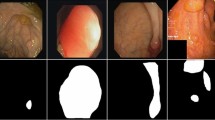
Abstract
Early diagnosis and prevention of colorectal cancer rely on colonoscopic polyp examination.Accurate automated polyp segmentation technology can assist clinicians in precisely identifying polyp regions, thereby conserving medical resources. Although deep learning-based image processing methods have shown immense potential in the field of automatic polyp segmentation, current automatic segmentation methods for colorectal polyps are still limited by factors such as the complex and variable intestinal environment and issues related to detection equipment like glare and motion blur. These limitations result in an inability to accurately distinguish polyps from surrounding mucosal tissue and effectively identify tiny polyps. To address these challenges, we designed a multi-attention-based model, PVT-MA. Specifically, we developed the Cascading Attention Fusion (CAF) Module to accurately identify and locate polyps, reducing false positives caused by environmental factors and glare. Additionally, we introduced the Series Channels Coordinate Attention (SCC) Module to maximize the capture of polyp edge information. Furthermore, we incorporated the Receptive Field Block (RFB) Module to enhance polyp features and filter image noise.We conducted quantitative and qualitative evaluations using six metrics across four challenging datasets. Our PVT-MA model achieved top performance on three datasets and ranked second on one. The model has only 26.39M parameters, a computational cost of 10.33 GFlops, and delivers inference at a high speed of 47.6 frames per second (FPS).










Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data Availability and Access
The data used to support the findings of this study is available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Bray F, Laversanne M, Weiderpass E, Soerjomataram I (2021) The ever-increasing importance of cancer as a leading cause of premature death worldwide. Cancer 127(16):3029–3030
Xia C, Dong X, Li H, Cao M, Sun D, He S, Yang F, Yan X, Zhang S, Li N et al (2022) Cancer statistics in china and united states, 2022: profiles, trends, and determinants. Chin Med J 135(05):584–590
Fan D-P, Ji G-P, Zhou T, Chen G, Fu H, Shen J, Shao L (2020) Pranet: Parallel reverse attention network for polyp segmentation. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-assisted Intervention, pp 263–273. Springer
Valle L, Monahan KJ (2023) Genetic predisposition to gastrointestinal polyposis: syndromes, tumour features, genetic testing, and clinical management. The Lancet Gastroenterol Hepa
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer-assisted intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5-9 October 2015, Proceedings, Part III 18, pp 234–241 . Springer
Cho K, Van Merriënboer B, Gulcehre C, Bahdanau D, Bougares F, Schwenk H, Bengio Y (2014) Learning phrase representations using rnn encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. arXiv:1406.1078
Badrinarayanan V, Kendall A, Cipolla R (2017) Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(12):2481–2495
Lin T-Y, Dollár P, Girshick R, He K, Hariharan B, Belongie S (2017) Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 2117–2125
Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Szegedy C, Reed S, Fu C-Y, Berg AC (2016) Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, October 11–14, 2016, Proceedings, Part I 14, pp 21–37 . Springer
Chen L-C, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, Murphy K, Yuille AL (2017) Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 40(4):834–848
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez AN, Kaiser Ł, Polosukhin I (2017) Attention is all you need. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst. 30
Dosovitskiy A, Beyer L, Kolesnikov A, Weissenborn D, Zhai X, Unterthiner T, Dehghani M, Minderer M, Heigold G, Gelly S, et al. (2020) An image is worth 16x16 words: Trans Image Recogn Scale. arXiv:2010.11929
Wang W, Xie E, Li X, Fan D-P, Song K, Liang D, Lu T, Luo P, Shao L (2021) Pyramid vision transformer: A versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 568–578
Dong B, Wang W, Fan D-P, Li J, Fu H, Shao L (2021) Polyp-pvt: Polyp segmentation with pyramid vision transformers. arXiv:2108.06932
Jha D, Smedsrud PH, Riegler MA, Halvorsen P, De Lange T, Johansen D, Johansen HD (2020) Kvasir-seg: A segmented polyp dataset. In: MultiMedia Modeling: 26th International Conference, MMM 2020, Daejeon, South Korea, January 5–8, 2020, Proceedings, Part II 26, pp 451–462 . Springer
Bernal J, Sánchez FJ, Fernández-Esparrach G, Gil D, Rodríguez C, Vilariño F (2015) Wm-dova maps for accurate polyp highlighting in colonoscopy: Validation vs. saliency maps from physicians. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 43:99–111
Tajbakhsh N, Gurudu SR, Liang J (2015) Automated polyp detection in colonoscopy videos using shape and context information. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35(2):630–644
Silva J, Histace A, Romain O, Dray X, Granado B (2014) Toward embedded detection of polyps in wce images for early diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 9:283–293
Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T (2015) Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 3431–3440
Zhang R, Lai P, Wan X, Fan D-J, Gao F, Wu X-J, Li G (2022) Lesion-aware dynamic kernel for polyp segmentation. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, pp 99–109 . Springer
Zhou Z, Rahman Siddiquee MM, Tajbakhsh N, Liang J (2018) Unet++: A nested u-net architecture for medical image segmentation. In: Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support: 4th International Workshop, DLMIA 2018, and 8th International Workshop, ML-CDS 2018, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2018, Granada, Spain, September 20, 2018, Proceedings 4, pp 3–11 . Springer
Xiao X, Lian S, Luo Z, Li S (2018) Weighted res-unet for high-quality retina vessel segmentation. In: 2018 9th International Conference on Information Technology in Medicine and Education (ITME), pp 327–331 . IEEE
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 770–778
Bahdanau D, Cho K, Bengio Y (2014) Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. arXiv:1409.0473
Alam S, Tomar NK, Thakur A, Jha D, Rauniyar A (2020) Automatic polyp segmentation using u-net-resnet50. arXiv:2012.15247
Tomar NK, Srivastava A, Bagci U, Jha D (2022) Automatic polyp segmentation with multiple kernel dilated convolution network. In: 2022 IEEE 35th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), pp 317–322 . IEEE
Fang Y, Chen C, Yuan Y, Tong K-y (2019) Selective feature aggregation network with area-boundary constraints for polyp segmentation. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2019: 22nd International Conference, Shenzhen, China, October 13–17, 2019, Proceedings, Part I 22, pp 302–310 . Springer
Wei Y, Feng J, Liang X, Cheng M-M, Zhao Y, Yan S (2017) Object region mining with adversarial erasing: A simple classification to semantic segmentation approach. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 1568–1576
Chen S, Tan X, Wang B, Hu X (2018) Reverse attention for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp 234–250
Han K, Xiao A, Wu E, Guo J, Xu C, Wang Y (2021) Transformer in transformer. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 34:15908–15919
Wang W, Xie E, Li X, Fan D-P, Song K, Liang D, Lu T, Luo P, Shao L (2022) Pvt v2: Improved baselines with pyramid vision transformer. Comput Vis Media. 8(3):415–424
Shi W, Xu J, Gao P (2022) Ssformer: A lightweight transformer for semantic segmentation. In: 2022 IEEE 24th International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing (MMSP), pp 1–5 . IEEE
Zhang Y, Liu H, Hu Q (2021) Transfuse: Fusing transformers and cnns for medical image segmentation. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2021: 24th International Conference, Strasbourg, France, September 27–October 1, 2021, Proceedings, Part I 24, pp 14–24 . Springer
Wang Y, Yuan W, Bai X (2023) Coam-net: coordinate asymmetric multi-scale fusion strategy for polyp segmentation. Appl Intell 53(24):30626–30641
Liu S, Huang D, et al. (2018) Receptive field block net for accurate and fast object detection. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp 385–400
Zhou D, Kang B, Jin X, Yang L, Lian X, Jiang Z, Hou Q, Feng J (2021) Deepvit: Towards deeper vision transformer. arXiv:2103.11886
Xie E, Wang W, Wang W, Sun P, Xu H, Liang D, Luo P (2021) Segmenting transparent object in the wild with transformer. arXiv:2101.08461
Liu Z, Lin Y, Cao Y, Hu H, Wei Y, Zhang Z, Lin S, Guo B (2021) Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 10012–10022
Zhang W, Fu C, Zheng Y, Zhang F, Zhao Y, Sham C-W (2022) Hsnet: A hybrid semantic network for polyp segmentation. Comput Biol Med 150:106173
Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Vanhoucke V, Rabinovich A (2015) Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 1–9
Yu F, Koltun V (2015) Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. arXiv:1511.07122
Szegedy C, Ioffe S, Vanhoucke V, Alemi A (2017) Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol 31
Xie L, Li C, Wang Z, Zhang X, Chen B, Shen Q, Wu Z (2023) Shisrcnet: Super-resolution and classification network for low-resolution breast cancer histopathology image. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, pp 23–32. Springer
Woo S, Park J, Lee J-Y, Kweon IS (2018) Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp 3–19
Hu J, Shen L, Sun G (2018) Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 7132–7141
Hou Q, Zhou D, Feng J (2021) Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 13713–13722
Wang X, Girshick R, Gupta A, He K (2018) Non-local neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 7794–7803
Hu J, Shen L, Sun G (2018) Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 7132–7141
Lu Y, Chen Y, Zhao D, Chen J (2019) Graph-fcn for image semantic segmentation. In: International Symposium on Neural Networks, pp 97–105. Springer
Wei J, Wang S, Huang Q (2020) F\(^3\)net: fusion, feedback and focus for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol 34, pp 12321–12328
Huang C-H, Wu H-Y, Lin Y-L (2021) Hardnet-mseg: A simple encoder-decoder polyp segmentation neural network that achieves over 0.9 mean dice and 86 fps. arxiv 2021. arXiv:2101.07172
Zhang R, Li G, Li Z, Cui S, Qian D, Yu Y (2020) Adaptive context selection for polyp segmentation. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2020: 23rd International Conference, Lima, Peru, October 4–8, 2020, Proceedings, Part VI 23, pp 253–262 . Springer
Yin Z, Liang K, Ma Z, Guo J (2022) Duplex contextual relation network for polyp segmentation. In: 2022 IEEE 19th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), pp 1–5. IEEE
Patel K, Bur AM, Wang G (2021) Enhanced u-net: A feature enhancement network for polyp segmentation. In: 2021 18th Conference on Robots and Vision (CRV), pp 181–188 . IEEE
Wei J, Hu Y, Zhang R, Li Z, Zhou SK, Cui S (2021) Shallow attention network for polyp segmentation. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2021: 24th International Conference, Strasbourg, France, September 27–October 1, 2021, Proceedings, Part I 24, pp 699–708. Springer
Qiu Z, Wang Z, Zhang M, Xu Z, Fan J, Xu L (2022) Bdg-net: boundary distribution guided network for accurate polyp segmentation. In: Medical Imaging 2022: Image Process, vol 12032, pp 792–799 . SPIE
Kim T, Lee H, Kim D (2021) Uacanet: Uncertainty augmented context attention for polyp segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp 2167–2175
Kirillov A, Mintun E, Ravi N, Mao H, Rolland C, Gustafson L, Xiao T, Whitehead S, Berg AC, Lo W-Y, et al. (2023) Segment anything. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 4015–4026
Gu A, Goel K, Ré C (2021) Efficiently modeling long sequences with structured state spaces. arXiv:2111.00396
Funding
This work was supported in part by Shijiazhuang Introducing High-level Talents’ Startup Funding Project(248790067A) and by the Startup Foundation for PhD of Hebei GEO University(No. BQ201322) and by Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province(H2024403001) and by Scientific Research Project of Hebei Provincial Department of Education(BJK2024099).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The data collection, deep learning model design, and experimental design were completed by Shang. Wu provided clinical medical guidance and partially participated in the coding work. Liu and Zhao completed the experimental implementation and the collection and organization of experimental results. Wang provided overall guidance for the work and collaborated with Shang on the writing of this paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
All the authors declare that they have no competing financial interests or personal relationships that could influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical and Informed Consent for Data Used
This article does not contain studies with human participants or animals. Statement of informed consent is not applicable since the manuscript does not contain any patient data.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shang, X., Wu, S., Liu, Y. et al. PVT-MA: pyramid vision transformers with multi-attention fusion mechanism for polyp segmentation. Appl Intell 55, 17 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-06041-5
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-06041-5