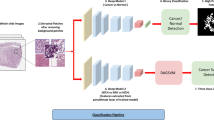
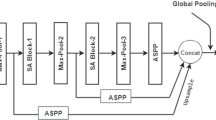
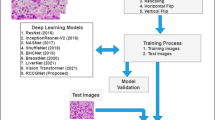
Abstract
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) represents the primary type of kidney cancer, responsible for approximately 85% of kidney cancer-related fatalities. Precise grading of this cancer is pivotal for tailoring effective treatments. Detecting RCC early, before metastasis, significantly improves survival rates. While Artificial intelligence-based classification methods have emerged for RCC, advancements in accuracy, processing efficiency, and memory utilization remain imperative. This study introduces the Efficient Enhanced Feature Framework (EFF-Net), a deep neural network architecture designed for RCC grading using histopathological image analysis. EFF-Net amalgamates potent feature extraction from convolutional layers with efficient Separable convolutional layers, aiming to accelerate model inference, reduce trainable parameters, mitigate overfitting, and elevate RCC grading precision. Evaluation across three distinct datasets showcases the EFF-Net's outstanding performance: achieving 91.90% accuracy, a precision of 91.4%, a recall of 91.8%, and a harmonic mean of precision and recall (F1 score) of 91.9% on the Kasturba Medical College (KMC) dataset. Additionally, on the Lung and Colon Dataset, EFF-Net achieved 99.8% accuracy, a precision of 99.7%, a recall of 99.9%, and a 98.7% F1 score. Similarly, the Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia dataset demonstrated remarkable performance: 99.8% accuracy, a precision of 99%, a recall of 99%, and a 99.7% F1 score. EFF-Net's superior accuracy surpasses existing state-of-the-art approaches while exhibiting reduced trainable parameters and computational requirements.
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
The data used for this work is publicly available.
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I et al (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: Cancer J Clinic 68(6):394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Du Z, Chen W, Xia Q et al (2020) Trends and projections of kidney cancer incidence at the global and national levels, 1990–2030: a Bayesian age-period-cohort modeling study. Biomarker Res 8:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40364-020-00195-3
Ayyad SM, Shehata M et al (2021) Role of AI and histopathological images in detecting prostate cancer: a survey. Sensors 21(8):2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082586
Hassan MR, Islam MF et al (2022) Prostate cancer classification from ultrasound and MRI images using deep learning based explainable artificial intelligence. Future Gen Comp Syst 127:462–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2021.09.030
Zajnulina M (2022) Advances of artificial intelligence in classical and novel spectroscopy-based approaches for cancer diagnostics. A review. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.04008
Trivizakis E, Manikis GC, Nikiforaki, et al (2018) Extending 2-D convolutional neural networks to 3-D for advancing deep learning cancer classification with application to MRI liver tumor differentiation. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 23(3):923–930. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2018.2886276
Yu S, Jia S, Xu C (2017) Convolutional neural networks for hyperspectral image classification. Neurocomputing 219:88–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2016.09.010
Öztürk Ş, Akdemir B (2019) HIC-net: a deep convolutional neural network model for classification of histopathological breast images. Comput Electr Eng 76:299–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2019.04.012
Nawaz M, Sewissy AA, Soliman THA (2018) Multi-class breast cancer classification using deep learning convolutional neural network. Int J Adv Comput Sci Appl 9(6):316–332. https://doi.org/10.14569/ijacsa.2018.090645
Chanchal AK, Lal S, Kumar R et al (2023) A novel dataset and efficient deep learning framework for automated grading of renal cell carcinoma from kidney histopathology images. Sci Rep 13(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-31275-7
Yin Y, Tang Z, Weng H (2024) Application of visual transformer in renal image analysis. BioMed Eng OnLine 23:27. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12938-024-01209-z
Mahmood T, Wahid A, Hong JS et al (2024) A novel convolution transformer-based network for histopathology-image classification using adaptive convolution and dynamic attention. Eng Appl Artif Intell 135:108824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2024.108824
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 770–778. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1512.03385
Szegedy C, Ioffe S, Vanhoucke V, Alemi A (2017) Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, vol. 31, No. 1. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v31i1.11231
Zoph B, Vasudevan V, Shlens J, Le QV (2018) Learning transferable architectures for scalable image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, pp 8697–8710. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00907
Zhang X, Zhou X, Lin M, Sun J (2018) Shufflenet: an extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, pp 6848–6856. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00716
Spanhol FA, Oliveira LS, Petitjean C et al (2016) Breast cancer histopathological image classification using convolutional neural networks. In 2016 international joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN) (pp. 2560–2567). IEEE, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24-29 July 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/IJCNN.2016.7727519
Toğaçar M, Özkurt KB, Ergen B, Cömert Z (2020) BreastNet: A novel convolutional neural network model through histopathological images for the diagnosis of breast cancer. Physica A 545:123592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2019.123592
Aatresh AA, Alabhya K, Lal S, Kini J, Saxena PP (2021) LiverNet: efficient and robust deep learning model for automatic diagnosis of sub-types of liver hepatocellular carcinoma cancer from H&E stained liver histopathology images. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 16:1549–1563. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-021-02410-4
Dosovitskiy A, Beyer L, Kolesnikov A et al (2020) An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929
Maqsood F (2023) “EFF-Net.”. [Online]. Available: https://github.com/faiqa24/EFF-Net. Accessed 1 Aug 2024
Wu J et al (2021) A precision diagnostic framework of renal cell carcinoma on whole-slide images using deep learning. In 2021 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM) (pp. 2104-2111). IEEE, Houston, TX, USA, 09-12 December 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/BIBM52615.2021.9669870
Kuanar S, Athitsos V, Mahapatra D, Rajan A (2021) Multi-scale deep learning architecture for nucleus detection in renal cell carcinoma microscopy image. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.13557
Chen S, Wang X, Zhang J, Jiang L et al (2023) Artificial intelligence for diagnosing and predicting survival of patients with renal cell carcinoma: retrospective multi-center study. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.04889
Sabharwal Y (2023) NephroNet: a novel program for identifying renal cell carcinoma and generating synthetic training images with convolutional neural networks and diffusion models. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.05830
Zhu M, Ren B, Richards R, Suriawinata M et al (2021) Development and evaluation of a deep neural network for histologic classification of renal cell carcinoma on biopsy and surgical resection slides. Sci Rep 11(1):7080. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-86540-4
Papageorgiou VE, Dogoulis P, Papageorgiou DP (2023) A convolutional neural network of low complexity for tumor anomaly detection. In International Congress on Information and Communication Technology (pp. 973–983). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-3236-8_78
Santini G, Moreau N, Rubeaux M (2019) Kidney tumor segmentation using an ensembling multi-stage deep learning approach. A contribution to the KiTS19 challenge. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.00735
Iliyas II, Saidu IR, Dauda AB, Tasiu S (2020) Prediction of chronic kidney disease using deep neural network. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/pdf/2012.12089
Bhat RR, Viswanath V, Li X (2016) DeepCancer: detecting cancer through gene expressions via deep generative learning. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1612.03211
Dimitriou N, Arandjelović O, Caie PD (2019) Deep learning for whole slide image analysis: an overview. Front Med 6:264. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2019.00264
Janowczyk A, Madabhushi A (2016) Deep learning for digital pathology image analysis: A comprehensive tutorial with selected use cases. J Path Inform 7(1):29. https://doi.org/10.4103/2153-3539.186902
Wang D, Khosla A, Gargeya R, Irshad H, Beck AH (2016) Deep learning for identifying metastatic breast cancer. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1606.05718
Liao H, Long Y, Han R et al (2020) Deep learning‐based classification and mutation prediction from histopathological images of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Transl Med 10(2). https://doi.org/10.1002/ctm2.102
O’Reilly JA, Sangworasil M (2019) Kidney and kidney tumor segmentation using a logical ensemble of u-nets with volumetric validation. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.02625
Hu S, Liao Z, Ye Y, Xia Y (2022) Boundary-aware network for kidney parsing. In MICCAI challenge on correction of brainshift with intra-operative ultrasound (pp. 9–17). Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-27324-7_2
Bu Z (2022) Multi-structure segmentation for renal cancer treatment with modified nn-UNet. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.05241
Hosny A, Parmar C, Coroller TP et al (2018) Deep learning for lung cancer prognostication: a retrospective multi-cohort radiomics study. PLoS Med 15(11):e1002711. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002711
Lu S, Xia K, Wang SH (2023) Diagnosis of cerebral microbleed via VGG and extreme learning machine trained by Gaussian map bat algorithm. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 14(5):5395–5406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-01789-3
Lu S, Lu Z, Zhang YD (2019) Pathological brain detection based on AlexNet and transfer learning. J Comput Sci 30:41–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocs.2018.11.008
Huang G, Liu Z, Van Der Maaten L, Weinberger KQ (2017) Densely connected convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 4700–4708. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.243
Shukla PK, Behera AR (2024) A framework for breast cancer prediction and classification using deep learning. Int J Comput Vis Robot. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJCVR.2024.136998
Borkowski AA, Bui MM, Thomas LB et al (2019) Lung and colon cancer histopathological image dataset (lc25000). Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.12142
Ghaderzadeh M, Aria M, Hosseini A et al (2022) A fast and efficient CNN model for B-ALL diagnosis and its subtypes classification using peripheral blood smear images. Int J Intell Syst 37(8):5113–5133. https://doi.org/10.1002/int.22753
Nguyen BP, Nguyen-Vo TH, Nguyen L et al (2023) iR6mA-RNN: identifying N6-methyladenosine sites in eukaryotic transcriptomes using recurrent neural networks and sequence-embedded features. In 2023 IEEE Statistical Signal Processing Workshop (SSP) (pp. 374–377). IEEE, Hanoi, Vietnam, 02-05 July 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/SSP53291.2023.10207989.
Badrinarayanan V, Handa A, Cipolla R (2015) Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for robust semantic pixel-wise labelling. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1505.07293
Wei B, Han Z, He X, Yin Y (2017) Deep learning model based breast cancer histopathological image classification. In 2017 IEEE 2nd international conference on cloud computing and big data analysis (ICCCBDA) (pp. 348–353). IEEE, Chengdu, 28-30 April 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCCBDA.2017.7951937
Naylor P, Laé M, Reyal F, Walter T (2018) Segmentation of nuclei in histopathology images by deep regression of the distance map. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 38(2):448–459. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2018.2865709
Maqsood F, Zhenfei W, Ali MM, Qiu B, Rehman NU, Sabah F, Mahmood T, Din I, Sarwar R (2024) Artificial intelligence-based classification of CT images using a Hybrid SpinalZFNet. Interdiscip Sci: Comput Life Sci 16(4):907–925. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-024-00649-4
Ali MM, Maqsood F, Liu S (2023) Enhancing breast cancer diagnosis with channel-wise attention mechanisms in deep learning. Comput Mater Contin. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmc.2023.045310
Sheikholeslami S, Meister M, Wang T et al (2021) Autoablation: automated parallel ablation studies for deep learning. In proceedings of the 1st workshop on machine learning and systems. pp 55–61. https://doi.org/10.1145/3437984.3458834
Funding
This work was supported by the National key research and development plan (Grant NO: 2023YFB4502704) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant NO: 62302461)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Methodology: Faiqa Maqsood, Formal Analysis, the original draft, Writing—review and editing: Faiqa Maqsood and Muhammad Mumtaz Ali., and Wang Zhenfei. Review, editing, and supervision: Wang Zhenfei., Baozhi Qiu, Tahir Mahmood, and Raheem Sarwar. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical standard
The data used in this study does not require informed consent or ethical approval as others access and generate the data.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Maqsood, F., Wang, Z., Ali, M.M. et al. An efficient enhanced feature framework for grading of renal cell carcinoma using Histopathological Images. Appl Intell 55, 196 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-06047-z
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-06047-z