Abstract
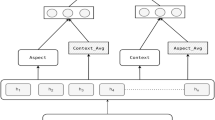
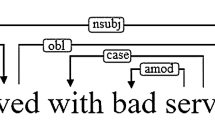
Aspect-based sentiment analysis (ABSA) focused on forecasting the sentiment orientation of a given aspect target within the input. Existing methods employ neural networks and attention mechanisms to encode input and discern aspect-context relationships. Bidirectional Encoder Representation from Transformer(BERT) has become the standard contextual encoding method in the textual domain. Researchers have ventured into utilizing graph attention networks(GAT) to incorporate syntactic information into the task, yielding cutting-edge results. However, current approaches overlook the potential advantages of considering word dependency relations. This work proposes a hybrid model combining contextual information obtained from a post-trained BERT with syntactic information from a relational GAT (RGAT) for the ABSA task. Our approach leverages dependency relation information effectively to improve ABSA performance in terms of accuracy and F1-score, as demonstrated through experiments on SemEval-14 Restaurant and Laptop, MAMS, and ACL-14 Twitter datasets.

Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J (1997) Long short-term memory. Neural Comput 9(8):1735–1780
LeCun Y et al (1989) Generalization and network design strategies. Connectionism Perspective 19(143–155):18
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 1097–1105
Bahdanau D, Cho K, Bengio Y (2015) Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. In: Bengio Y, LeCun Y (eds) 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2015, San Diego, CA, USA, May 7-9, 2015, Conference Track Proceedings
Wang S, Mazumder S, Liu B, Zhou M, Chang Y (2018) Target-sensitive memory networks for aspect sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of the 56th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers)
Tang D, Qin B, Liu T (2016) Aspect level sentiment classification with deep memory network. In: Proceedings of the 2016 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing, pp 214–224. Association for Computational Linguistics, Austin, Texas. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/D16-1021
Zhang C, Li Q, Song D (2019) Aspect-based sentiment classification with aspect-specific graph convolutional networks. In: Inui K, Jiang J, Ng V, Wan X (eds) Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), pp. 4568–4578. Association for Computational Linguistics, Hong Kong, China (2019). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/D19-1464
Sun K, Zhang R, Mensah S, Mao Y, Liu X (2019) Aspect-level sentiment analysis via convolution over dependency tree. In: Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), pp 5679–5688
Huang B, Carley K (2019) Syntax-aware aspect level sentiment classification with graph attention networks. In: Inui K, Jiang J, Ng V, Wan X (eds) Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), pp 5469–5477. Association for Computational Linguistics, Hong Kong, China. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/D19-1549
Kipf TN, Welling M (2017) Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR)
Veličković P, Cucurull G, Casanova A, Romero A, Liò P, Bengio Y (2018) Graph Attention Networks. International Conference on Learning Representations
Ke Q, Jing X, Woźniak M, Xu S, Liang Y, Zheng J (2024) Apgvae: Adaptive disentangled representation learning with the graph-based structure information. Inf Sci 657:119903
Dong L, Wei F, Tan C, Tang D, Zhou M, Xu K (2014) Adaptive recursive neural network for target-dependent twitter sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of the 52nd annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics (volume 2: Short Papers), pp 49–54
Devlin J, Chang M-W, Lee K, Toutanova K (2019) BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In: Burstein J, Doran C, Solorio T (eds) Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers), pp 4171–4186. Association for Computational Linguistics, Minneapolis, Minnesota. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/N19-1423
Xue W, Li T (2018) Aspect based sentiment analysis with gated convolutional networks. In: Gurevych I, Miyao Y (eds) Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), pp 2514–2523. Association for Computational Linguistics, Melbourne, Australia. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/P18-1234
Zheng Y, Zhang R, Mensah S, Mao Y (2020) Replicate, walk, and stop on syntax: an effective neural network model for aspect-level sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, vol 34, pp 9685–9692
Xu H, Liu B, Shu L, Yu P (2019) BERT post-training for review reading comprehension and aspect-based sentiment analysis. In: Burstein J, Doran C, Solorio T (eds) Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers), pp 2324–2335. Association for Computational Linguistics, Minneapolis, Minnesota. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/N19-1242
Xu H, Liu B, Shu L, Yu P (2020) DomBERT: Domain-oriented language model for aspect-based sentiment analysis. In: Cohn T, He Y, Liu Y (eds) Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2020, pp 1725–1731. Association for Computational Linguistics, Online. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2020.findings-emnlp.156
Li X, Bing L, Zhang W, Lam W (2019) Exploiting BERT for end-to-end aspect-based sentiment analysis. In: Xu W, Ritter A, Baldwin T, Rahimi A (eds) Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Noisy User-generated Text (W-NUT 2019), pp. 34–41. Association for Computational Linguistics, Hong Kong, China. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/D19-5505
Li X, Bing L, Li P, Lam W (2019) A unified model for opinion target extraction and target sentiment prediction. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, vol 33, pp 6714–6721
Song Y, Wang J, Jiang T, Liu Z, Rao Y (2019) Attentional encoder network for targeted sentiment classification. In: International conference on artificial neural networks
Gao Z, Feng A, Song X, Wu X (2019) Target-dependent sentiment classification with bert. IEEE Access 7:154290–154299
Sun C, Huang L, Qiu X (2019) Utilizing BERT for aspect-based sentiment analysis via constructing auxiliary sentence. In: Burstein J, Doran C, Solorio T (eds) Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers), pp 380–385. Association for Computational Linguistics, Minneapolis, Minnesota. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/N19-1035
Xu H, Shu L, Yu P, Liu B (2020) Understanding pre-trained BERT for aspect-based sentiment analysis. In: Scott D, Bel N, Zong C (eds) Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, pp. 244–250. International Committee on Computational Linguistics, Barcelona, Spain (Online). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2020.coling-main.21
Scarselli F, Gori M, Tsoi AC, Hagenbuchner M, Monfardini G (2008) The graph neural network model. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 20(1):61–80
Tang H, Ji D, Li C, Zhou Q (2020) Dependency graph enhanced dual-transformer structure for aspect-based sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of the 58th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics, pp 6578–6588
Li R, Chen H, Feng F, Ma Z, Wang X, Hovy E (2021) Dual graph convolutional networks for aspect-based sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 59th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics and the 11th international joint conference on natural language processing (Volume 1: Long Papers), pp 6319–6329
Bai X, Liu P, Zhang Y (2020) Investigating typed syntactic dependencies for targeted sentiment classification using graph attention neural network. IEEE/ACM Trans Audio Speech Language Process 29:503–514
Liang B, Yin R, Gui L, Du J, Xu R (2020) Jointly learning aspect-focused and inter-aspect relations with graph convolutional networks for aspect sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 28th international conference on computational linguistics, pp 150–161
Schlichtkrull M, Kipf TN, Bloem P, Van Den Berg R, Titov I, Welling M (2018) Modeling relational data with graph convolutional networks. In: The Semantic Web: 15th International Conference, ESWC 2018, Heraklion, Crete, Greece, June 3–7, 2018, Proceedings 15, Springer, pp 593–607
Wang K, Shen W, Yang Y, Quan X, Wang R (2020) Relational graph attention network for aspect-based sentiment analysis. In: Jurafsky D, Chai J, Schluter N, Tetreault J (eds) Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 3229–3238. Association for Computational Linguistics, Online. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2020.acl-main.295
Hou X, Huang J, Wang G, Qi P, He X, Zhou B (2021) Selective attention based graph convolutional networks for aspect-level sentiment classification. In: Panchenko A, Malliaros FD, Logacheva V, Jana A, Ustalov D, Jansen P (eds) Proceedings of the Fifteenth Workshop on Graph-Based Methods for Natural Language Processing (TextGraphs-15), pp 83–93. Association for Computational Linguistics, Mexico City, Mexico. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2021.textgraphs-1.8
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez AN, Kaiser Ł, Polosukhin I (2017) Attention is all you need. Advan Neural Inform Process Syst 30
Mikolov T, Sutskever I, Chen K, Corrado GS, Dean J (2013) Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 3111–3119
Pennington J, Socher R, Manning CD (2014) Glove: Global vectors for word representation. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pp 1532–1543
Peters M, Neumann M, Iyyer M, Gardner M, Clark C, Lee K, Zettlemoyer L (2018) Deep contextualized word representations. In: Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long Papers), pp 2227–2237. Association for Computational Linguistics, New Orleans, Louisiana. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/N18-1202
Cho K, van Merriënboer B, Gulcehre C, Bahdanau D, Bougares F, Schwenk H, Bengio Y (2014) Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. In: Moschitti A, Pang B, Daelemans W (eds) Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pp 1724–1734. Association for Computational Linguistics, Doha, Qatar. https://doi.org/10.3115/v1/D14-1179
Pontiki M, Galanis D, Pavlopoulos J, Papageorgiou H, Androutsopoulos I, Manandhar S (2014) SemEval-2014 task 4: Aspect based sentiment analysis. In: Nakov P, Zesch T (eds) Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval 2014), pp 27–35. Association for Computational Linguistics, Dublin, Ireland. https://doi.org/10.3115/v1/S14-2004
Jiang Q, Chen L, Xu R, Ao X, Yang M (2019) A challenge dataset and effective models for aspect-based sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), pp 6280–6285
Dozat T, Manning CD (2017) Deep biaffine attention for neural dependency parsing. In: International conference on learning representations. https://openreview.net/forum?id=Hk95PK9le
Ma D, Li S, Zhang X, Wang H (2017) Interactive attention networks for aspect-level sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of the 26th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. IJCAI’17, AAAI Press, Melbourne, Australia, pp 4068–4074
Fan F, Feng Y, Zhao D (2018) Multi-grained attention network for aspect-level sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of the 2018 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing, pp 3433–3442
Nguyen HT, Le Nguyen M (2018) Effective attention networks for aspect-level sentiment classification. In: 2018 10th International Conference on Knowledge and Systems Engineering (KSE), IEEE, pp 25–30
Funding
NA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interests/Competing interests
NA.
Ethics approval
NA.
Financial interests
NA
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, S., Kumar, A. & Sharan, A. WRGAT-PTBERT: weighted relational graph attention network over post-trained BERT for aspect based sentiment analysis. Appl Intell 55, 181 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-06011-x
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-06011-x