application, we also apply the proposed denoising network framework to investigate the co-movement behavior of PM\(_{2.5}\) air pollution of North China and the linkage of commodity futures prices in China. The results show that the denoising process significantly enhances the information content of the network, revealing several interesting insights regarding network properties.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Availability of data and materials
The PM\(_{2.5}\) data and China’s commodity futures data used in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code Availability
The code is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Comin CH, Peron T, Silva FN et al (2020) Complex systems: features, similarity and connectivity. Phys Rep 861:1–41
Wang F, Wang L, Chen YM (2022) Multi-affine visible height correlation analysis for revealing rich structures of fractal time series. Chaos Soliton Fract. 157:111893
Peng CK, Buldyrev SV, Havlin S et al (1994) Mosaic organization of DNA nucleotides. Phys Rev E 49(2):1685–1689
Podobnik B, Stanley HE (2008) Detrended cross-correlation analysis: a new method for analyzing two nonstationary time series. Phys Rev Lett 100(8):084102
Zebende GF (2011) DCCA cross-correlation coefficient: Quantifying level of cross-correlation. Phys A 390(4):614–618
Wang F (2016) A novel coefficient for detecting and quantifying asymmetry of California electricity market based on asymmetric detrended cross-correlation analysis. Chaos 26(6):063109
Shen CH (2015) Analysis of detrended time-lagged cross-correlation between two nonstationary time series. Phys Lett A 379(7):680–687
Kwapień J, Oświȩcimka P, Drożdż S (2015) Detrended fluctuation analysis made flexible to detect range of cross-correlated fluctuations. Phys Rev E 92:052815
Zebende GF, da Silva Filho AM (2018) Detrended multiple cross-correlation coefficient. Phys. A 510:91–97
Wang F, Xu J, Fan QJ (2021) Statistical properties of the detrended multiple cross-correlation coefficient. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 99:105781
Qian XY, Liu YM, Jiang ZQ et al (2015) Detrended partial cross-correlation analysis of two time series influenced by common external forces. Phys Rev E 91:062816
Yuan NM, Fu ZT, Zhang H et al (2015) Detrended partial-cross-correlation analysis: a new method for analyzing correlations in complex system. Sci Rep 5(1):8143
Mieghem PV (2023) Graph spectra for complex networks. Cambridge university press
Zou Y, Donner RV, Marwan N et al (2019) Complex network approaches to nonlinear time series analysis. Phys Rep 787:1–97
Zhang Z, Wang F, Shen L et al (2022) Multiscale time-lagged correlation networks for detecting air pollution interaction. Phys A 602:127627
Xu M, Han M, Lin H (2018) Wavelet-denoising multiple echo state networks for multivariate time series prediction. Inform Sci 465:439–458
Wigner EP (1993) On a class of analytic functions from the quantum theory of collisions. The Collected Works of Eugene Paul Wigner: Part A: The Scientific Papers 409–440
Wang GJ, Xie C, Chen S et al (2013) Random matrix theory analysis of cross-correlations in the US stock market: Evidence from Pearson’s correlation coefficient and detrended cross-correlation coefficient. Phys A 392(17):3715–3730
Zhao XJ, Shang PJ, Lin AJ (2014) Distribution of eigenvalues of detrended cross-correlation matrix. EPL (Eur Phys Lett) 107(4):40008
Xie C, Hu J, Wang GJ (2018) Study on Topological Property of Stock Market’s Network Based on Random Matric Method. Oper Res Manage Sci 27(1):144. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Vahabi H, Namaki A, Raei R (2022) Comparing the collective behavior of banking industry in emerging markets versus mature ones by random matrix approach. Front Phys 10:896303
Namaki A, Raei R, Ardalankia J et al (2021) Analysis of the global banking network by random matrix theory. Front Phys 8:586561
Tu L, Chen Y (2021) An unequal adjacent grey forecasting air pollution urban model. Appl Math Model 99:260–275
Abbood ZM, Al-Taai OT, Nassif WG (2021) Impact of wind speed and direction on low cloud cover over Baghdad city. Curr Appl Sci Tech 590–600
Maiorino E, Bianchi FM, Livi L et al (2017) Data-driven detrending of nonstationary fractal time series with echo state networks. Inform Sci 382:359–373
Wang GJ, Xie C, Stanley HE (2018) Correlation structure and evolution of world stock markets: Evidence from Pearson and partial correlation-based networks. Comput Econ 51:607–635
Pereira E, Ferreira P, da Silva MF et al (2019) Multiscale network for 20 stock markets using DCCA. Phys A 529:121542
Wang Y, Li H, Guan J et al (2019) Similarities between stock price correlation networks and co-main product networks: Threshold scenarios. Phys A 516:66–77
Filho O, Mendes F, Guedes EF et al (2023) Networks analysis of Brazilian climate data based on the DCCA cross-correlation coefficient. PLoS ONE 18(9):e0290838
Plerou V, Gopikrishnan P, Rosenow B et al (2002) Random matrix approach to cross correlations in financial data. Phys Rev E 65(6):066126
Barbier J, Nicolas M (2022) Statistical limits of dictionary learning: random matrix theory and the spectral replica method. Phys Rev E 106(2):024136
Couillet R, Liao ZY (2022) Random matrix methods for machine learning. Cambridge University Press
Zhu W, Ma X, Zhu XH et (2022) Denoise Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging with Random Matrix Theory Based Principal Component Analysis. IEEE T Bio-med Eng 69(11):3377–3388
Laloux L, Cizeau P, Bouchaud JP et al (1999) Noise dressing of financial correlation matrices. Phys Rev Lett 83(7):1467
Tian J, Zhao K (2020) Optimal selection of financial risk investment portfolio based on random matrix method. J Comput Methods Sci Engine 20(3):859–868
Liu YX, Lang B, Quan FN (2023) MST-HGCN: a minimum spanning tree hyperbolic graph convolutional network. Appl Intell 53(11):14515–14526
Tumminello M, Aste T, Matteo TD et al (2005) A tool for filtering information in complex systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(30):10421–10426
Holme P, Park SM, Kim BJ et al (2007) Korean university life in a network perspective: Dynamics of a large affiliation network. Phys A 373:821–830
Foster JG, Foster DV, Grassberger P et al (2010) Edge direction and the structure of networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(24):10815–10820
Leung CC, Chau HF (2007) Weighted assortative and disassortative networks model. Phys A 378(2):591–602
Frusque G, Fink O (2022) Robust time series denoising with learnable wavelet packet transform. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.06126
Peitgen HO, Jürgens H, Saupe D et al (2004) Chaos and fractals: new frontiers of science. New York: Springer 106:560–604
Gulich D, Zunino L (2012) The effects of observational correlated noises on multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis. Phys A 391(16):4100–4110
Wang F, Zhang Z (2023) Correlation Structure and Co-Movement of Hunan Province’s Air Pollution: Evidence from the Multiscale Temporal Networks. Atmosphere 14(1):55
Wang F, Wang L, Chen YM (2017) Detecting PM2.5’s correlations between neighboring cities using a time- lagged cross-correlation coefficient. Sci Rep 7(1):10109
Wang F, Wang L, Chen YM (2018) A DFA-based bivariate regression model for estimating the dependence of PM2.5 among neighbouring cities. Sci Rep 8(1):7475
Wang F, Zhao WC, Jiang S (2020) Detecting asynchrony of two series using multiscale cross-trend sample entropy. Nonlinear Dyn 99(2):1451–1465
Wang F, Fan QJ (2021) Coupling correlation detrended analysis for multiple nonstationary series. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 94:105579
Jiang S, Li BG, Yu ZG et al (2020) Multifractal temporally weighted detrended cross-correlation analysis of multivariate time series. Chaos 30(2):023134
Fan QJ, Liu SG, Wang KH (2019) Multiscale multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis of multivariate time series. Phys A 532:121864
Wang F, Han GS, Fan QJ (2023) Statistical test for detrending-moving-average-based multivariate regression model. Appl Math Model 124:661–677
Wang F, Han GS (2023) Coupling correlation adaptive detrended analysis for multiple nonstationary series. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals 177:114295
Bardoscia M, Barucca P, Battiston S et al (2021) The physics of financial networks. Nat Rev Phys 3(7):490–507
Zhou Y, Chen Z, Liu Z (2023) Dynamic analysis and community recognition of stock price based on a complex network perspective. Expert Syst Appl 213:118944
Wen S, Li J, Huang C et al (2023) Extreme risk spillovers among traditional financial and FinTech institutions: A complex network perspective. Q Rev Econ Finance 88:190–202
Lyu Y, Yi H, Hu Y et al (2021) Economic uncertainty shocks and China’s commodity futures returns: A time-varying perspective. Resour Policy 70:101979
Cui J, Goh M, Zou H (2021) Coherence, extreme risk spillovers, and dynamic linkages between oil and China’s commodity futures markets. Energy 225:120190
Blondel VD, Guillaume JL, Lambiotte R et al (2008) Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. J Stat Mech Theory Exp (10):P1000
Chi KT, Liu J, Lau FCM (2010) A network perspective of the stock market. J Empir Financ 17(4):659–667
Jian Z, Wu S, Zhu Z (2018) Asymmetric extreme risk spillovers between the Chinese stock market and index futures market: An MV-CAViaR based intraday CoVaR approach. Emerg Mark Rev 37:98–113
Acknowledgements
The author wishes to thank the anonymous reviewers and the handling editor for their constructive comments and suggestions, which led to a great improvement to the presentation of this work.
Funding
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant nos. 12371088, 12471489) and the Key Research Project of the Department of Education of Hunan Province (CN) (Grant no. 22A0135).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation and data collection were performed by Z Zhang and M Wang. Visualization and analysis were performed by F Wang and Z Zhang. Method design were partially performed by F Wang and G Ling. The first draft of the manuscript was written by F Wang and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. The revision was made by F Wang and Z Zhang. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix A: 42 China’s commodity futures
Appendix A: 42 China’s commodity futures
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Zhang, Z., Wang, M. et al. Detrended partial cross-correlation analysis-random matrix theory for denoising network construction. Appl Intell 55, 16 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-05975-0
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-05975-0