Abstract
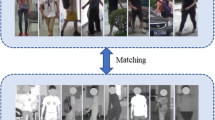
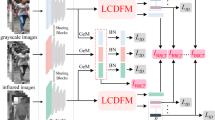
Visible-infrared person re-identification (VI Re-ID) is designed to perform pedestrian retrieval on non-overlapping visible-infrared cameras, and it is widely employed in intelligent surveillance. For the VI Re-ID task, one of the main challenges is the huge modality discrepancy between the visible and infrared images. Therefore, mining more shared features in the cross-modality task turns into an important issue. To address this problem, this paper proposes a novel framework for feature learning and feature embedding in VI Re-ID, namely Channel Enhanced Cross-modality Relation Network (CECR-Net). More specifically, the network contains three key modules. In the first module, to shorten the distance between the original modalities, a channel selection operation is applied to the visible images, the robustness against color variations is improved by randomly generating three-channel R/G/B images. The module also exploits the low- and mid-level information of the visible and auxiliary modal images through a feature parameter-sharing strategy. Considering that the body sequences of pedestrians are not easy to change with modality, CECR-Net designs two modules based on relation network for VI Re-ID, namely the intra-relation learning and the cross-relation learning modules. These two modules help to capture the structural relationship between body parts, which is a modality-invariant information, disrupting the isolation between local features. Extensive experiments on the two public benchmarks indicate that CECR-Net is superior compared to the state-of-the-art methods. In particular, for the SYSU-MM01 dataset, the Rank1 and mAP reach 76.83% and 71.56% in the "All Search" mode, respectively.








Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability and access
The additional datasets generated during and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Zheng L, Yang Y, Hauptmann AG (2016) Person re-identification: Past, present and future. CoRR. abs/1610.02984
Wu A, Zheng W-S, Yu H-X, Gong S, Lai J (2017) Rgb-infrared cross-modality person re-identification. In: 2017 IEEE International conference on computer vision (ICCV), pp 5390–5399
Ye M, Shen J, Lin G, Xiang T, Shao L, Hoi SCH (2021) Deep learning for person re-identification: A survey and outlook. IEEE Transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, pp 1–1
Ye M, Wu Z, Chen C, Du B (2024) Channel augmentation for visible-infrared re-identification. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 46(4):2299–2315
Wei L, Zhang S, Yao H, Gao W, Tian Q (2019) Glad: Global local alignment descriptor for scalable person re-identification. IEEE Transactions multimedia 21(4):986–999
Dai J, Zhang P, Wang D, Lu H, Wang H (2019) Video person re-identification by temporal residual learning. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(3):1366–1377
Ye M, Lan X, Li J, Yuen PC (2018) Hierarchical discriminative learning for visible thermal person re-identification. In: AAAI
Liu H, Tan X, Zhou X (2020) Parameter sharing exploration and hetero-center triplet loss for visible-thermal person re-identification. IEEE Transactions on multimedia, pp 1–1
Zhang Y, Wang H (2023) Diverse embedding expansion network and low-light cross-modality benchmark for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 2153–2162
Kim S, Gwon S, Seo K (2024) Enhancing diverse intra-identity representation for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: 2024 IEEE/CVF Winter conference on applications of computer vision (WACV), pp 2501–2510
Cheng Y, Xiao G, Tang X, Ma W, Gou X (2021) Two-phase feature fusion network for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: 2021 IEEE International conference on image processing (ICIP), pp 1149–1153
Zhang Y, Kang Y, Zhao S, Shen J (2023) Dual-semantic consistency learning for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 18:1554–1565
Wei Z, Yang X, Wang N, Gao X (2021) Flexible body partition-based adversarial learning for visible infrared person re-identification. IEEE Transactions on neural networks and learning systems, pp 1–12
Liu Q, Teng Q, Chen H, Li B, Qing L (2022) Dual adaptive alignment and partitioning network for visible and infrared cross-modality person re-identification. Appl Intell 52:547–563
Kim M, Kim S, Park J, Park S, Sohn K (2023) Partmix: Regularization strategy to learn part discovery for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 18621–18632
Ye M, Lan X, Wang Z, Yuen PC (2020) Bi-directional center-constrained top-ranking for visible thermal person re-identification. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 15:407–419
Zhu Y, Yang Z, Wang L, Zhao S, Hu X, Tao D (2020) Hetero-center loss for cross-modality person re-identification. Neurocomputing 386:97–109
Ye H, Liu H, Meng F, Li X (2021) Bi-directional exponential angular triplet loss for rgb-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:1583–1595
Ye H, Liu H, Meng F, Li X (2021) Bi-directional exponential angular triplet loss for rgb-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:1583–1595
Zhong X, Lu T, Huang W, Ye M, Jia X, Lin C-W (2021) Grayscale enhancement colorization network for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Transactions on circuits and systems for video technology, pp 1–1
Zhang Y, Yan Y, Lu Y, Wang H (2021) Towards a unified middle modality learning for visible-infrared person re-identification. New York, NY, USA, pp 788–796
Tan X, Chai Y, Chen F, Liu H (2022) A fourier-based semantic augmentation for visible-thermal person re-identification. IEEE Signal Process Lett 29:1684–1688
Liu J, Song W, Chen C, Liu F (2021) Cross-modality person re-identification via channel-based partition network. Appl Intell (8)
Li D, Wei X, Hong X, Gong Y (2020) Infrared-visible cross-modal person re-identification with an x modality. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp 4610–4617
Liu H, Xia D, Jiang W (2023) Towards homogeneous modality learning and multi-granularity information exploration for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Journal of selected topics in signal processing, 17(3):545–559
Varior RR, Shuai B, Lu J, Xu D, Wang G (2016) A siamese long short-term memory architecture for human re-identification. In: Computer vision – ECCV 2016, Springer, Cham, pp 135–153
Park H, Ham B (2020) Relation network for person re-identification. In: 2020 AAAI Conference on artificial intelligence
Zhang Z, Lan C, Zeng W, Jin X, Chen Z (2020) Relation-aware global attention for person re-identification. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 3183–3192
Liao S, Hu Y, Zhu X et al (2015) Person re-identification by local maximal occurrence representation and metric learning. In: IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Boston, USA, pp 2197–2206
You J, Wu A, Li X, Zheng WS (2016) Top-push video-based person re-identification. In: IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition., Las Vegas, USA, pp 1345–1353
Yao H, Zhang S, Hong R, Zhang Y, Xu C, Tian Q (2019) Deep representation learning with part loss for person re-identification. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(6):2860–2871
Liu H, Cheng J, Wang W, Su Y, Bai H (2020) Enhancing the discriminative feature learning for visible-thermal cross-modality person re-identification. Neurocomputing 398:11–19
Yin J, Ma Z, Xie J, Nie S, Liang K, Guo J (2022) Dual-granularity feature alignment for cross-modality person re-identification. Neurocomputing 511:78–90
Zhang L, Du G, Liu F, Tu H, Shu X (2021) Global-local multiple granularity learning for cross-modality visible-infrared person reidentification. IEEE Transactions on neural networks and learning systems, pp 1–11
Feng J, Wu A, Zheng W-S (2023) Shape-erased feature learning for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 22752–22761
Ye M, Wang Z, Lan X, Yuen PC (2018) Visible thermal person re-identification via dual-constrained top-ranking. In: Proceedings of the twenty-seventh international joint conference on artificial intelligence, IJCAI-18, pp 1092–1099
Wen Y, Zhang K, Li Z, Qiao Y (2016) A discriminative feature learning approach for deep face recognition. In: Leibe B, Matas J, Sebe N, Welling M (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2016, Cham, pp 499–515
Liu H, Chai Y, Tan X, Li D, Zhou X (2021) Strong but simple baseline with dual-granularity triplet loss for visible-thermal person re-identification. IEEE Signal Process Lett 28:653–657
Dai P, Ji R, Wang H, Wu Q, Huang Y (2018) Cross-modality person re-identification with generative adversarial training. In: Proceedings of the twenty-seventh international joint conference on artificial intelligence, pp 677–683
Wang Z, Wang Z, Zheng Y, Chuang Y-Y, Satoh S (2019) Learning to reduce dual-level discrepancy for infrared-visible person re-identification. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 618–626
Wang G, Zhang T, Cheng J, Liu S, Yang Y, Hou Z (2019) Rgb-infrared cross-modality person re-identification via joint pixel and feature alignment. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF International conference on computer vision (ICCV), pp 3622–3631
Wang GA, Yang T, Cheng J, Chang J, Liang X, Hou Z (2020) Cross-modality paired-images generation for rgb-infrared person re-identification. Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence
Ye M, Ruan W, Du B, Shou MZ (2021) Channel augmented joint learning for visible-infrared recognition. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF International conference on computer vision (ICCV), pp 13547–13556. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.01331
Liu H, Xia D, Jiang W (2023) Towards homogeneous modality learning and multi-granularity information exploration for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing. 17(3):545–559
Cui Z, Zhou J, Peng Y (2024) Dma: Dual modality-aware alignment for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 19:2696–2708
Sun Y, Zheng L, Yang Y, Tian Q, Wang S (2018) Beyond part models: Person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline). In: Ferrari V, Hebert M, Sminchisescu C, Weiss Y (eds) Computer Vision - ECCV 2018. Springer, Cham, pp 501–518
Dat N, Hyung H, Ki K, Kang P (2017) Person recognition system based on a combination of body images from visible light and thermal cameras. Sensors. 17(3):605
Hao Y, Wang N, Li J, Gao X (2019) Hsme: Hypersphere manifold embedding for visible thermal person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp 8385–8392
Ye M, Lan X, Wang Z, Yuen PC (2020) Bi-directional center-constrained top-ranking for visible thermal person re-identification. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 15:407–419
Ye M, Shen J, Shao L (2021) Visible-infrared person re-identification via homogeneous augmented tri-modal learning. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 16:728–739
Zhao J, Wang H, Zhou Y, Yao R, Chen S, El Saddik A (2022) Spatial-channel enhanced transformer for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Transactions on multimedia, pp 1–1. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2022.3163847
Liu H, Ma S, Xia D, Li S (2023) Sfanet: A spectrum-aware feature augmentation network for visible-infrared person reidentification. IEEE Transactions on neural networks and learning systems 34(4):1958–1971
Gwon S, Kim S, Seo K (2024) Balanced and essential modality-specific and modality-shared representations for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Signal Process Lett 31:491–495
Lu Y, Wu Y, Liu B, Zhang T, Li B, Chu Q, Yu N (2020) Cross-modality person re-identification with shared-specific feature transfer. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 13376–13386
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 62177029 and 61807020, and in part by the Startup Foundation for Introducing Talent of Nanjing University of Posts and Communications under Grant NY221041 and NY222034, and in part by General Project of The Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Higher Education Institution of China 22KJB520025.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Conceptualization: Wanru Song; Methodology: Wanru Song; Writing - original draft preparation: Wanru Song, Xinyi Wang; Writing - review and editing: Weimin Wu,Yuan Zhang; Funding acquisition: Feng Liu. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical and informed consent for data used
The data covered in this manuscript comes from publicly available datasets, and there are no ethical implications to discuss. All datasets involved in the current study are listed in the section of Experiments of the manuscript. Data used in the experiments, such as the Rank accuracy rate, has been cited by the manuscript. This manuscript is published with the informed consent of all authors.
Competing Interests
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Song, W., Wang, X., Wu, W. et al. Channel enhanced cross-modality relation network for visible-infrared person re-identification. Appl Intell 55, 4 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-06057-x
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-06057-x